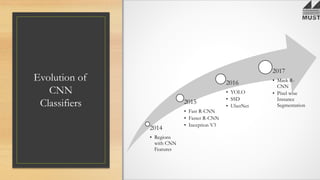
The document discusses the evolution of computer vision, highlighting old problems such as scene understanding, image segmentation, and depth perception, along with their associated challenges and limitations. It details advancements in solutions, especially through the development of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and techniques like fast R-CNN and Mask R-CNN, which improve speed and accuracy in object detection. The document also addresses the programmer's dilemma regarding image formats and emphasizes new technologies like OpenCV and Python libraries that democratize image processing.