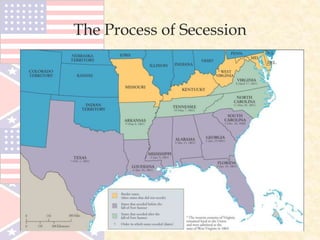
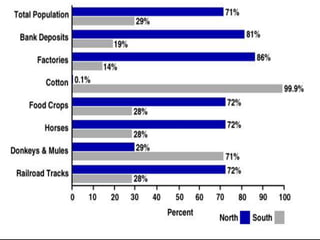
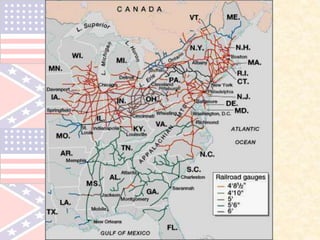
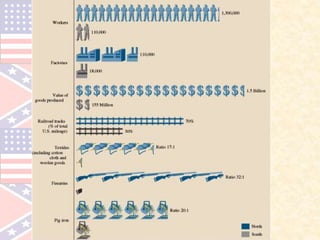
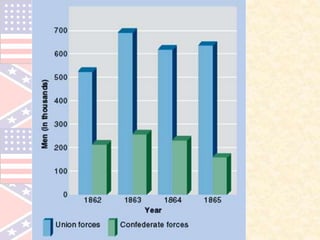
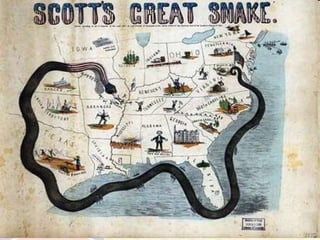
The document provides an overview of the key events leading up to the American Civil War from 1820 to 1861, including the Missouri Compromise, Compromise of 1850, Kansas-Nebraska Act, and Dred Scott decision. It also compares the advantages and disadvantages of the Union and Confederacy at the start of the war, such as the Union's larger population and industry versus the Confederacy's emotional commitment and better initial officers. Finally, it outlines the early strategies of the war, with the Confederacy pursuing a defensive strategy of attrition and the Union implementing the Anaconda Plan to blockade ports and divide the Eastern and Western sections of the Confederacy.