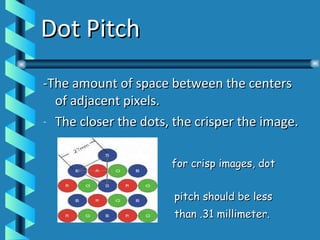
The document discusses various types of computer output devices, including display screens, printers, plotters, audio output, video output, virtual reality devices, and robots. It covers the different technologies used in common output devices like CRT and LCD screens, inkjet and laser printers, and provides examples of how output is used across different mediums like audio, video, and virtual reality simulations.