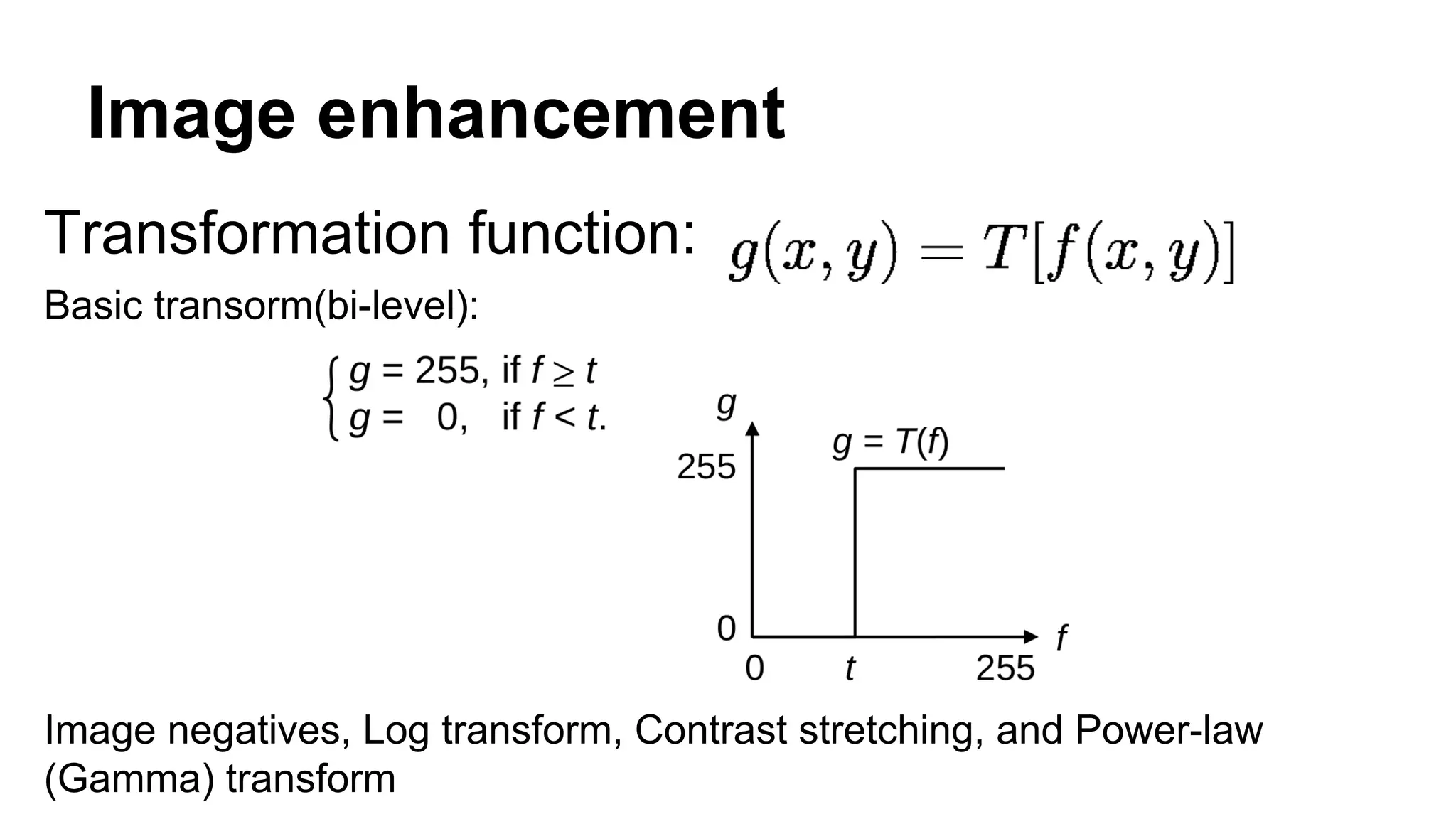
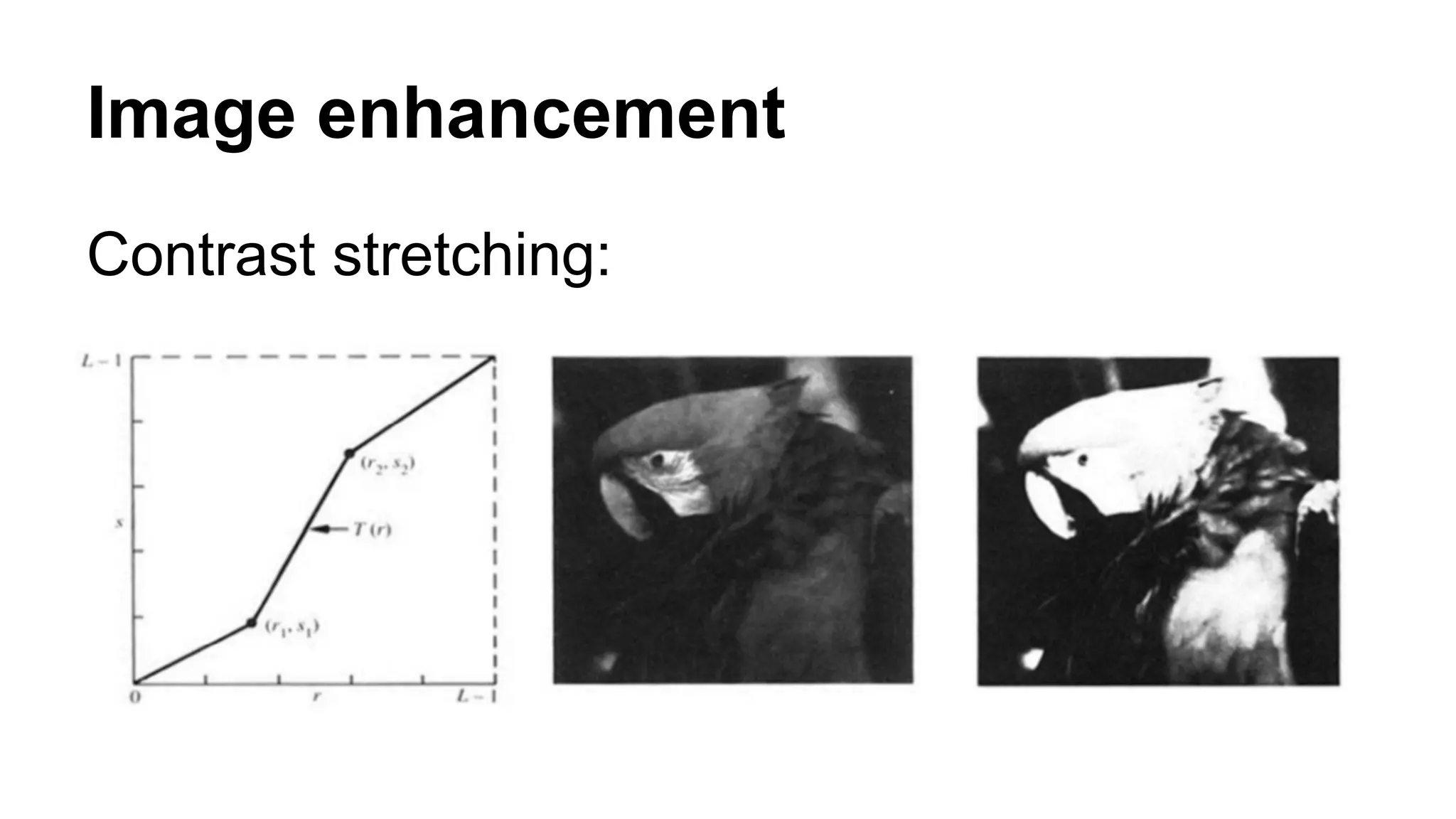
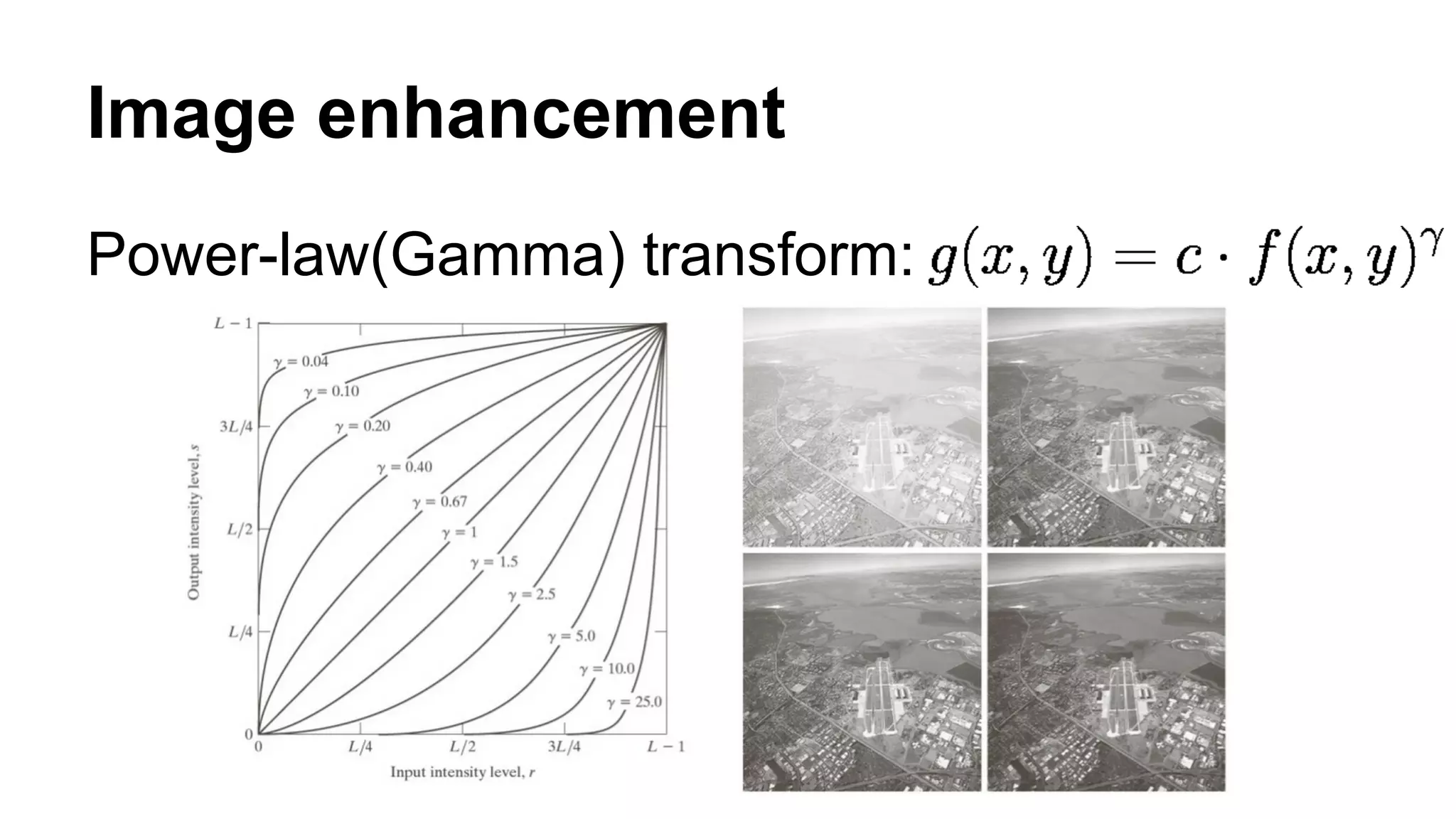
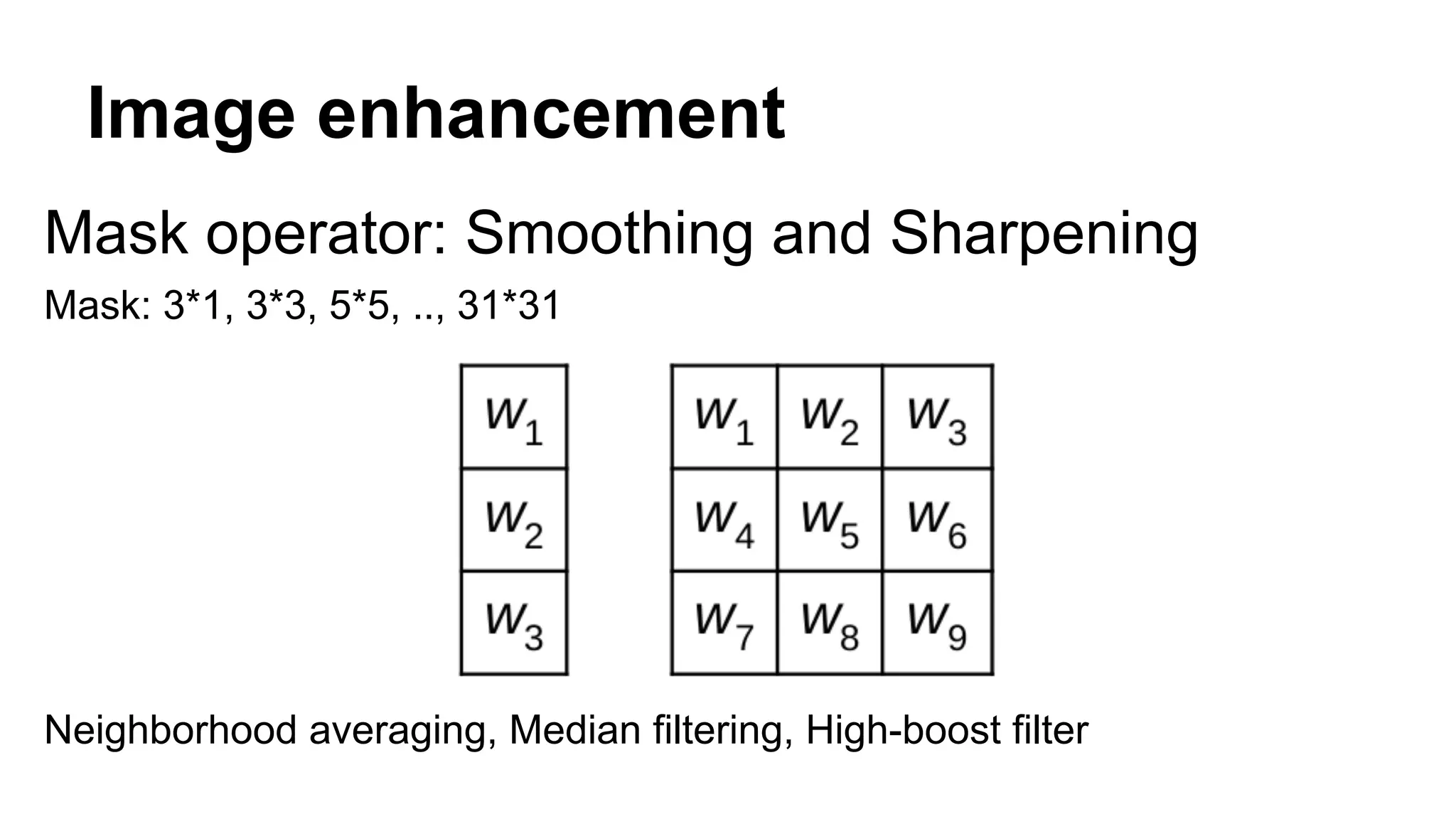
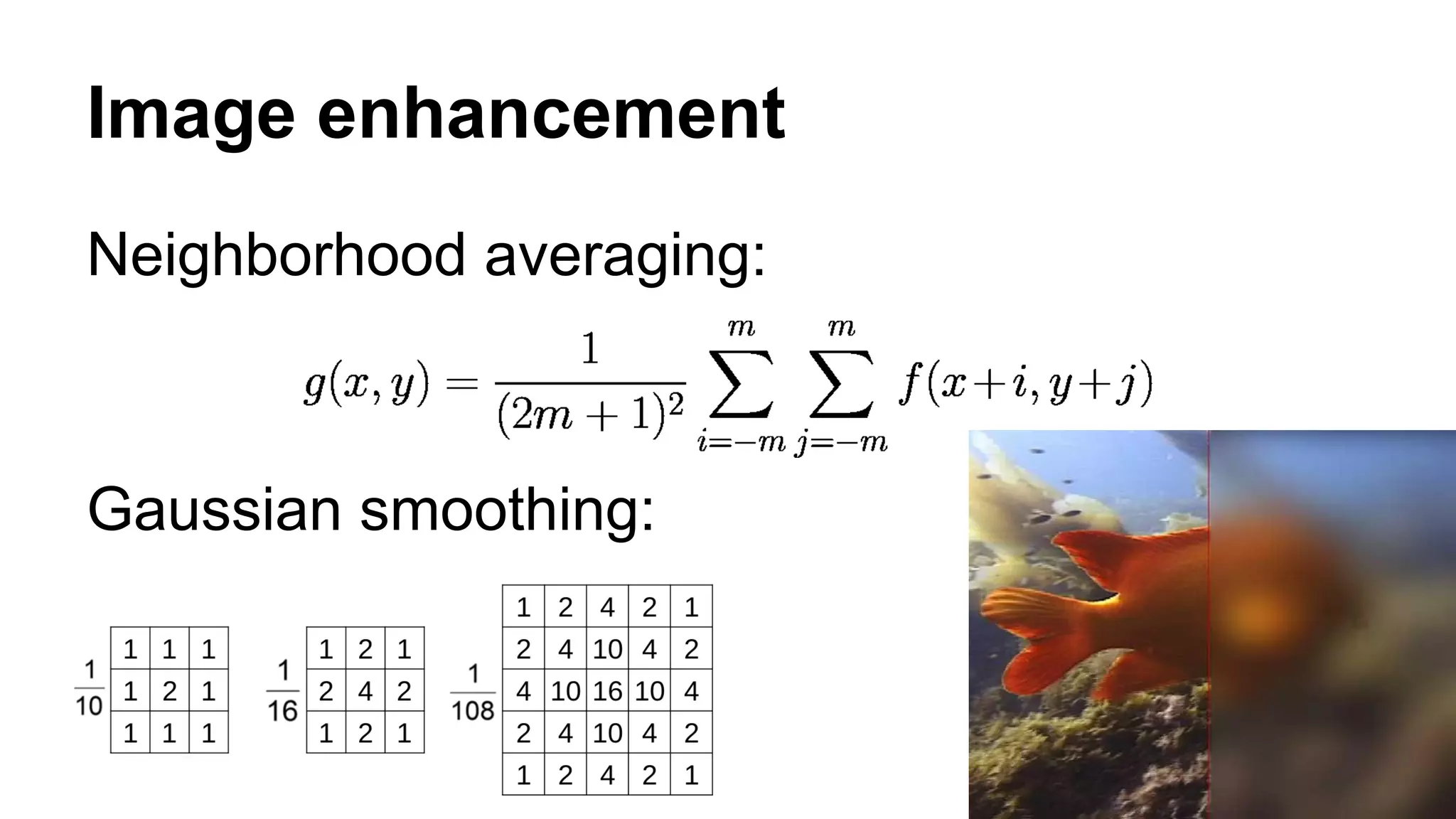
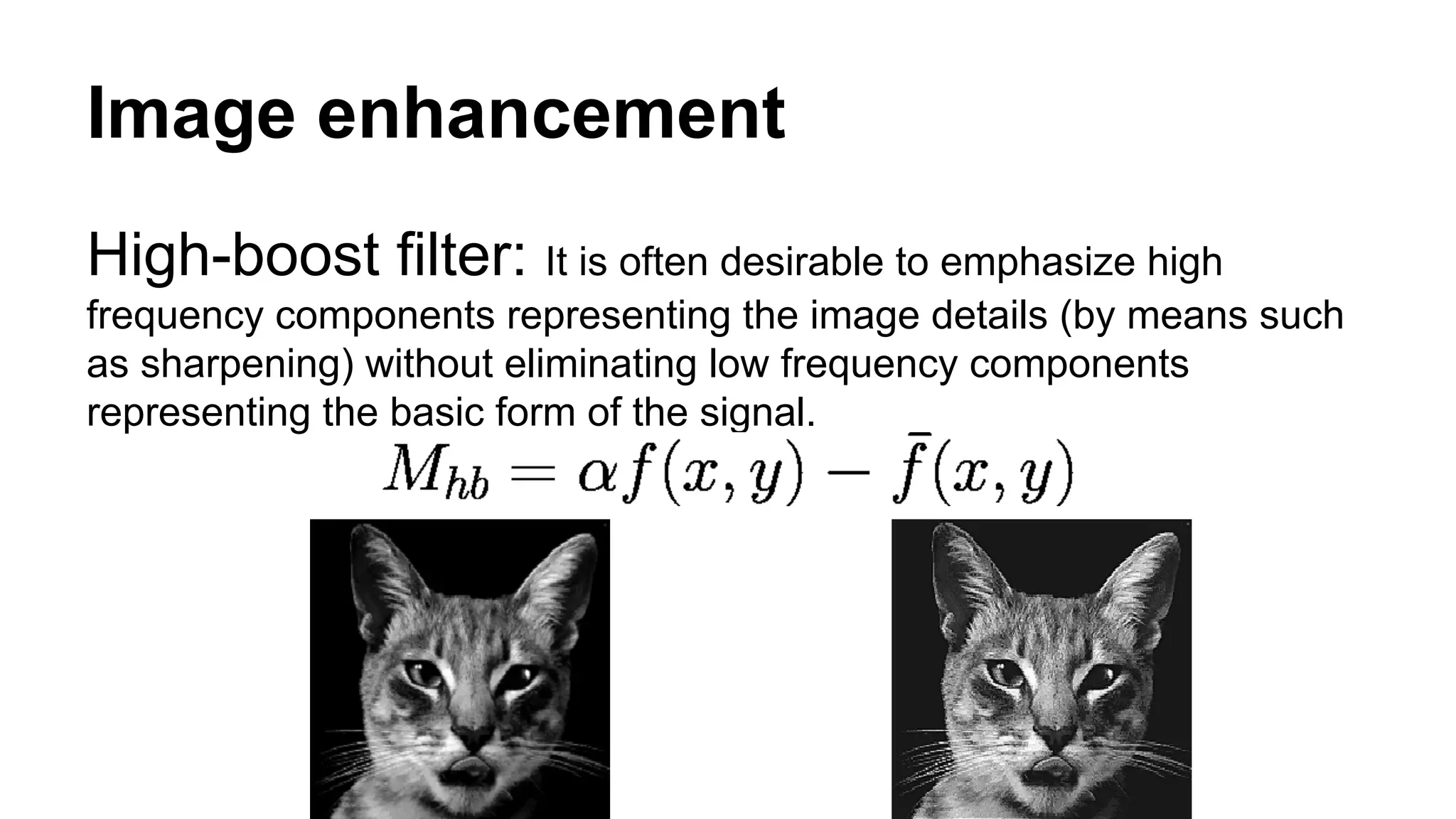
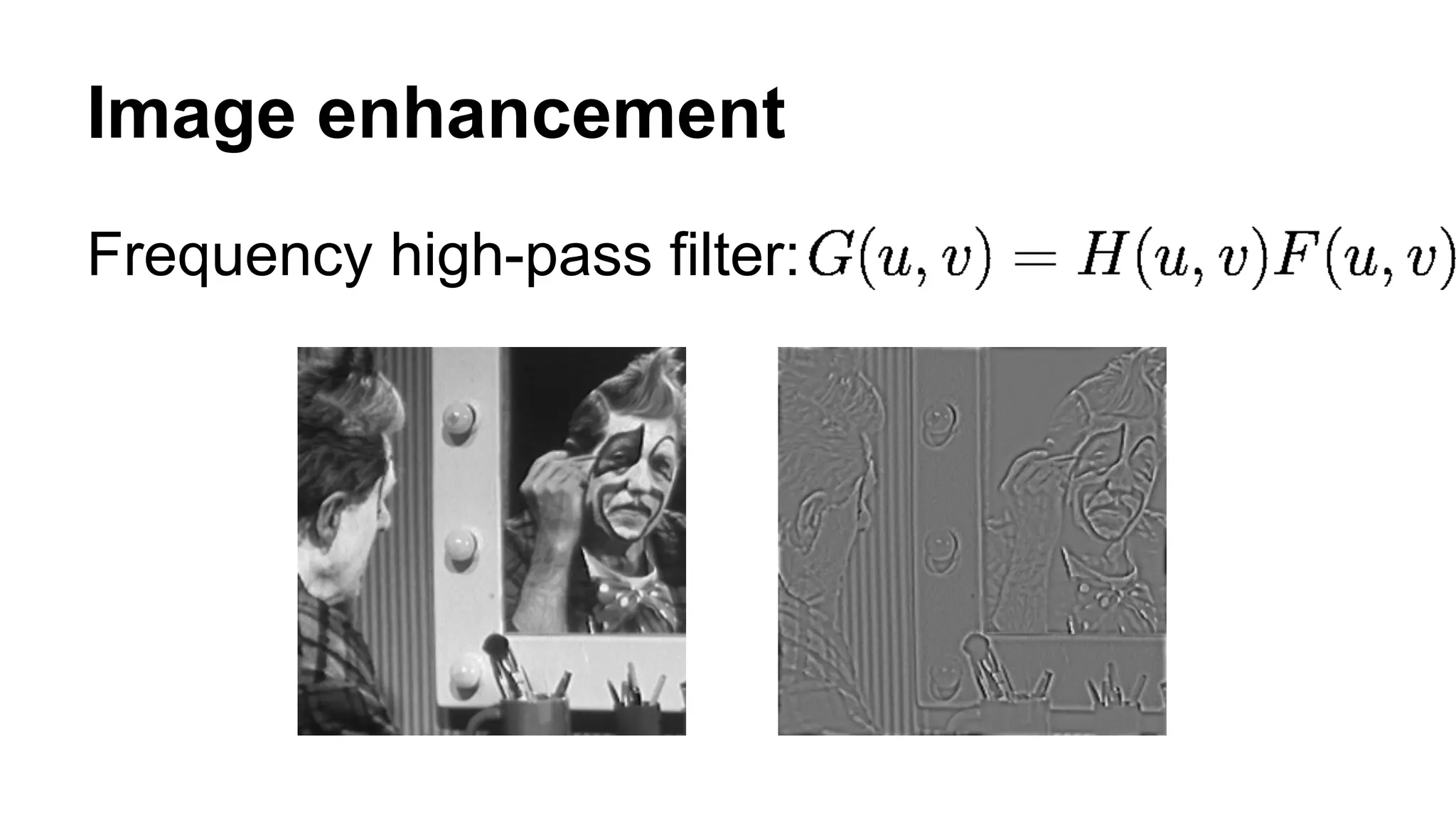
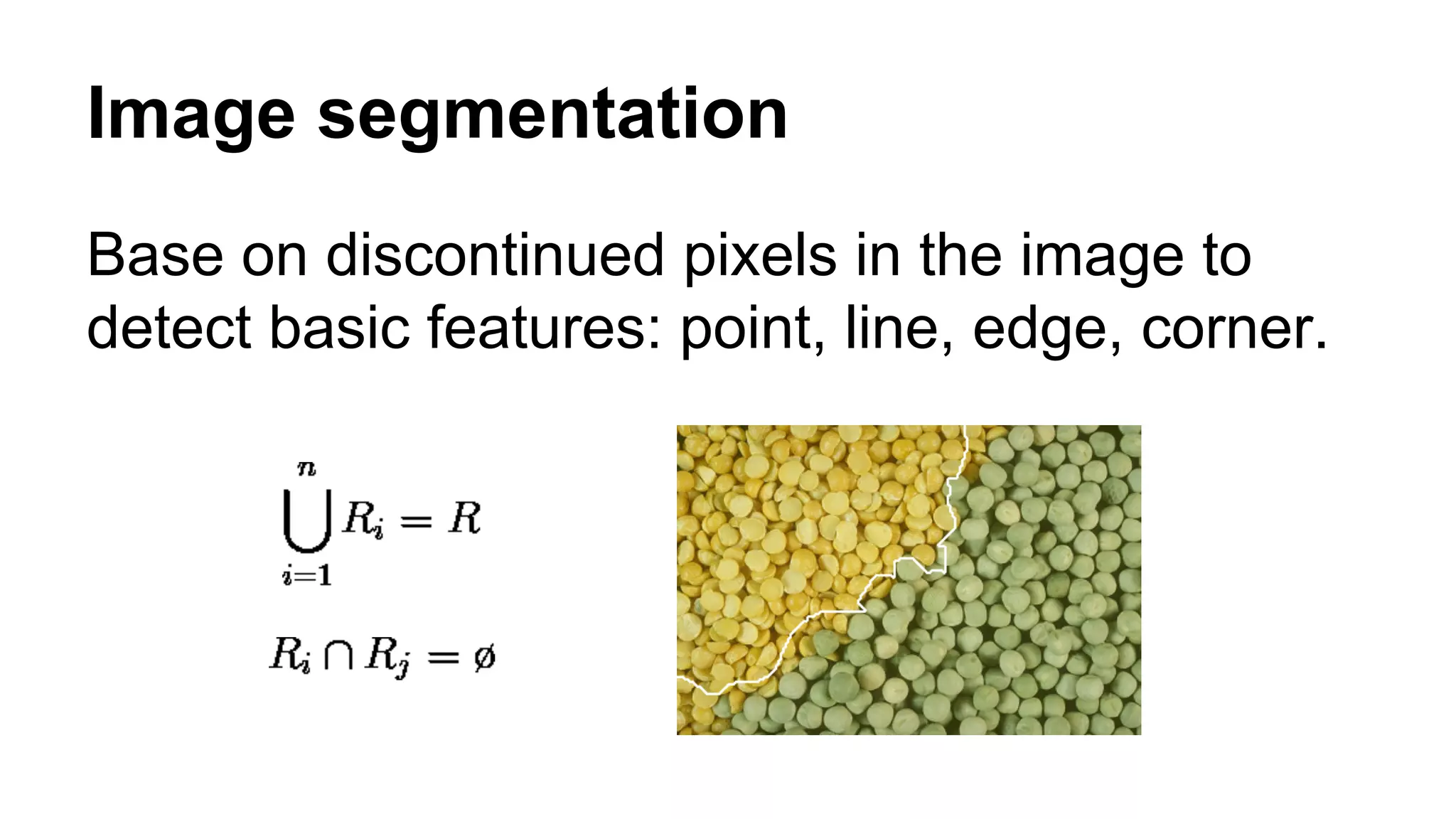
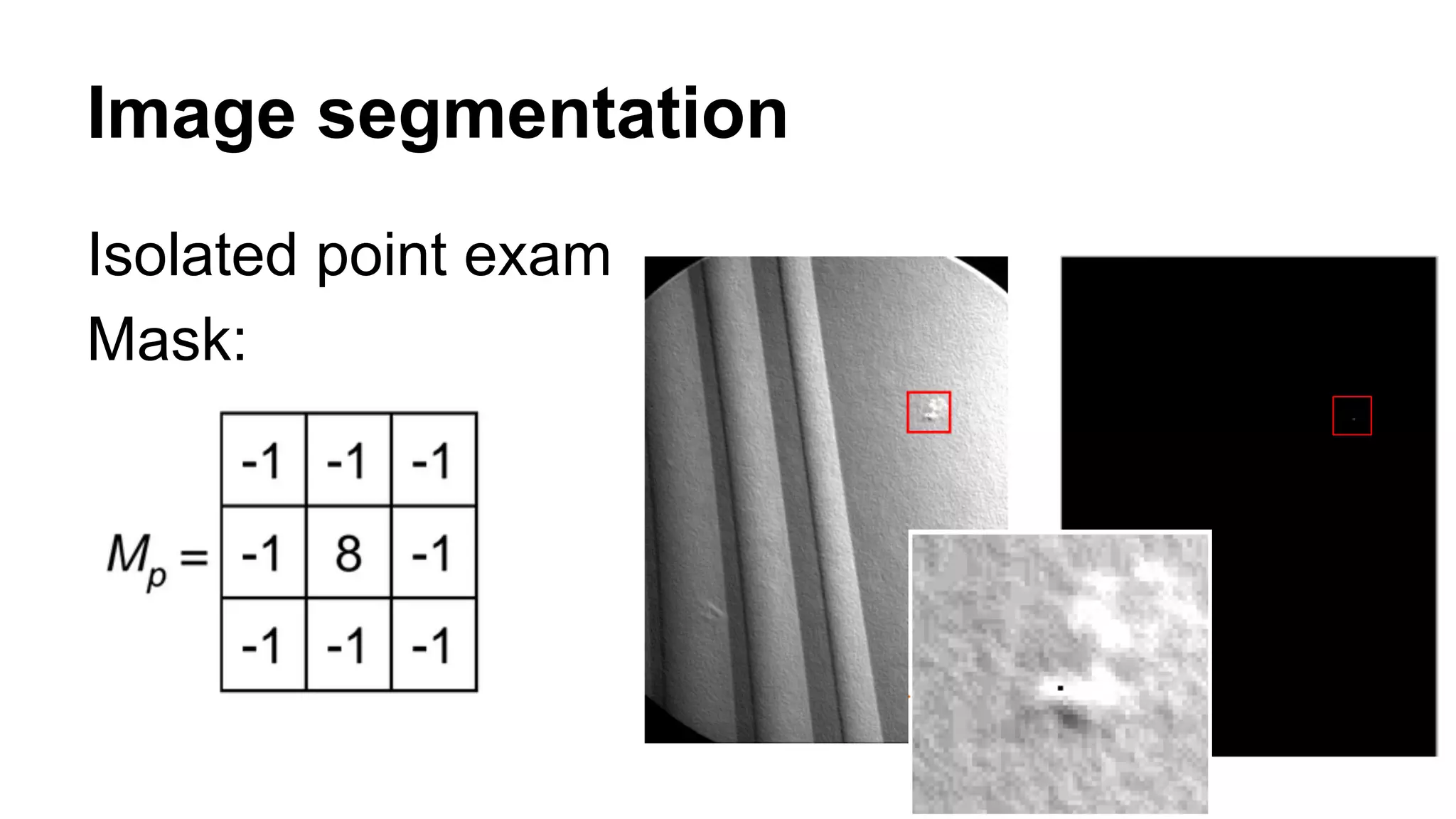
