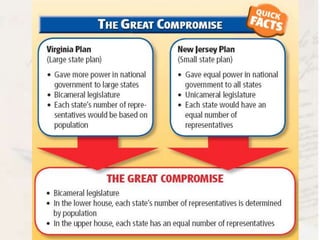
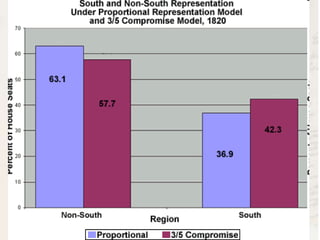
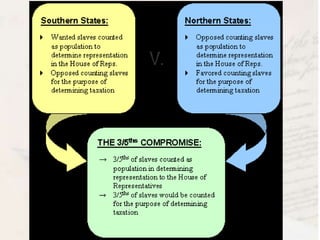
The delegates at the Constitutional Convention addressed weaknesses in the Articles of Confederation and made compromises between large and small states and northern and southern states. They established a bicameral legislature with representation based on population in the House and equal representation for each state in the Senate. The convention also addressed the issue of slavery through compromises, including counting enslaved people as three-fifths of persons for representation and prohibiting banning the slave trade for twenty years.