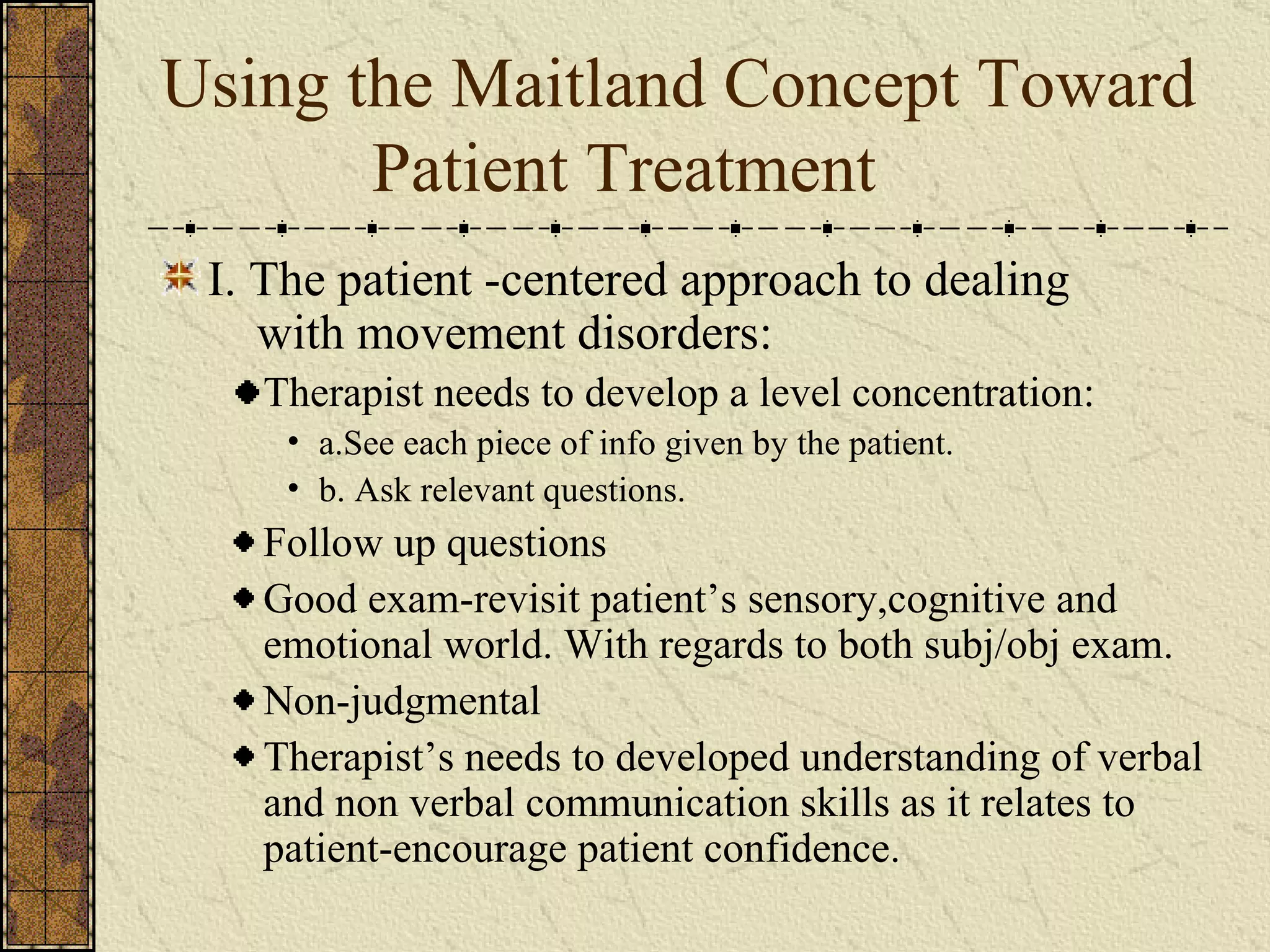
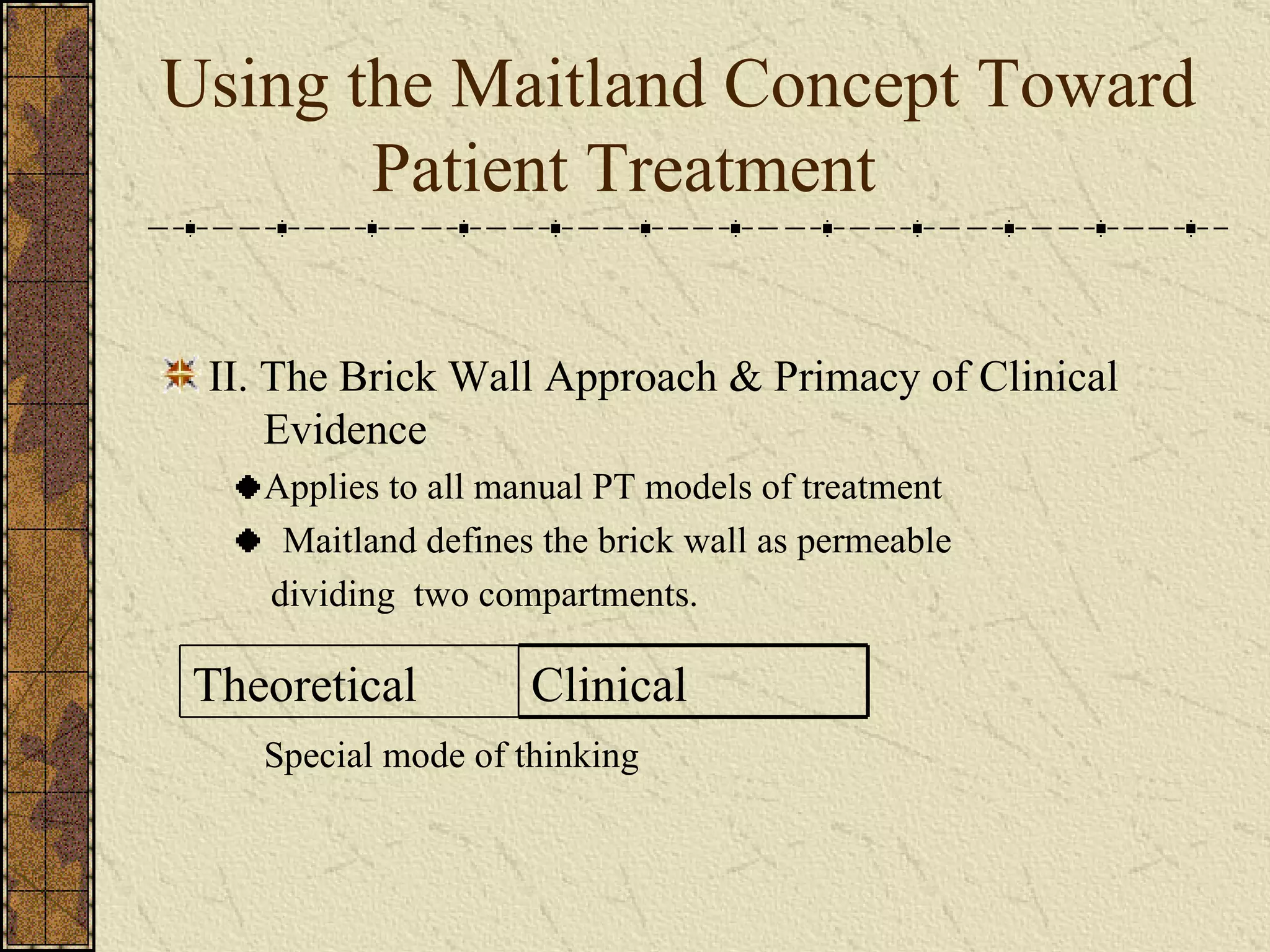
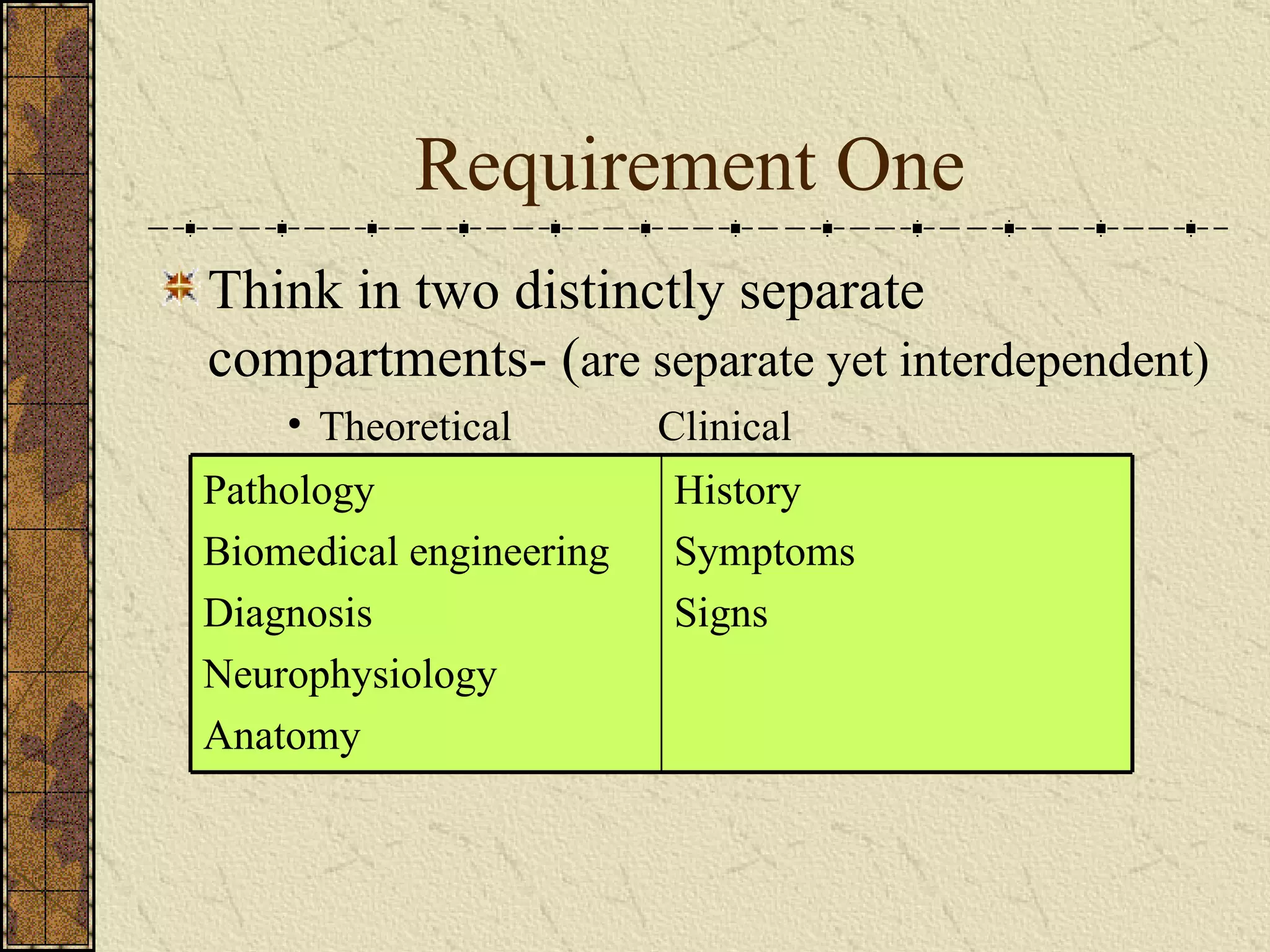
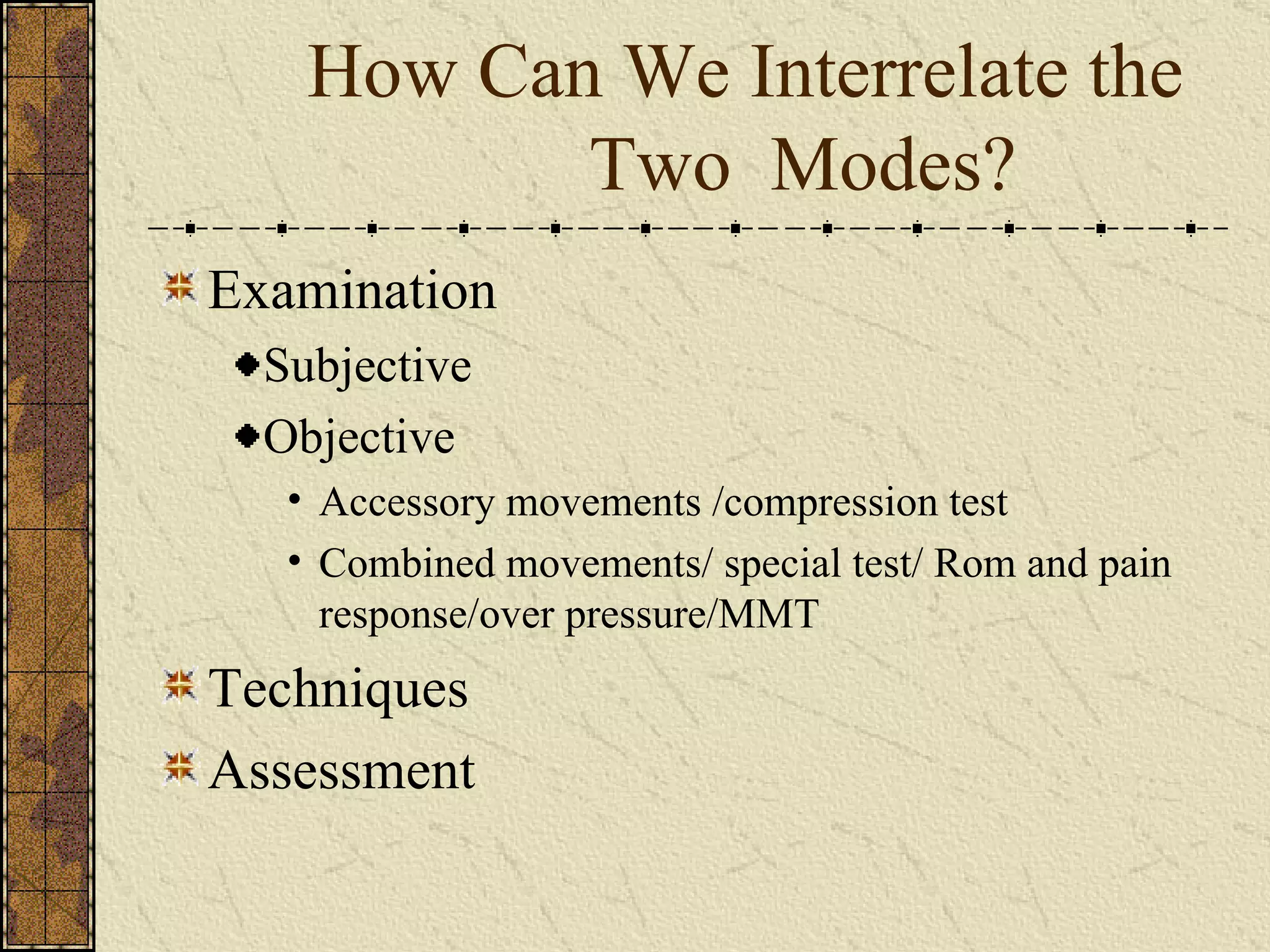
The document discusses Maitland's concept of using a "brick wall" approach to separate clinical evidence and theoretical thinking when treating patients. There are five requirements for this approach: 1) Think in two compartments of clinical and theoretical, 2) Prioritize the clinical compartment over theoretical, 3) Choose careful wording to separate theory from clinical findings, 4) Choose treatment techniques based on patient signs and symptoms rather than theory, 5) Apply the brick wall concept to clinical decision making. The two compartment approach allows speculation based on research but it must be consistent with the patient's clinical presentation.