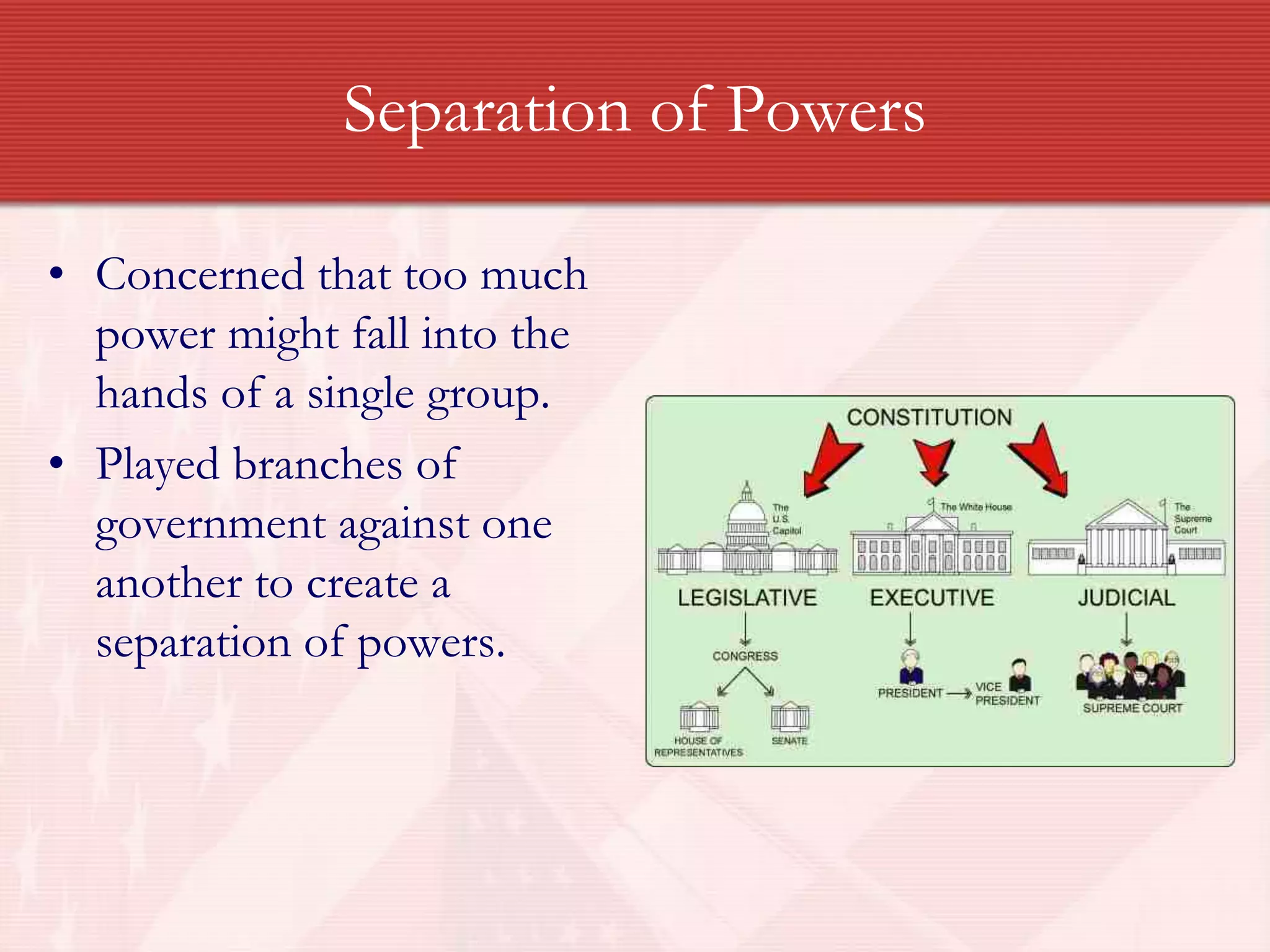
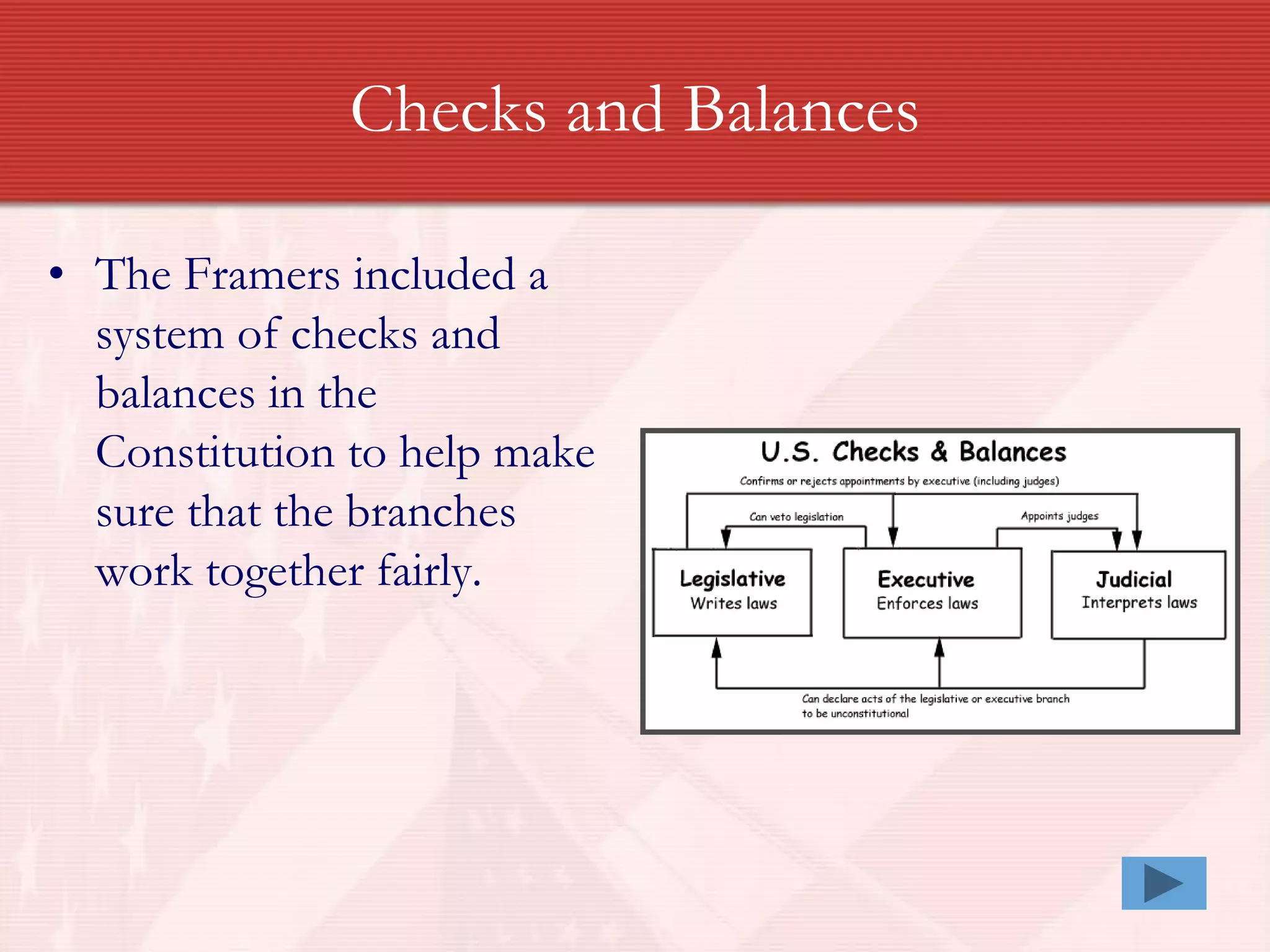
The United States Constitution was based on seven fundamental principles established by the Framers: popular sovereignty, where the government's authority comes from the people; republicanism, establishing a representative democracy where voters elect representatives; federalism, creating a partnership between strong central and state governments; separation of powers that divides government among branches; checks and balances allowing each branch to limit the others' power; limited government that restricts governmental power; and individual rights protecting citizens from an overly powerful government through guarantees like the Bill of Rights.