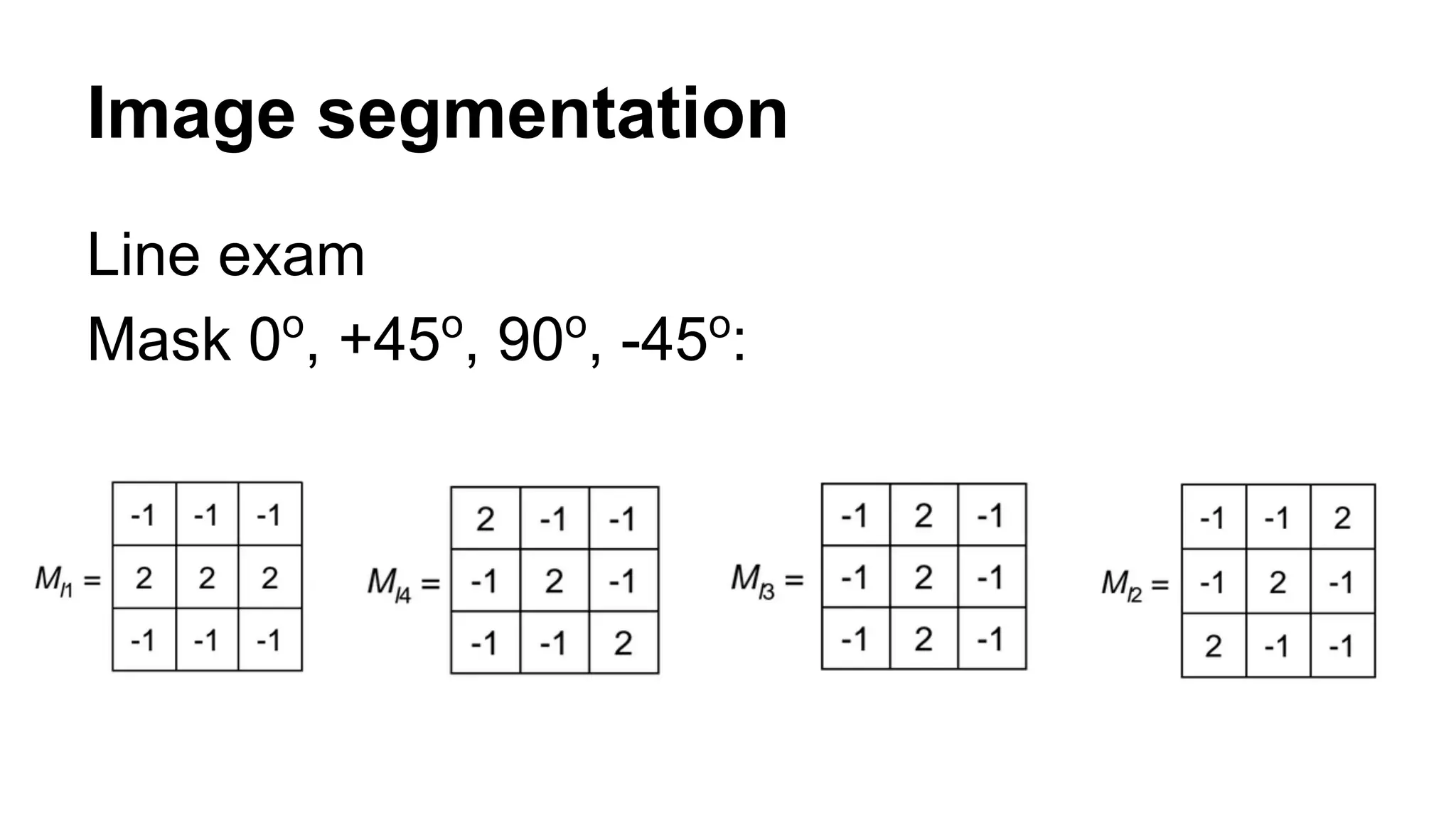
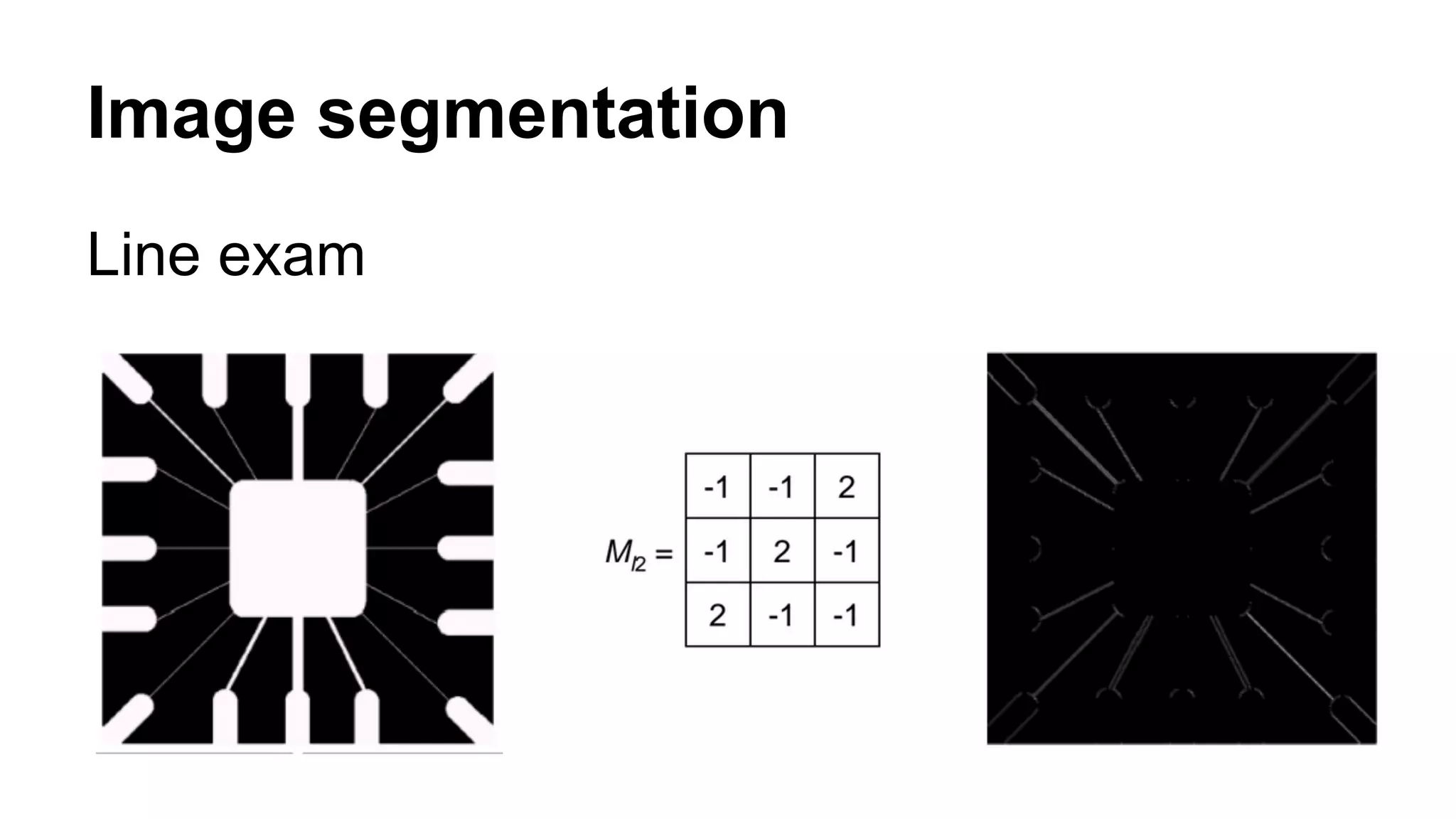
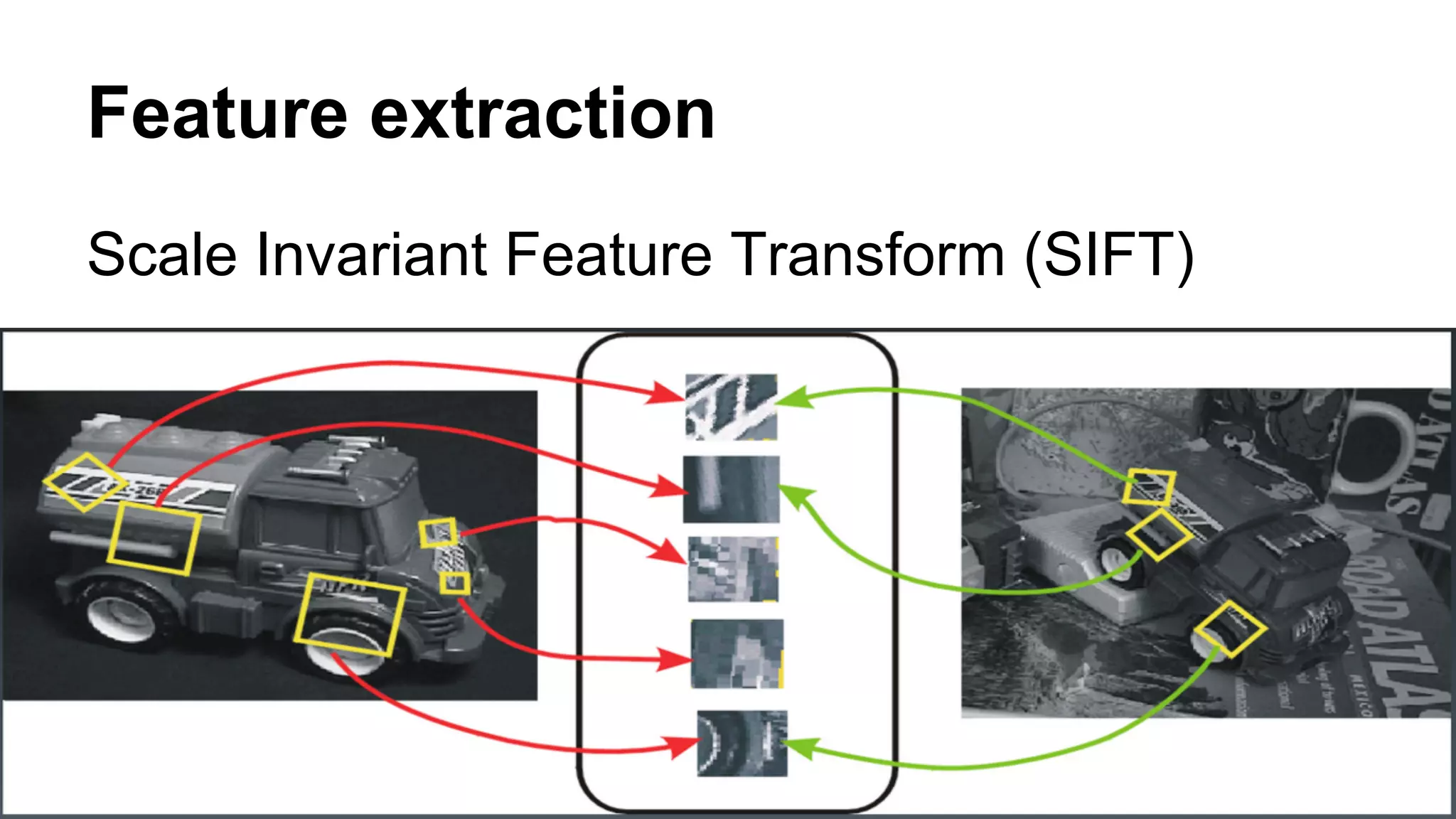
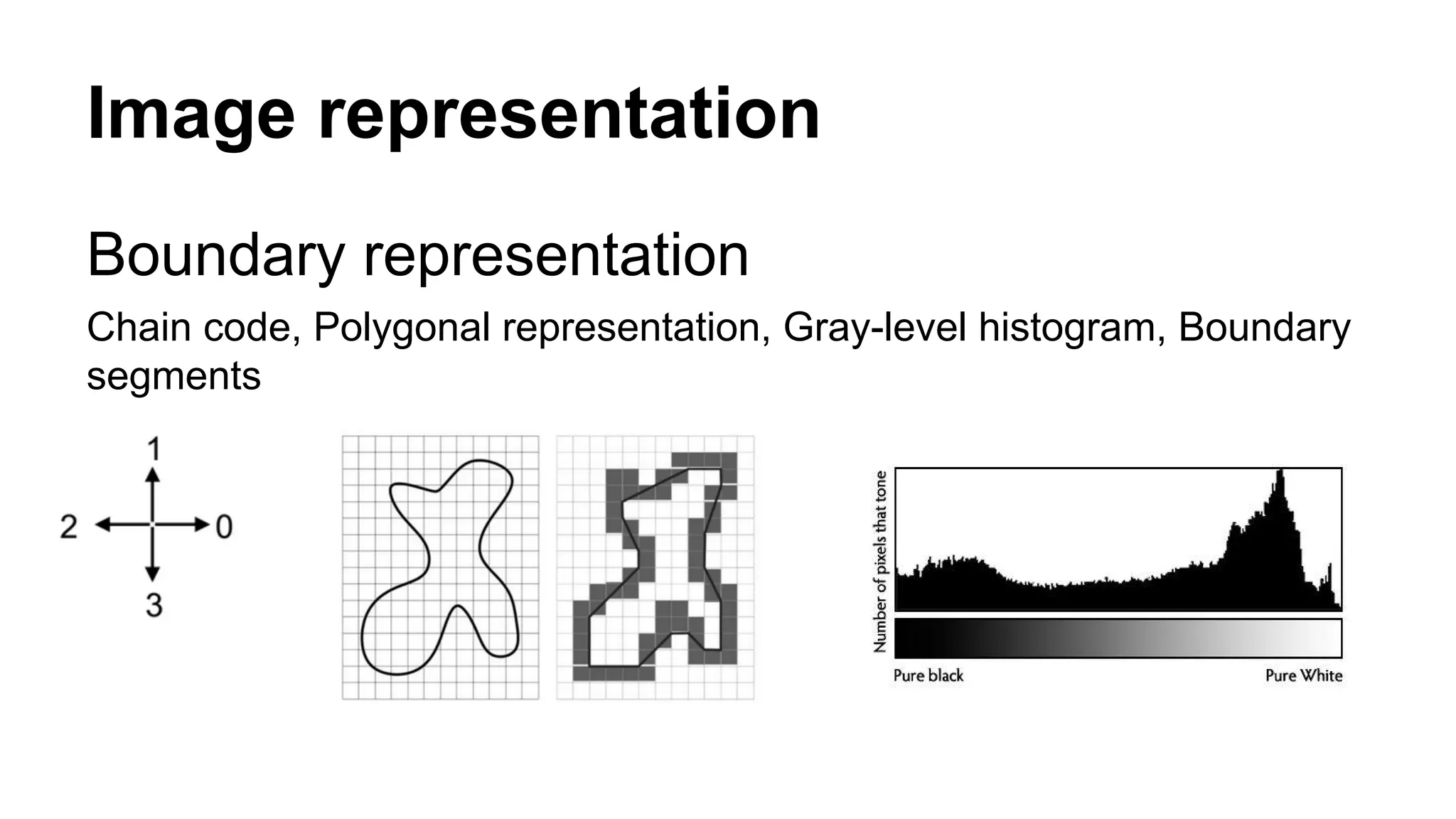
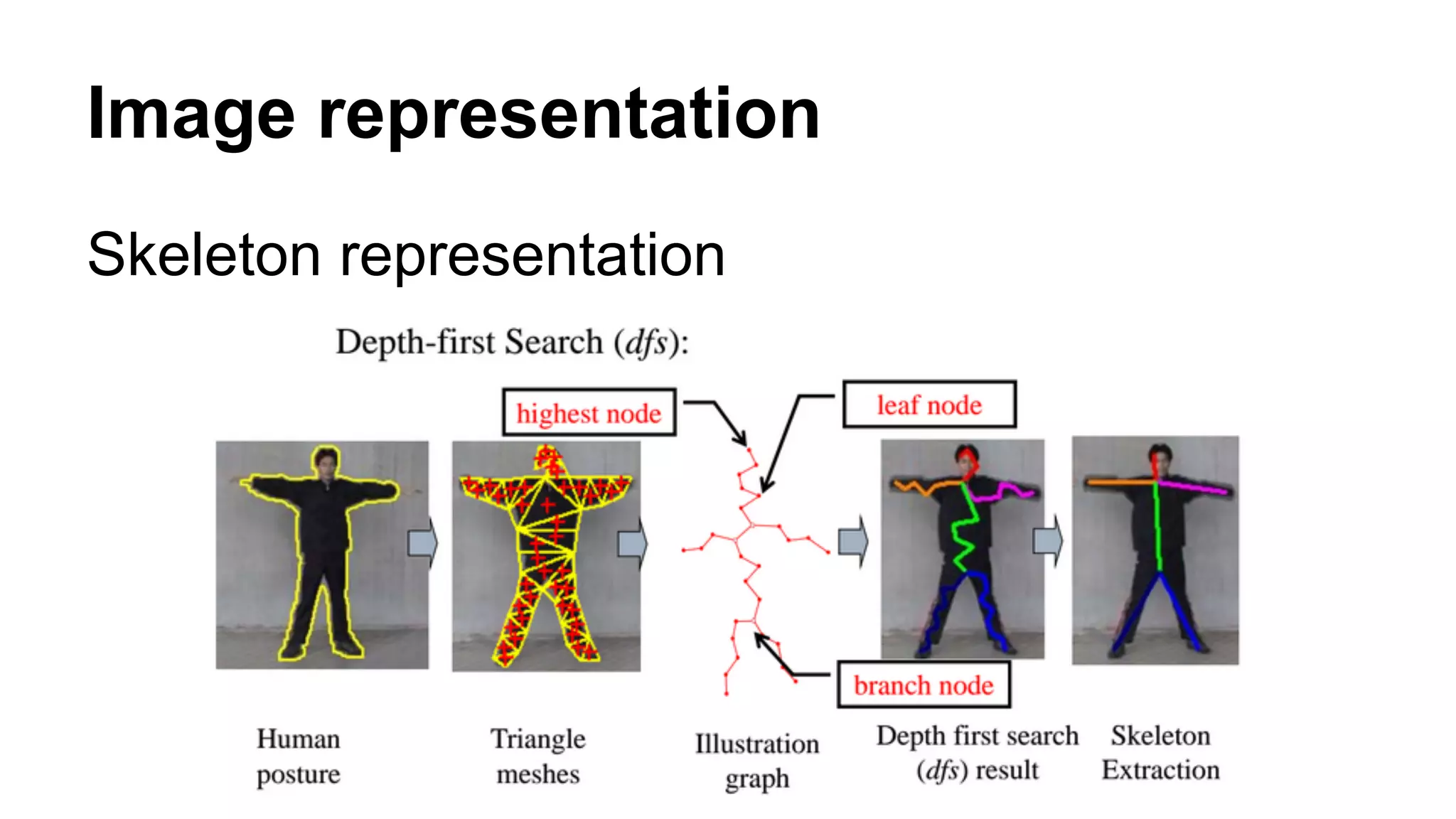
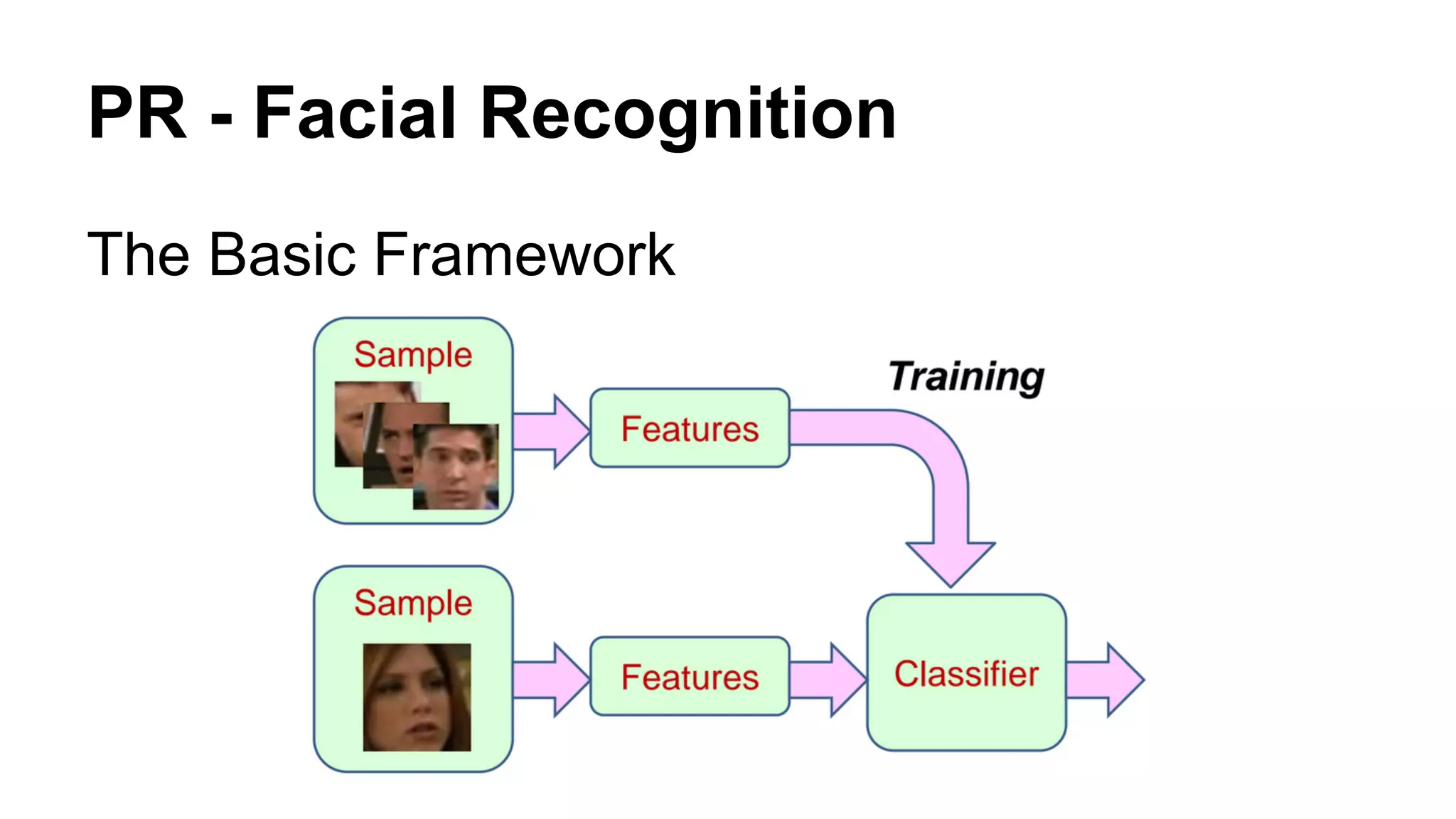
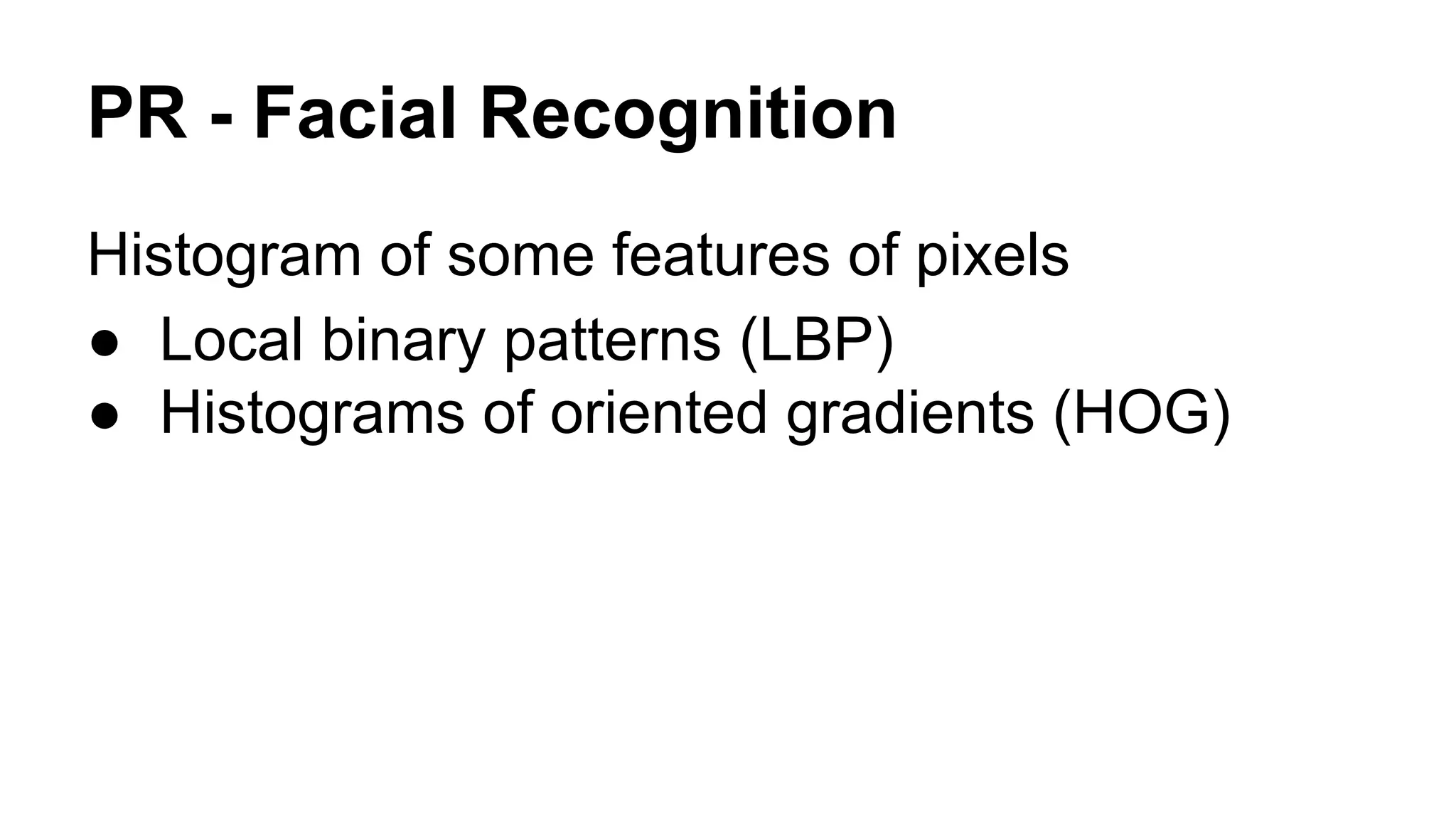
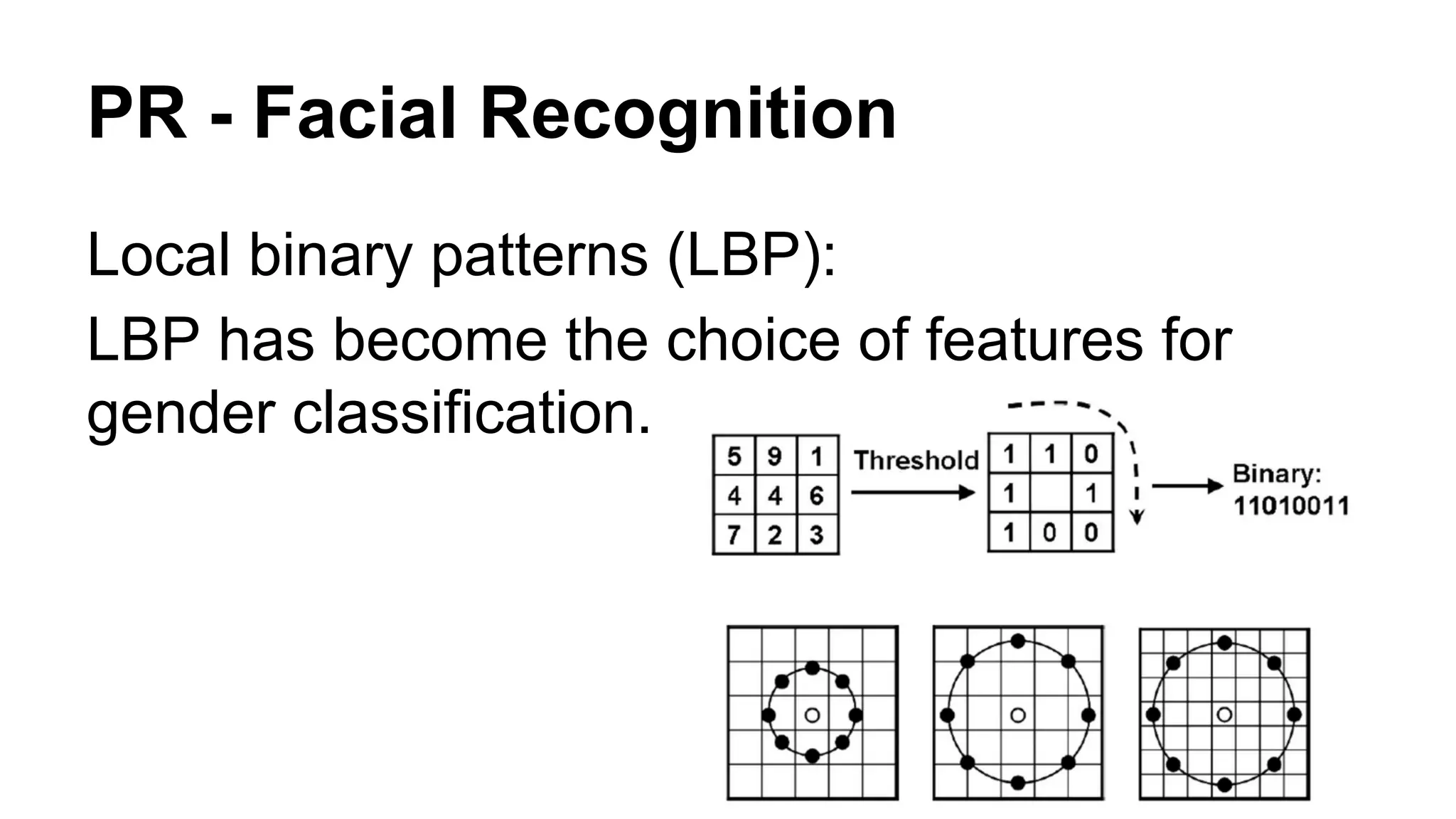
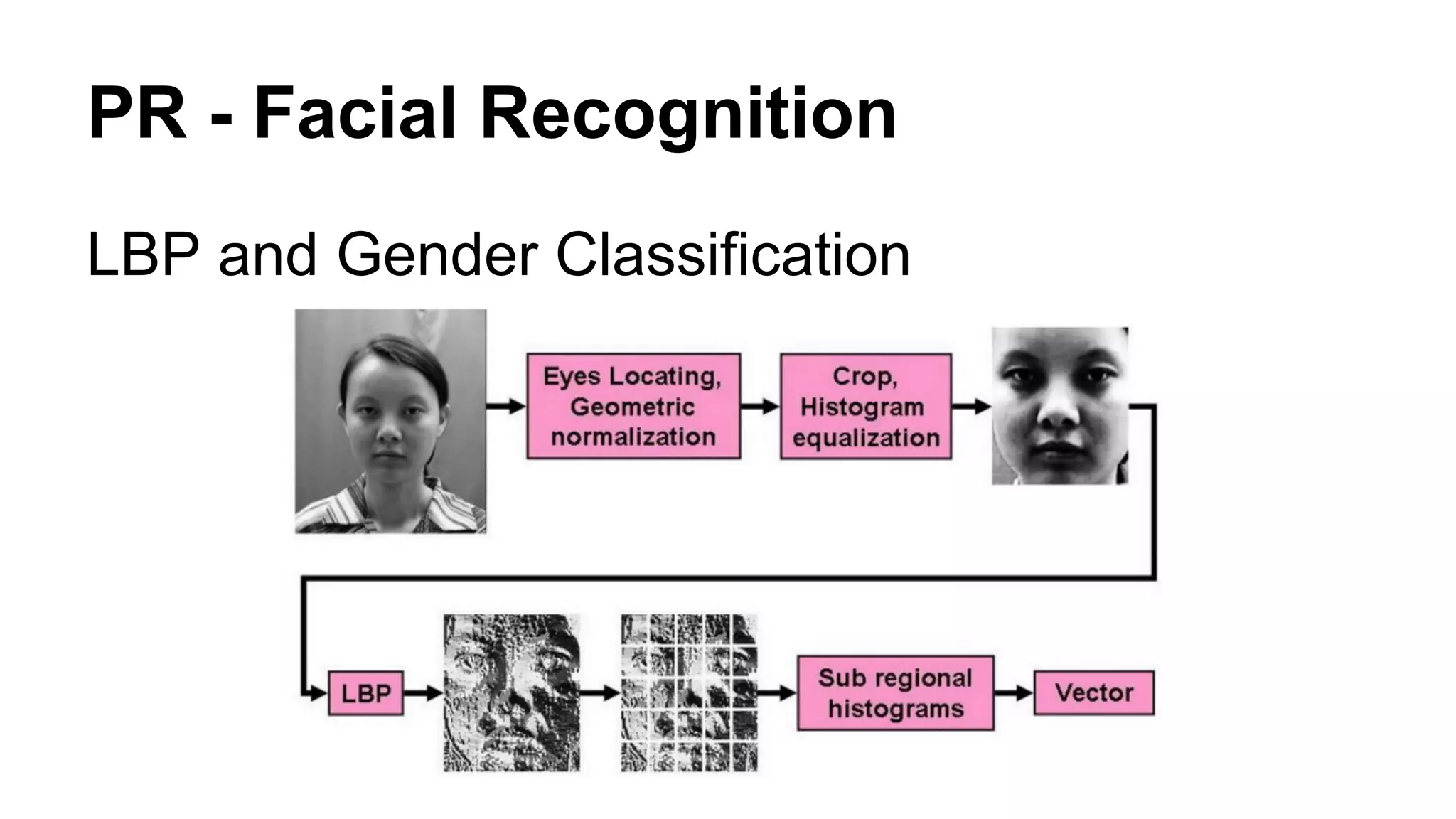
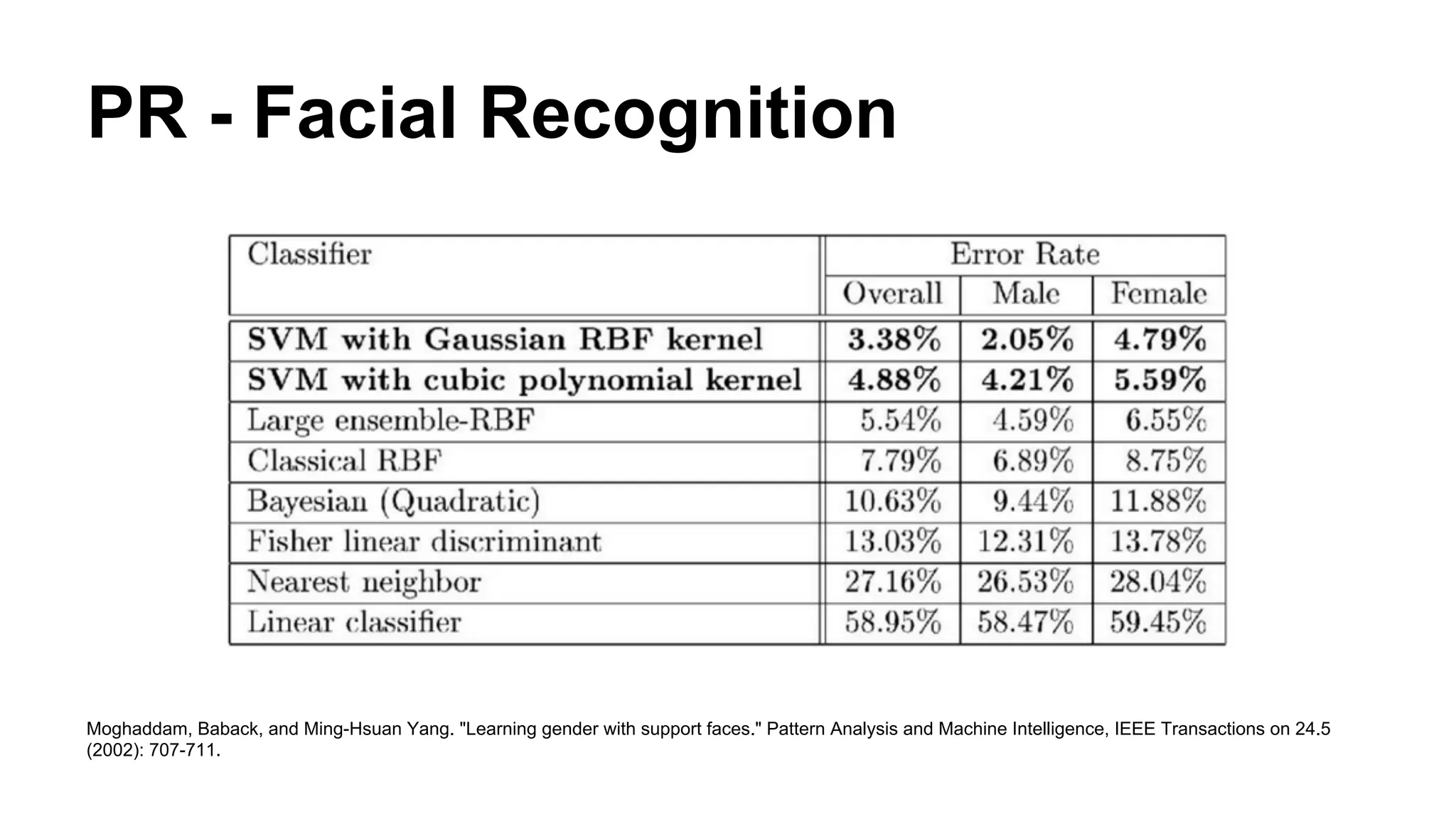
