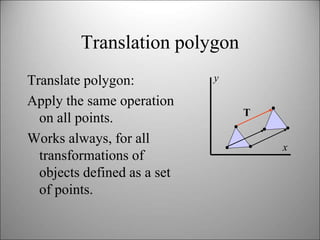
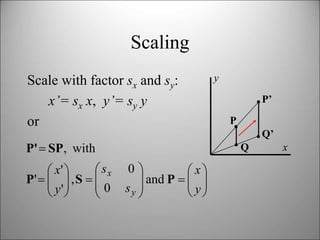
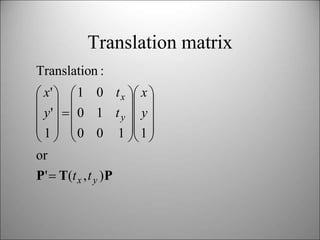
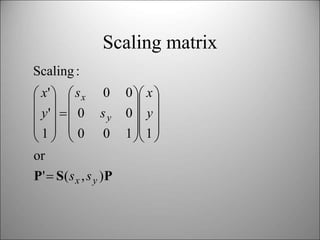
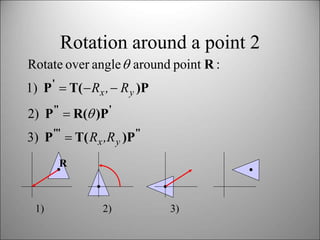
This document discusses 2D transformations in computer graphics including translation, rotation, scaling, and combining transformations using homogeneous coordinates and transformation matrices. It provides examples of translating, rotating, and scaling polygons and explains that the order of transformations matters as matrix multiplication does not commute, so the final result depends on the order the transformations are applied.