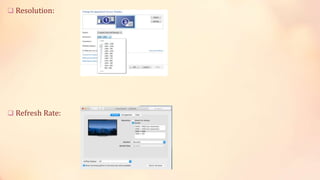
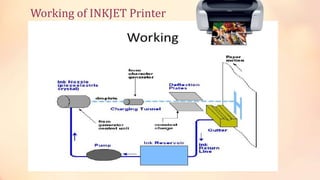
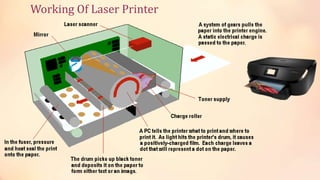
This document provides information about computer output devices and monitors. It discusses the types of monitors, including CRT and flat panel monitors. CRT monitors use electron guns to project beams onto phosphor screens to display images, while flat panel monitors like LCD and LED are thinner. It also discusses monitor features such as size, pixels, resolution, refresh rate, and dot pitch. The document then covers printers, including impact printers like dot matrix and non-impact printers like inkjet and laser printers. It compares different printers and discusses high quality printers used for photos.