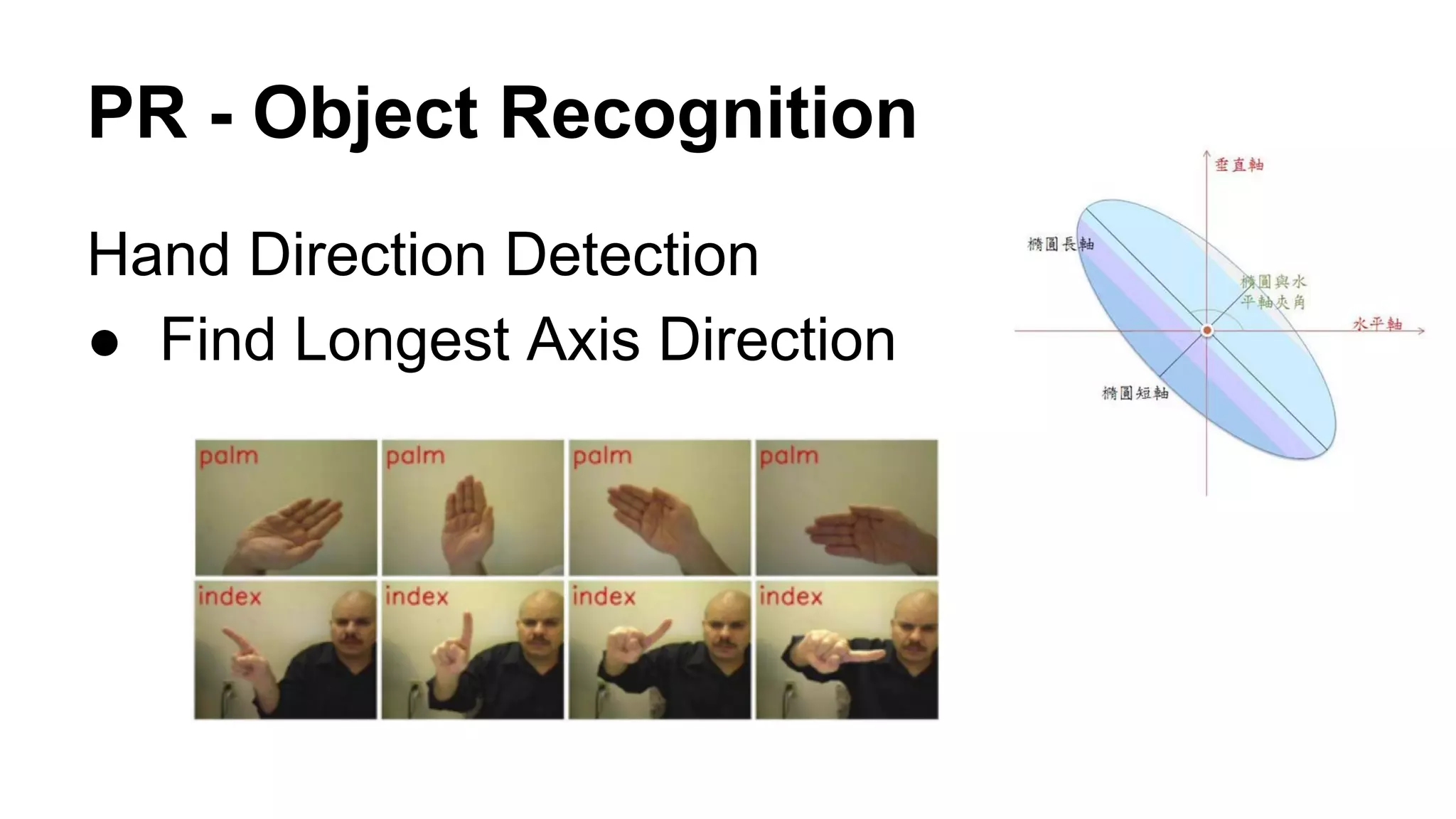
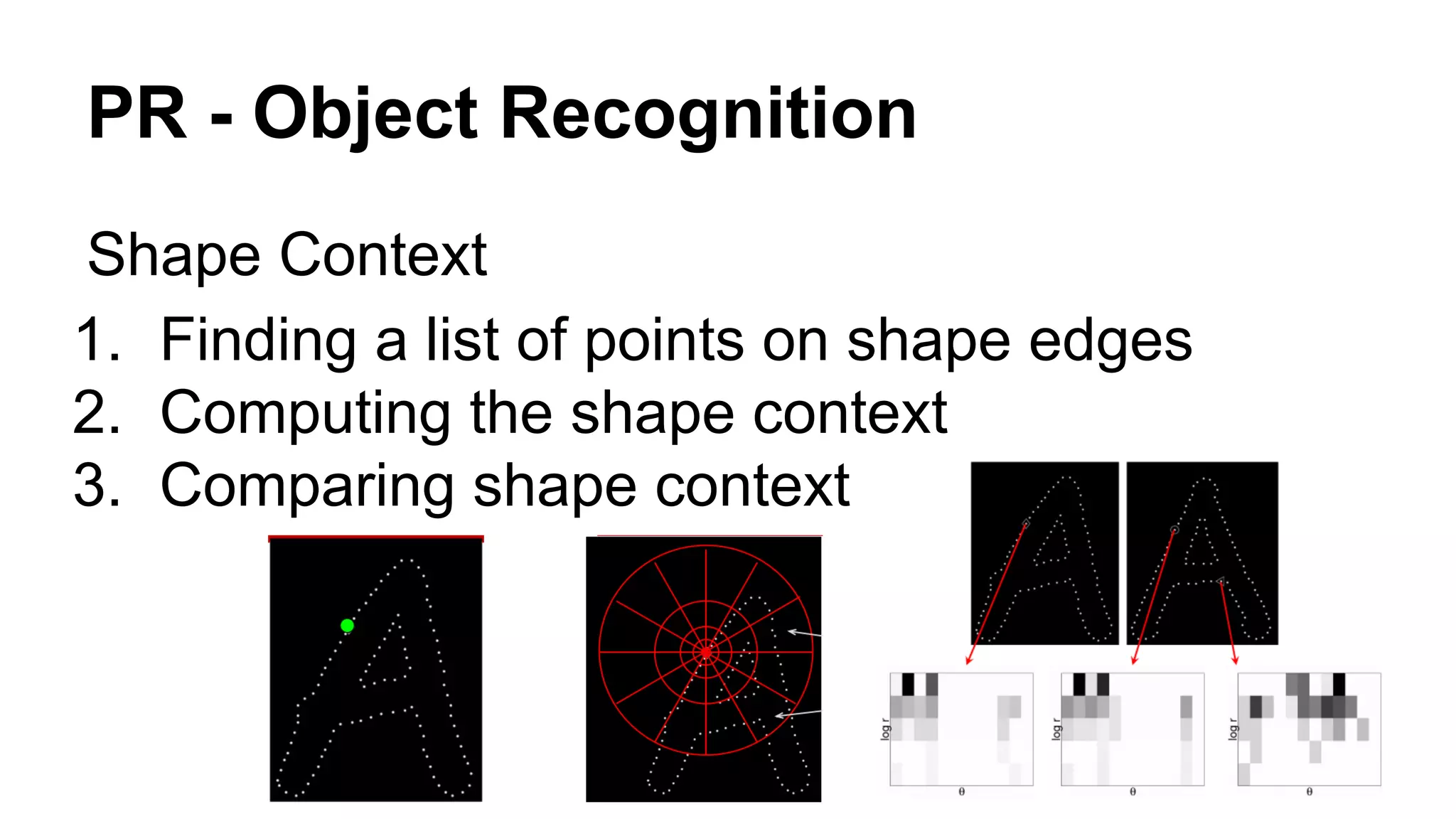
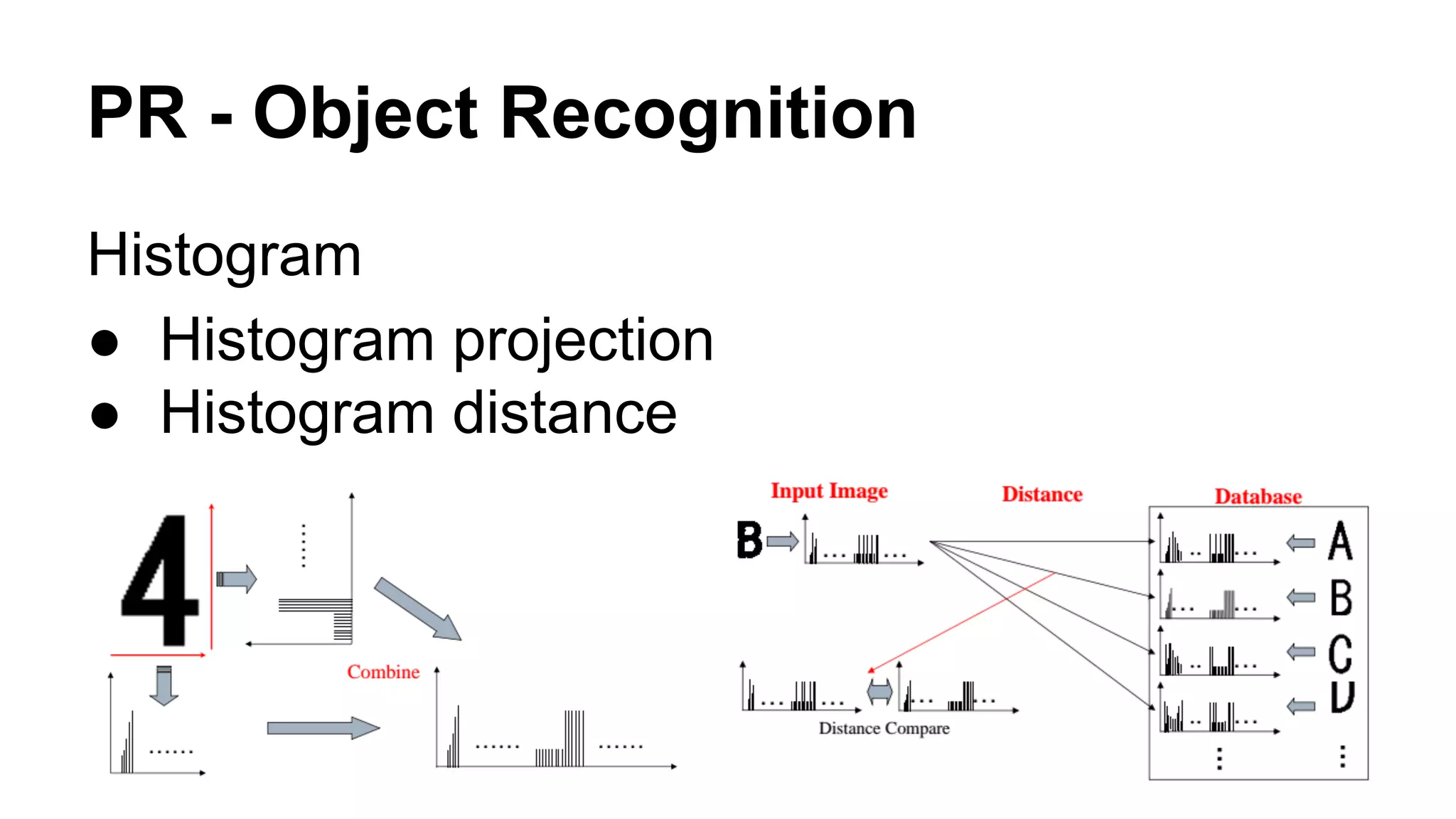
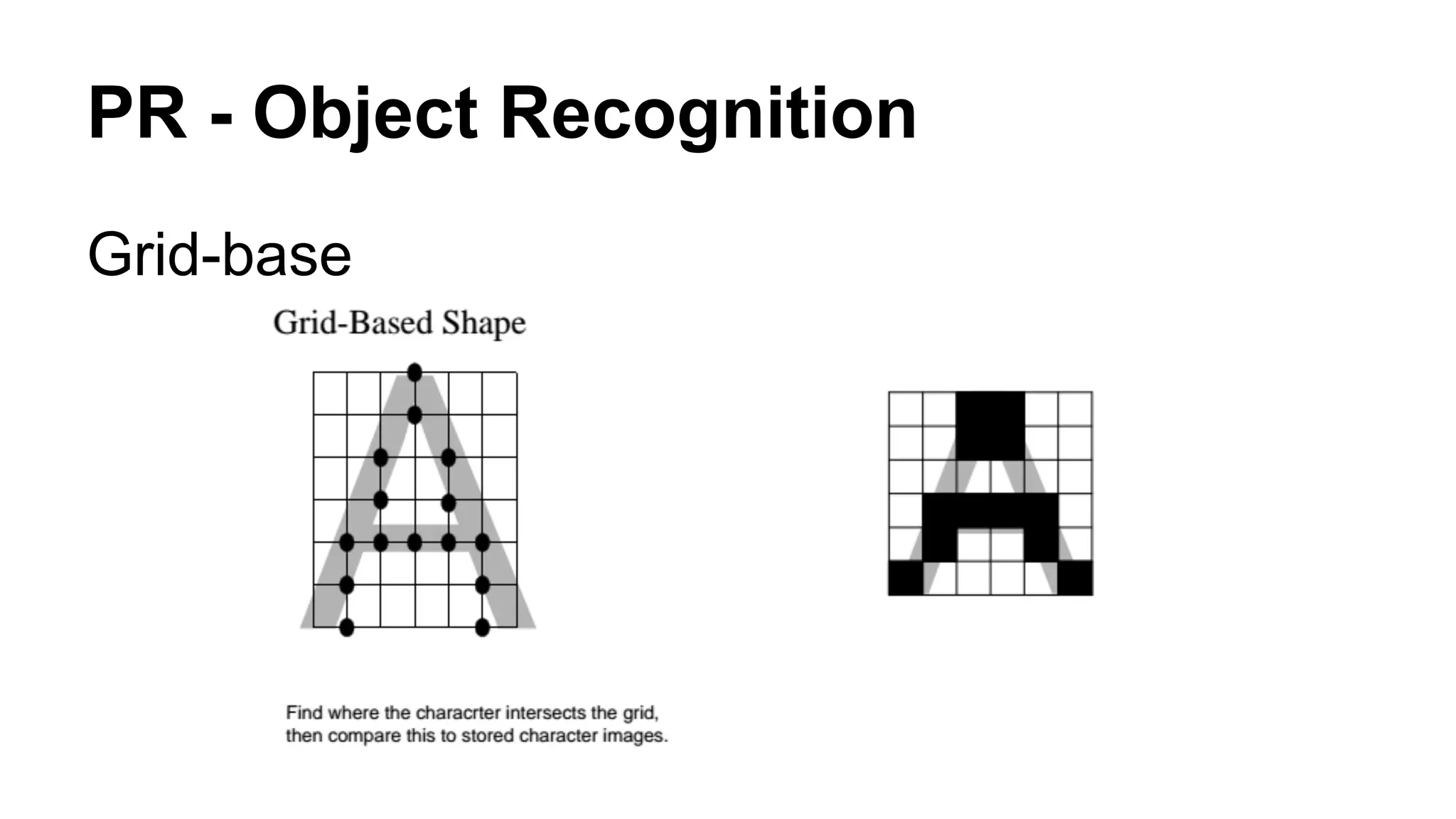
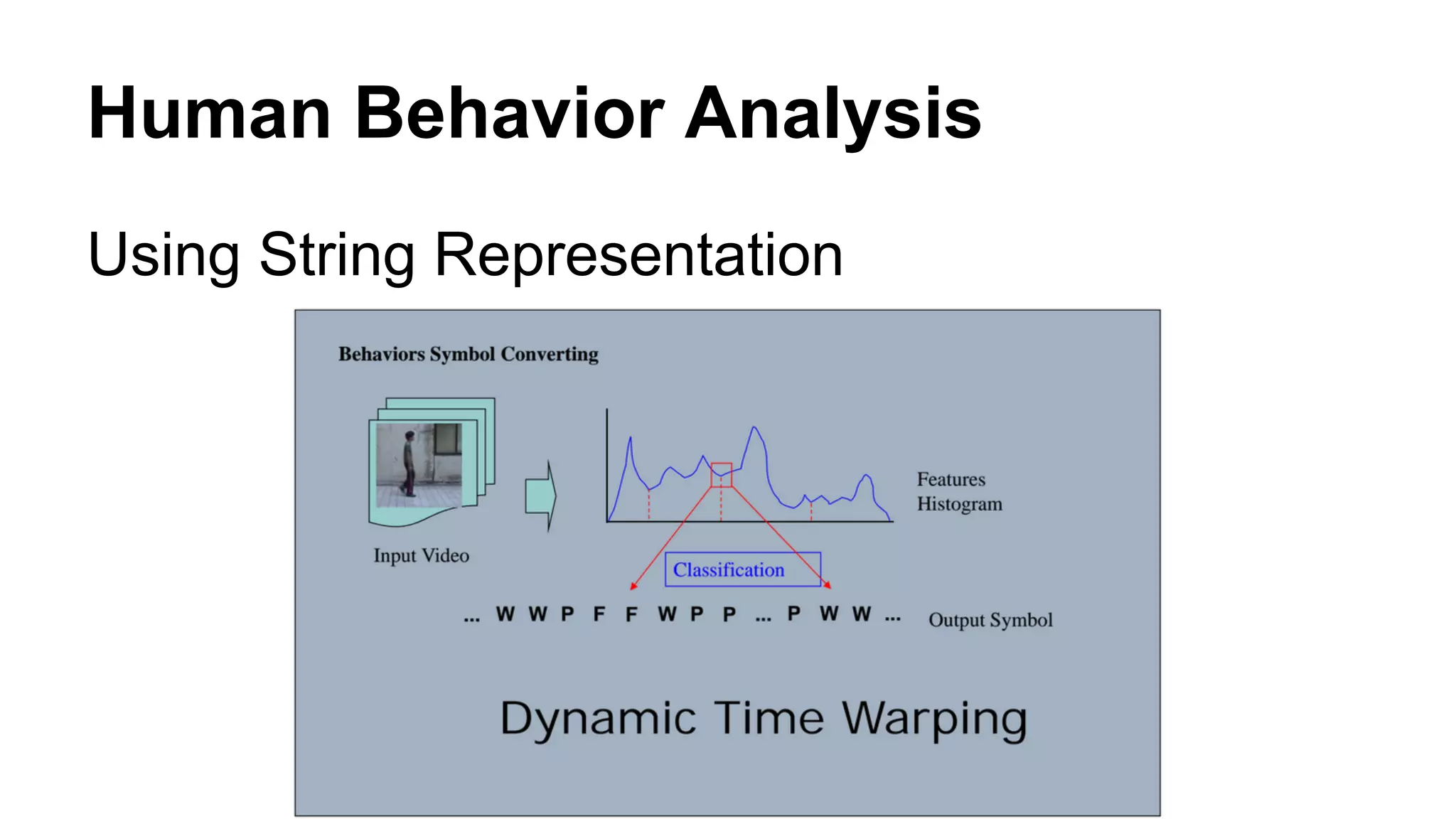
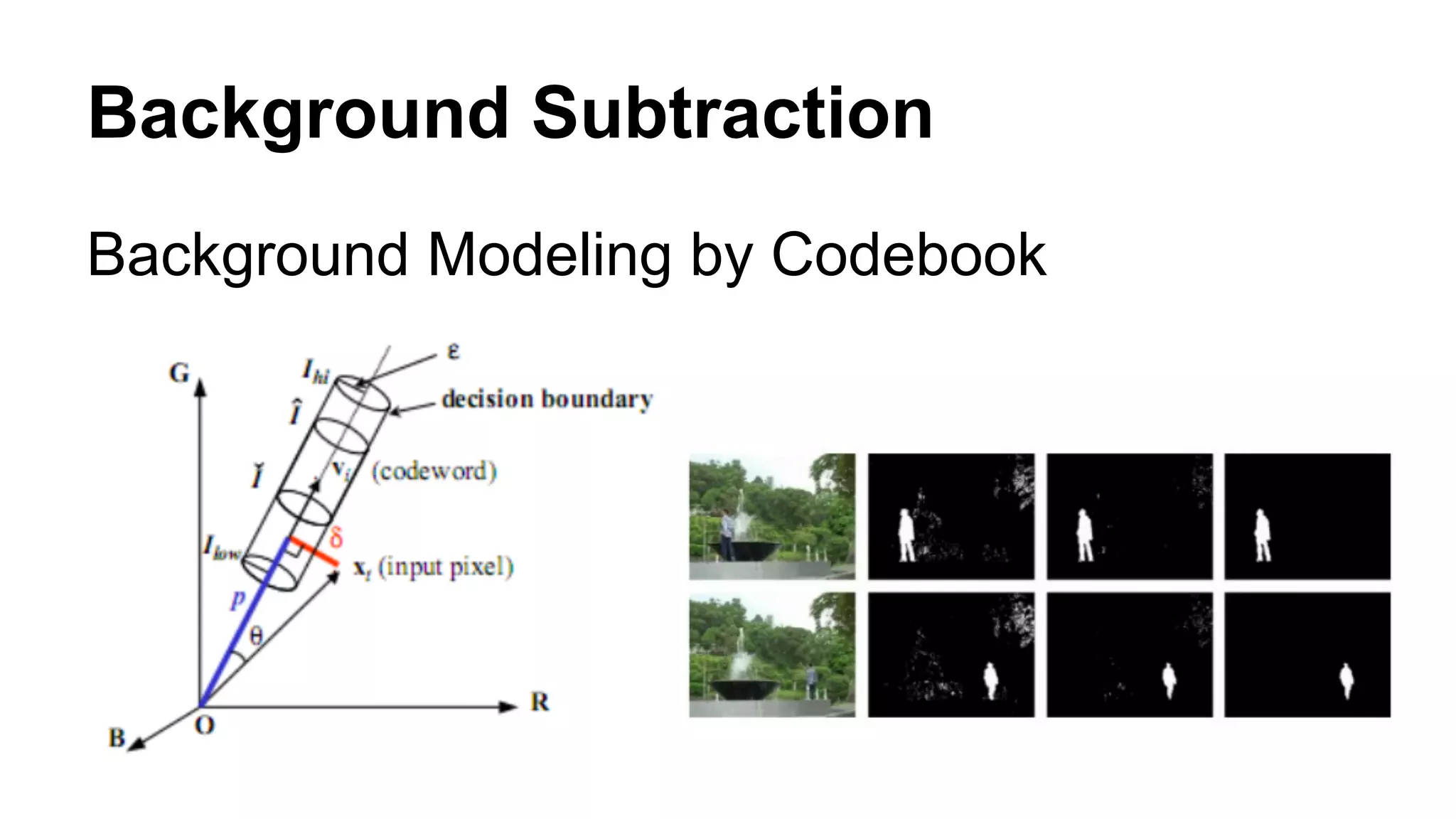
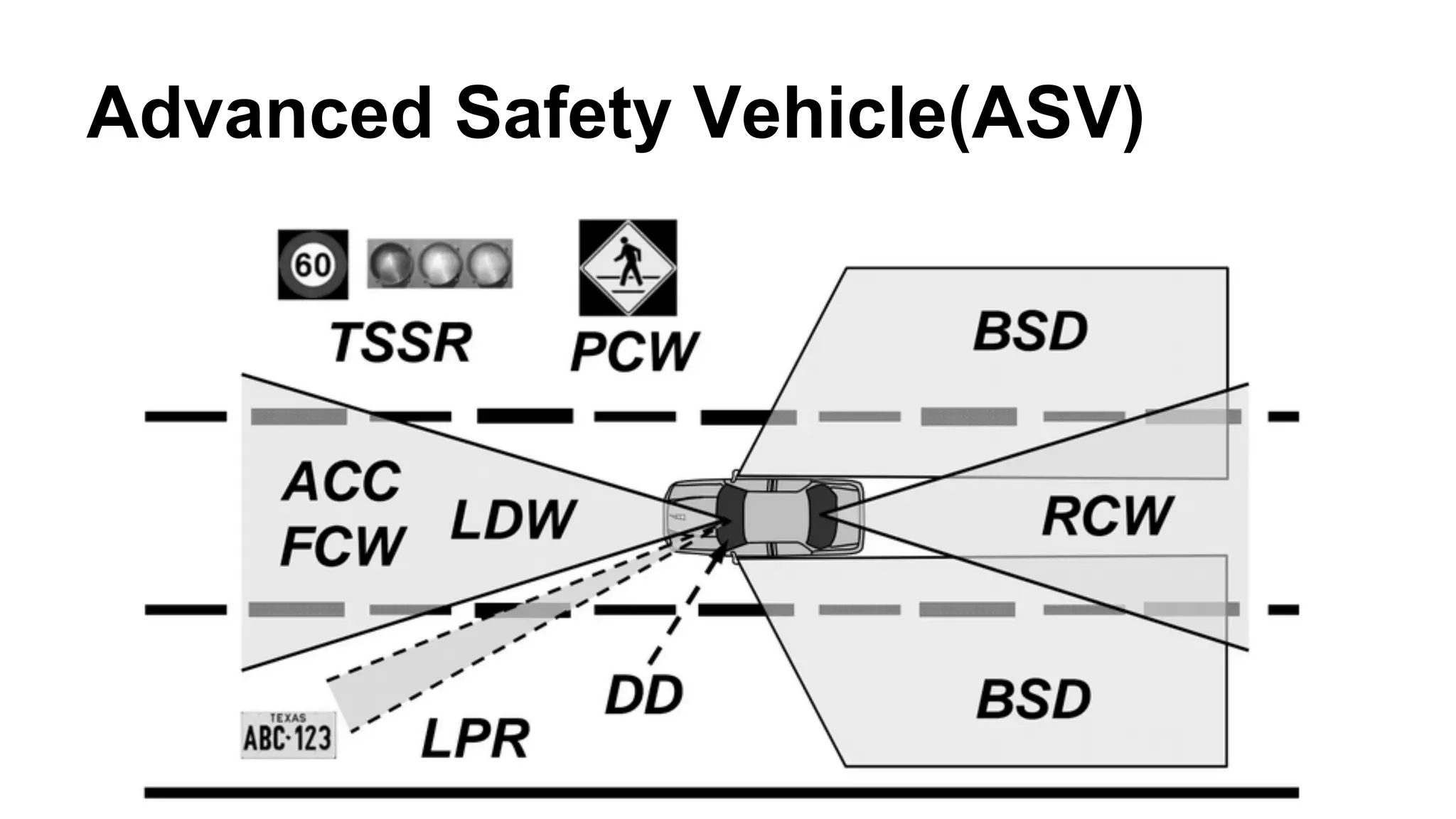
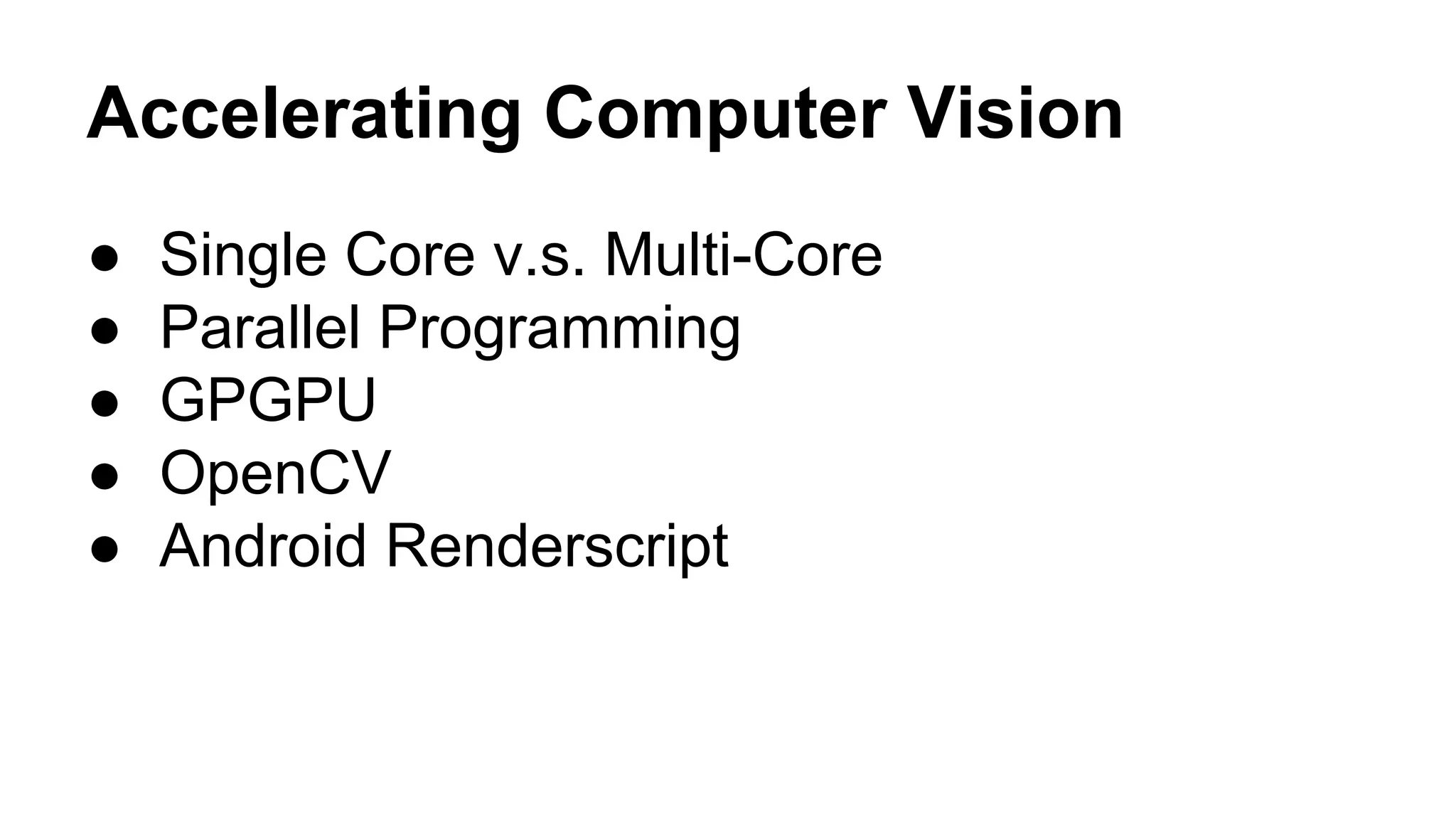
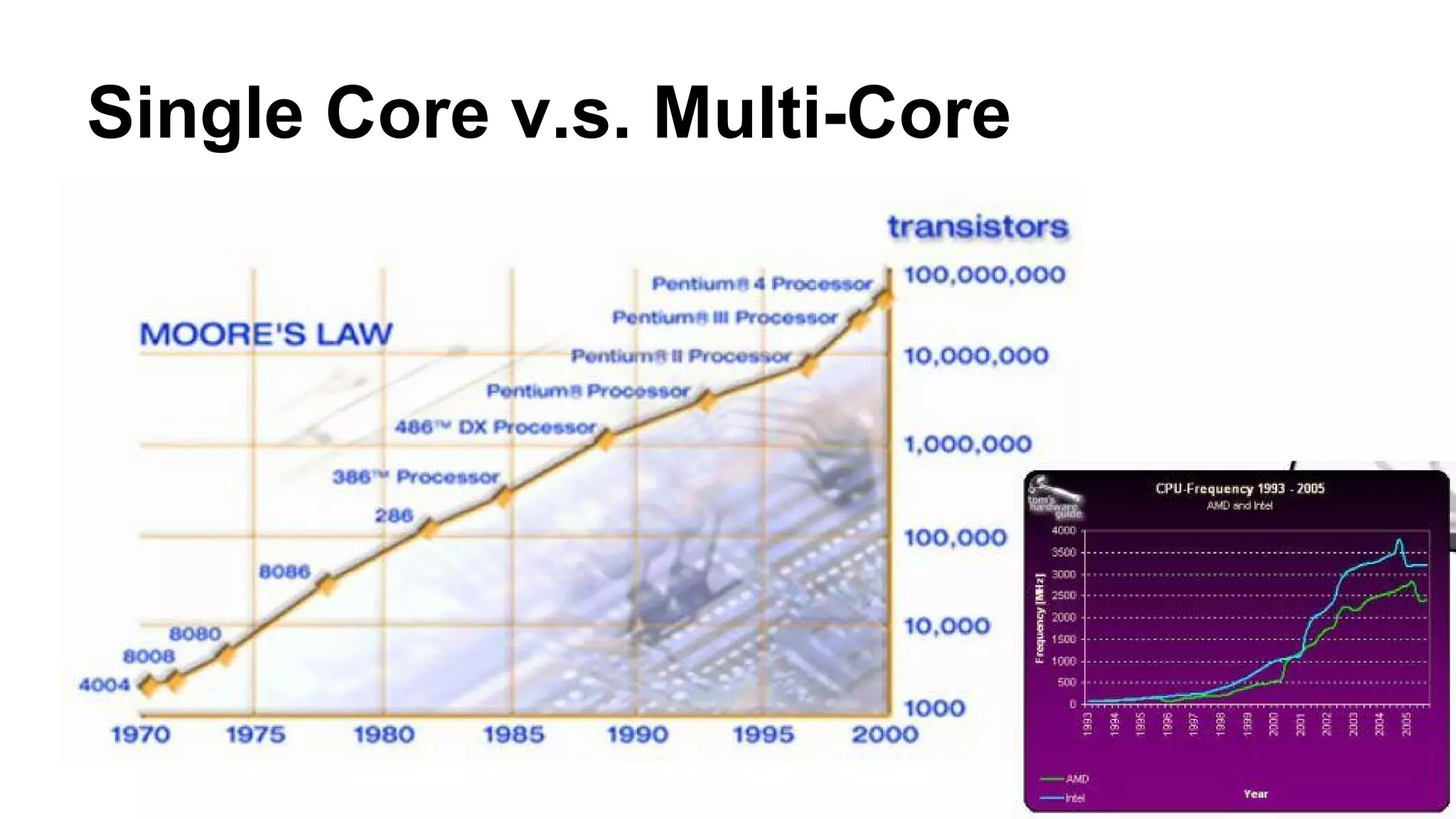
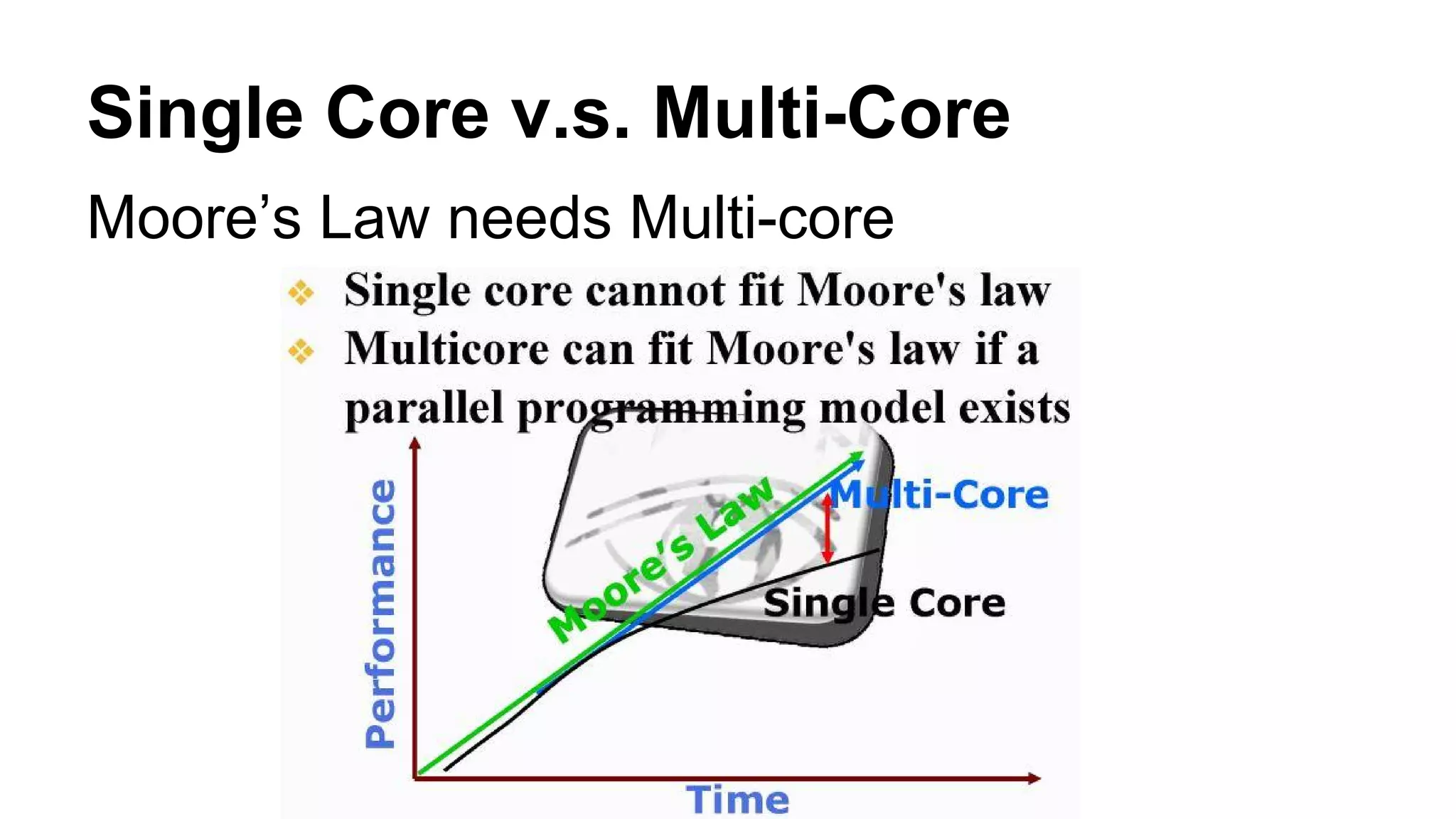
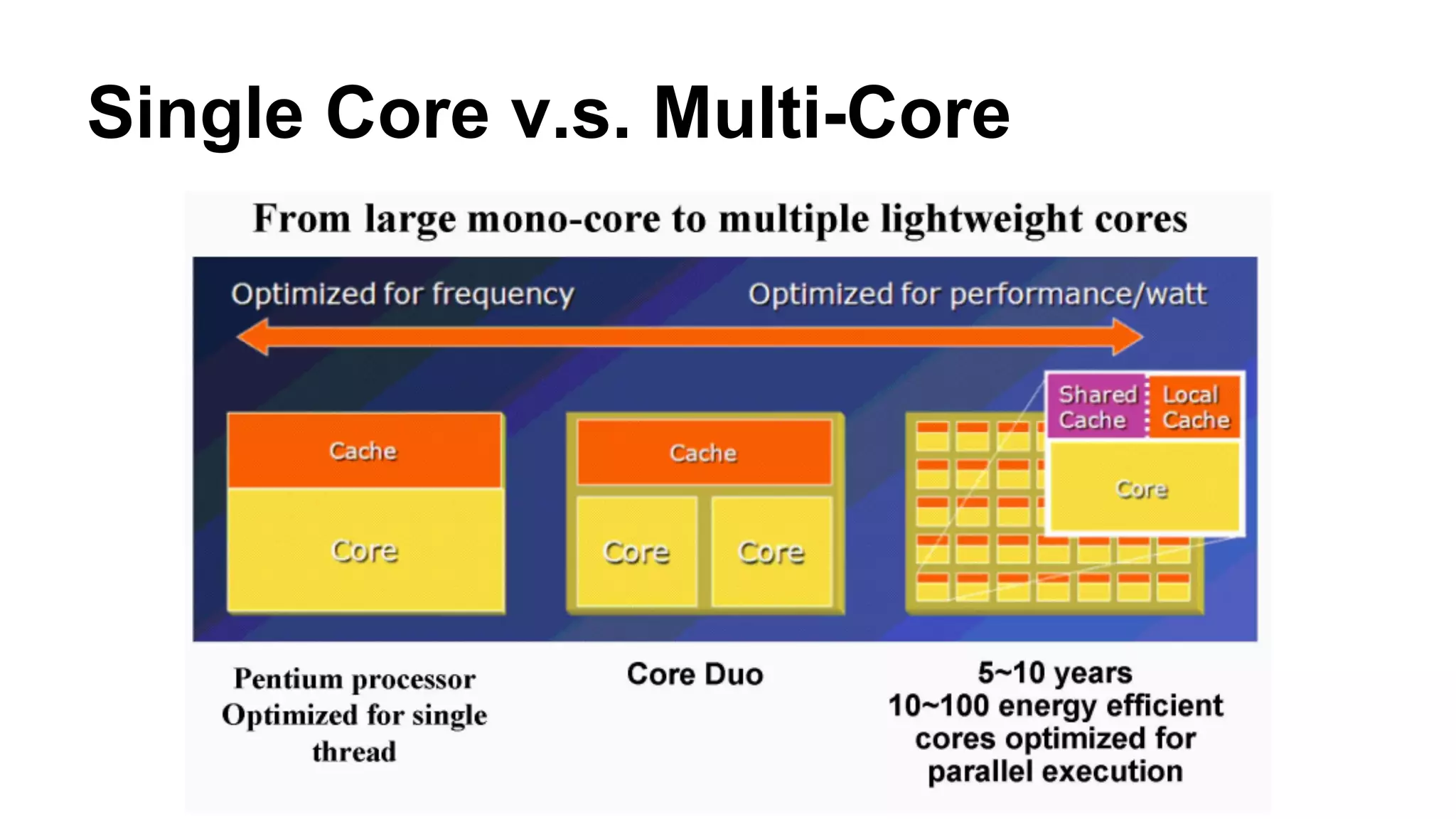
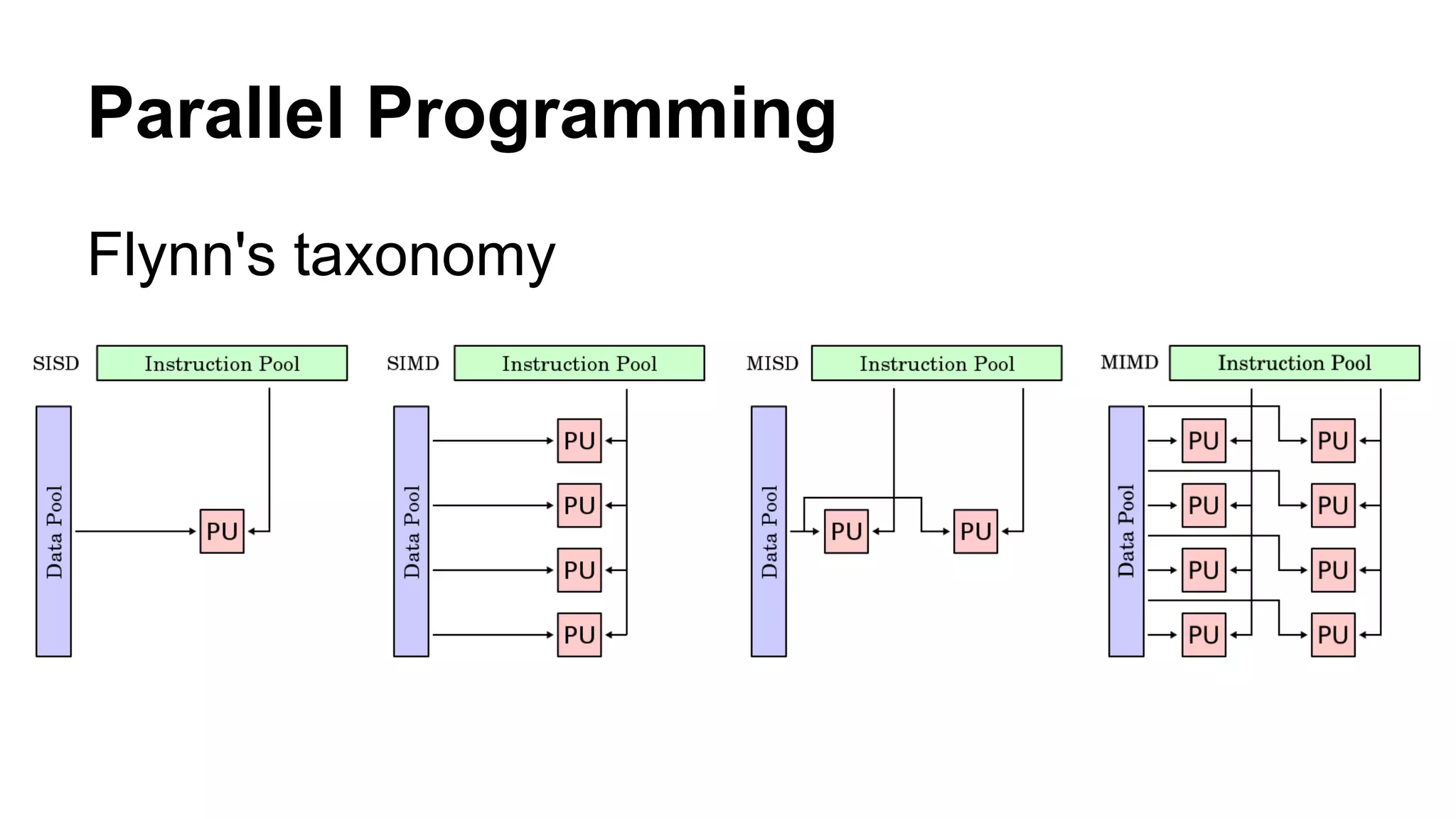
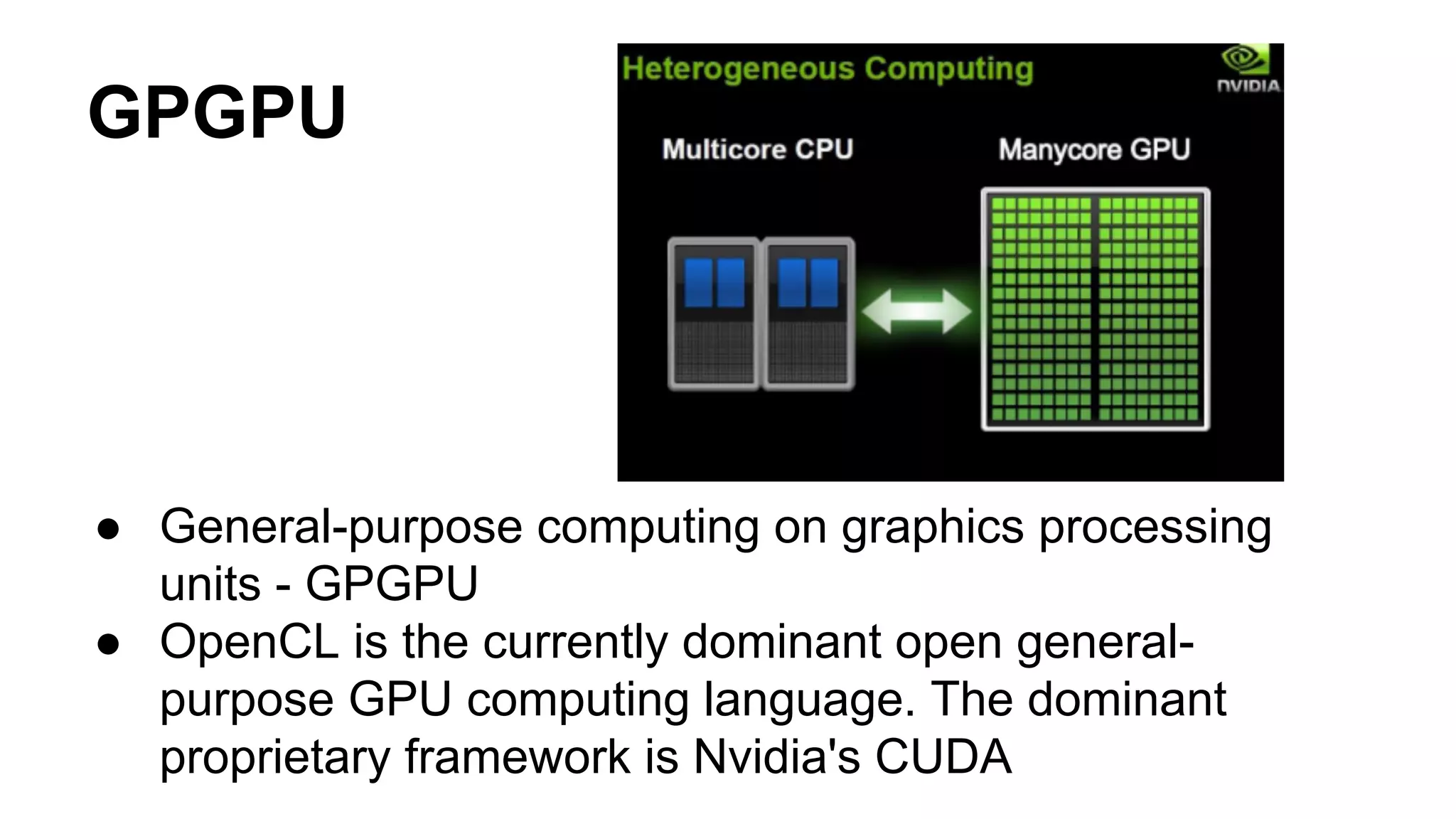
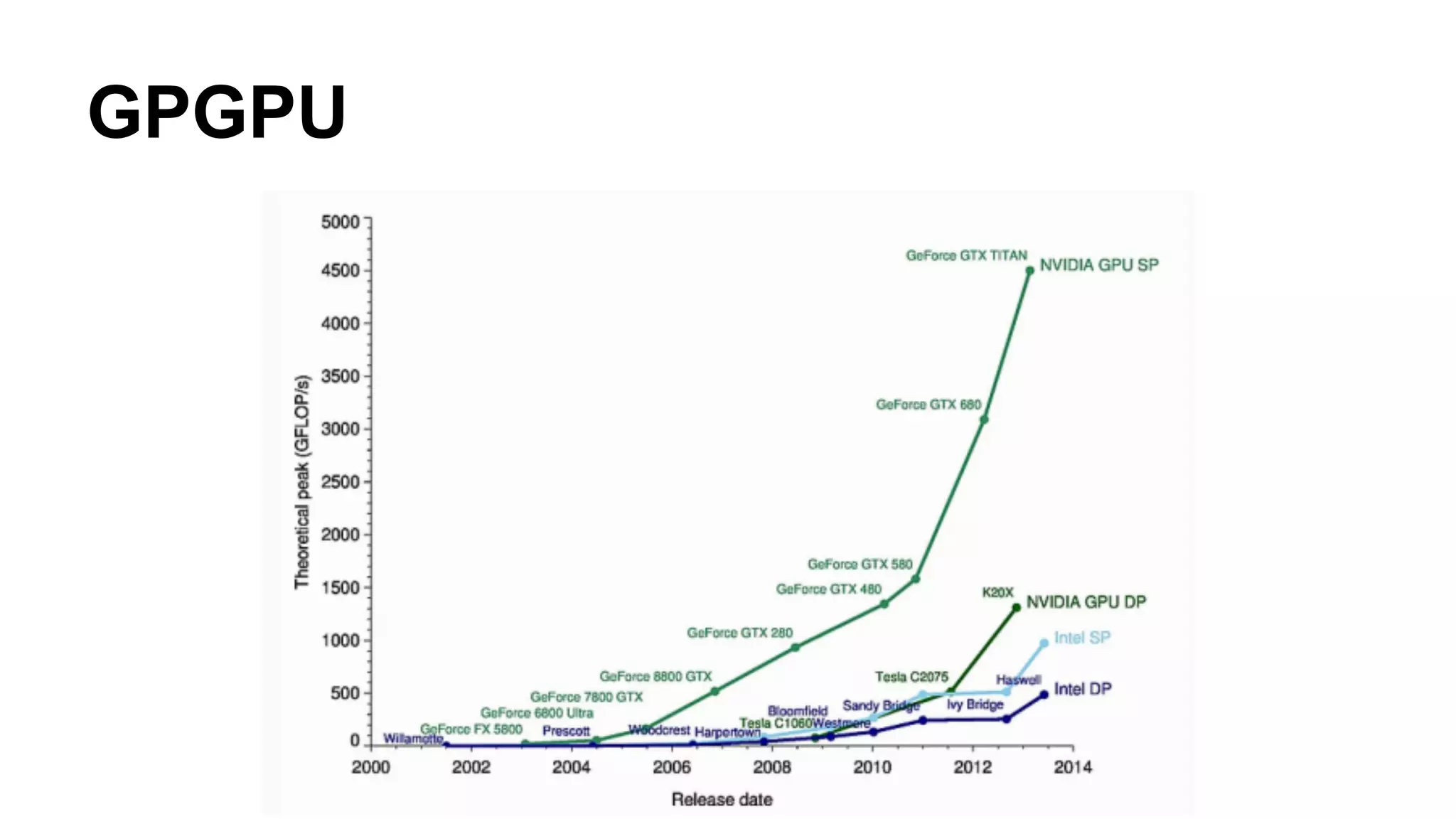
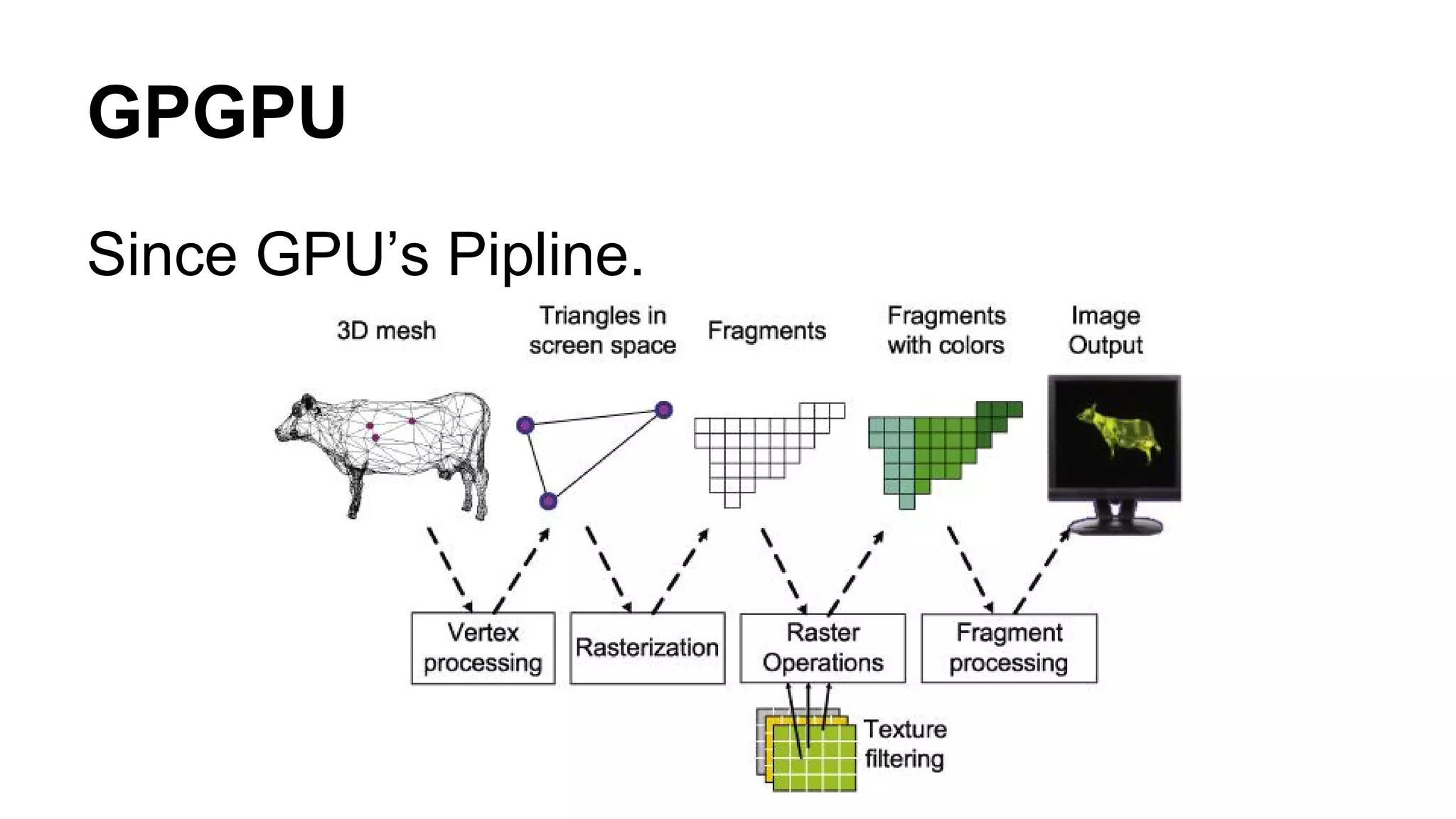
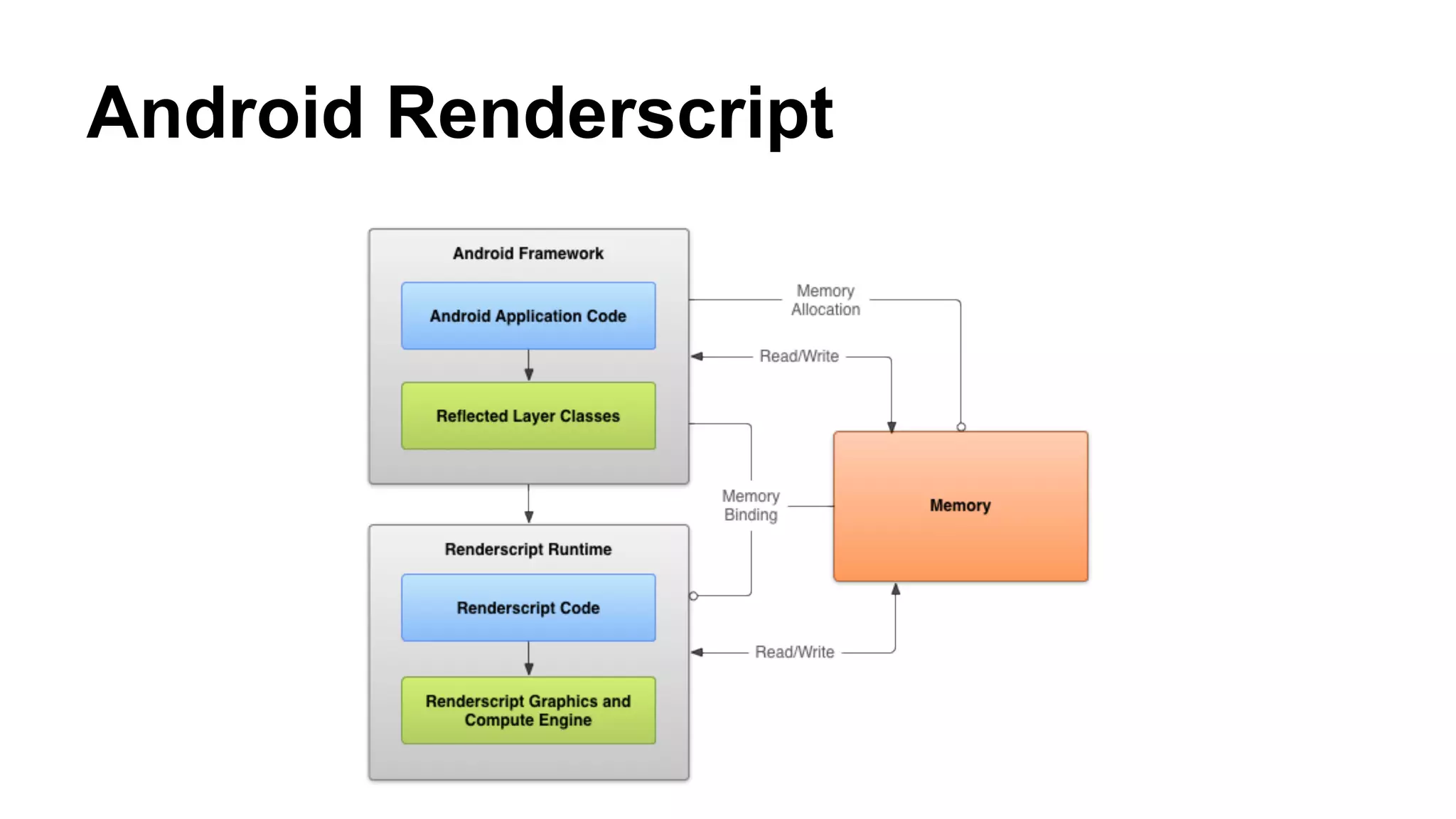
The document provides an overview of computer vision, including its definition, fundamental operations such as image enhancement and segmentation, and approaches like pattern recognition and motion analysis. It highlights the differences from human vision, emphasizing the necessity for high processing performance and cognitive adaptability in various environmental conditions. Additionally, the document discusses technologies that accelerate computer vision, including parallel programming and GPU computing, and concludes that the future of computer vision relies on advancing software technology.




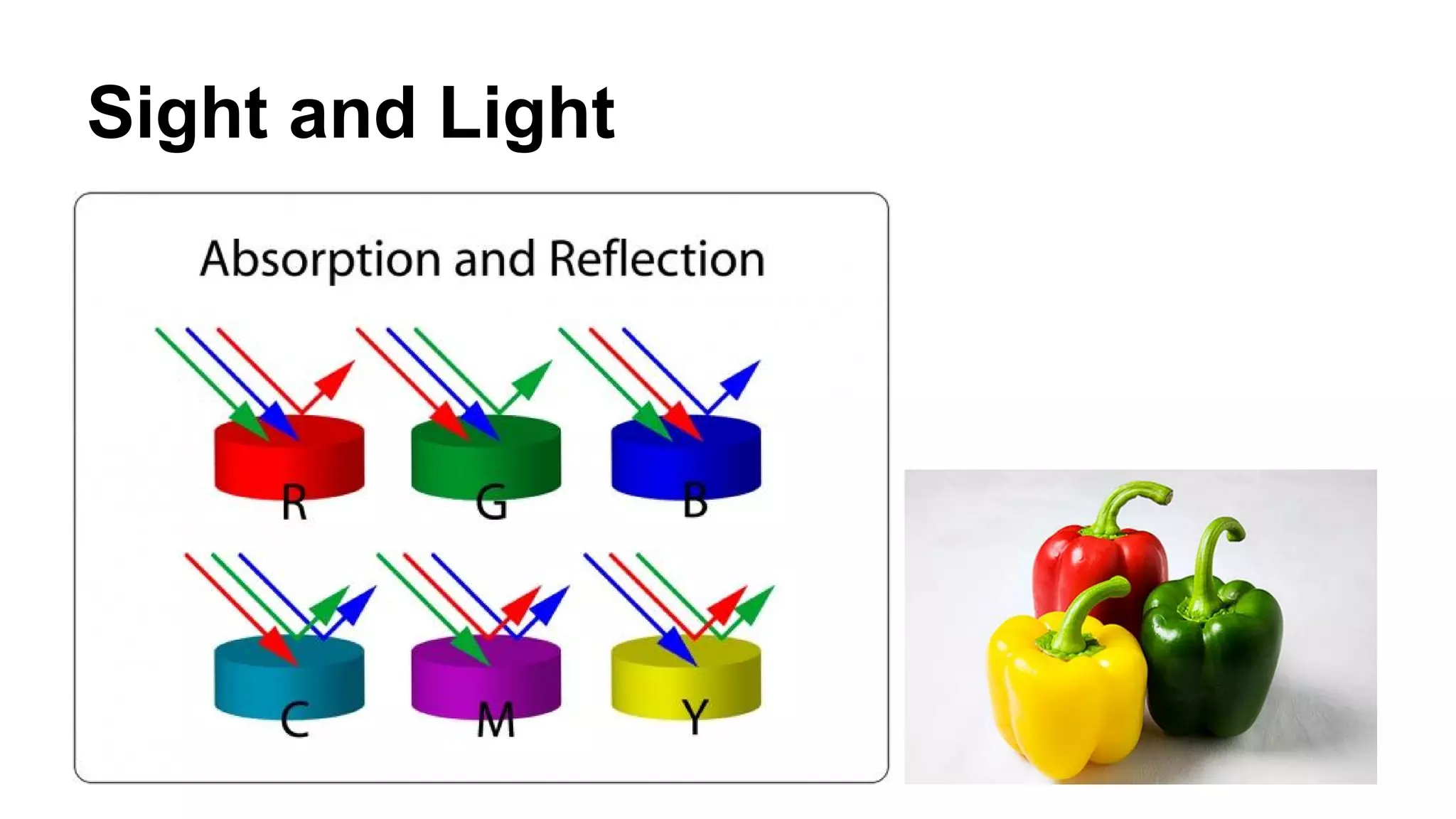
![Sight and Light
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is
visible to (can be detected by) the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this
range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye
will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 700 nm.[1] In terms of
frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 430–790 THz.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computervision-140923034212-phpapp02/75/Computer-Vision-5-2048.jpg)
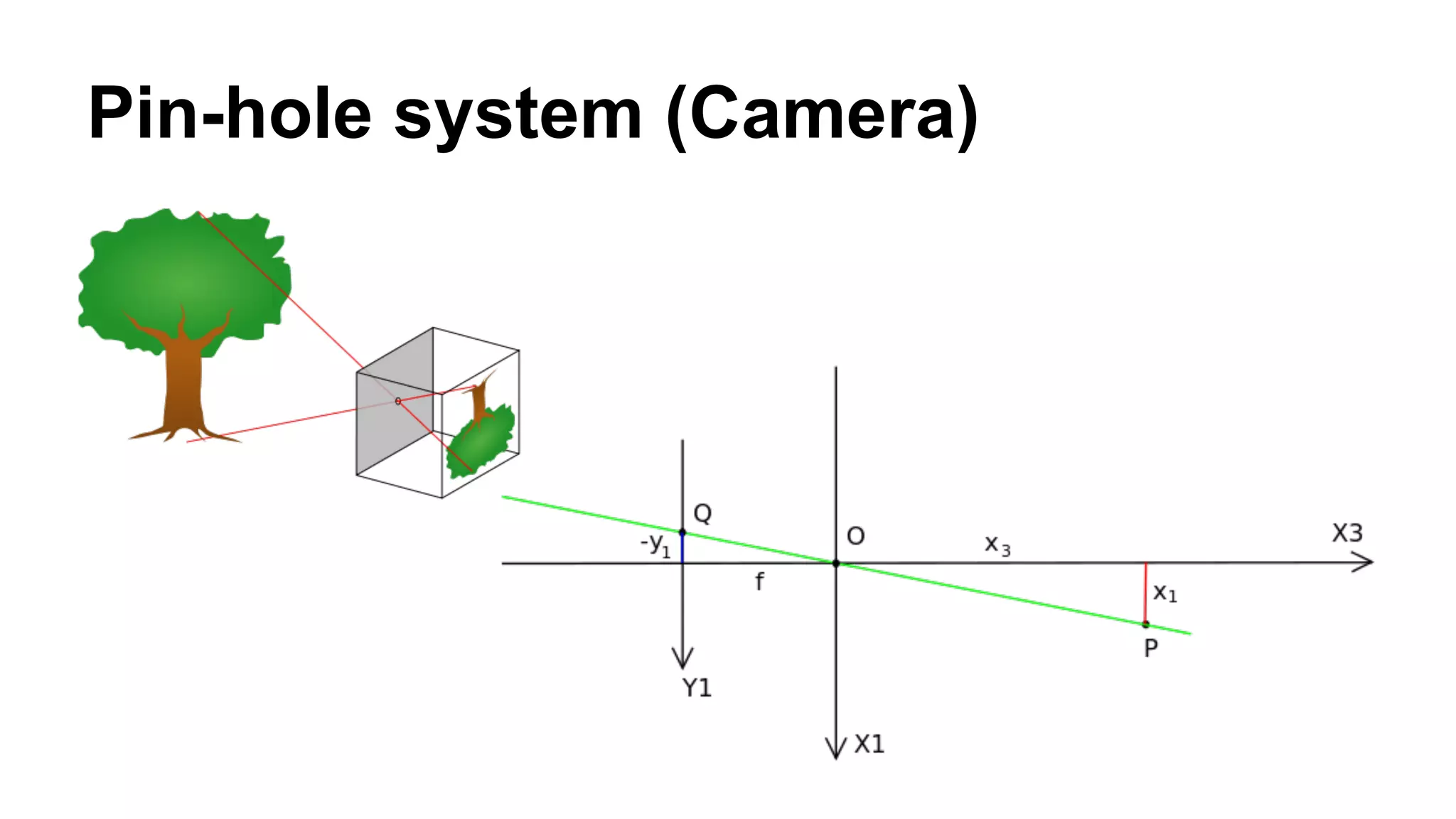
![Quantization & Resolution
How to make an Image: Digitalization
● Resolution: Sampling corresponds to a discretization of
the space. That is, of the domain of the function, into f :
[1, . . . ,N] × [1, . . . , M] −→ Rm.
● Quantization corresponds to a discretization of the
intensity values. That is, of the co-domain of the
function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computervision-140923034212-phpapp02/75/Computer-Vision-10-2048.jpg)