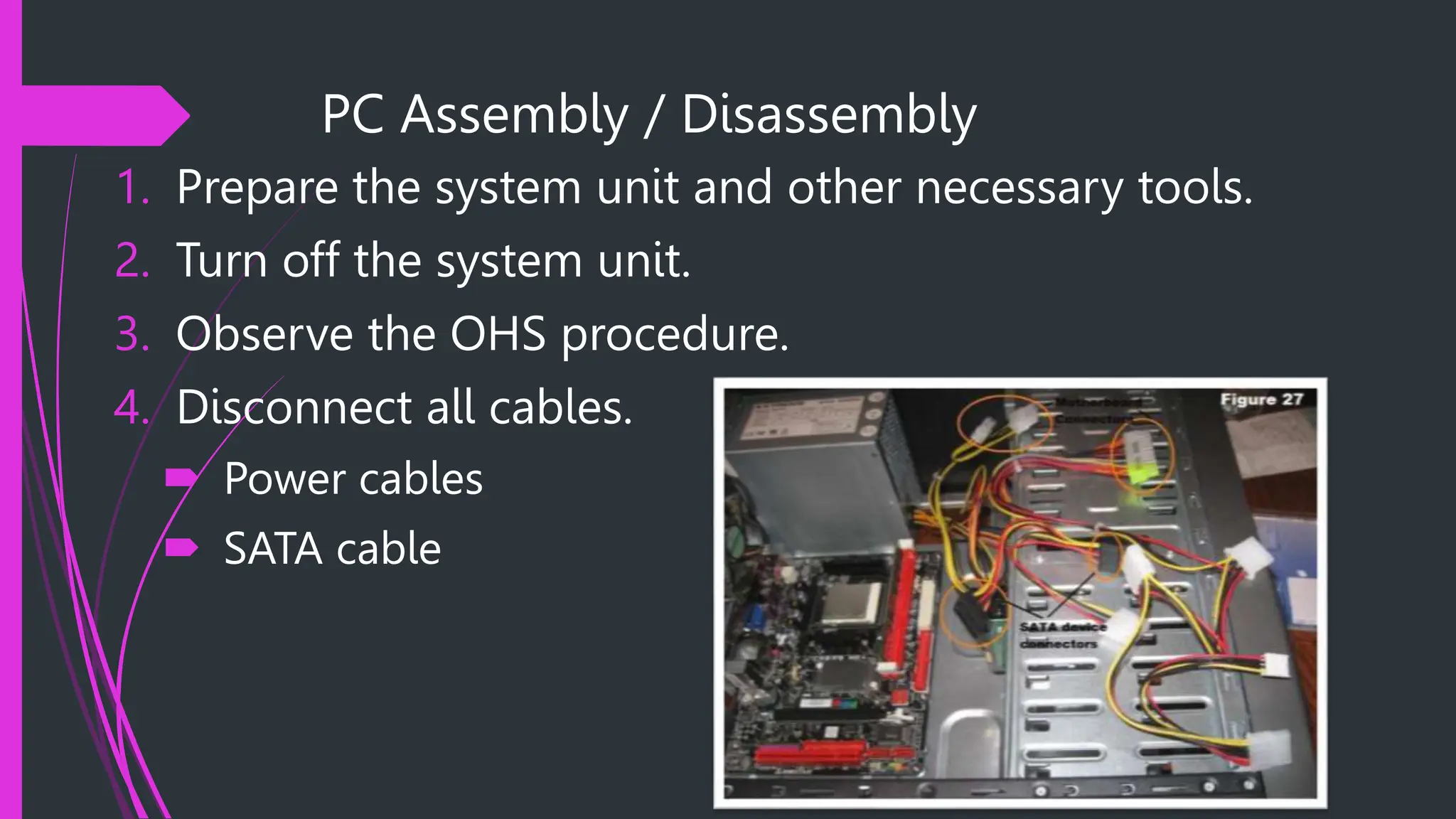
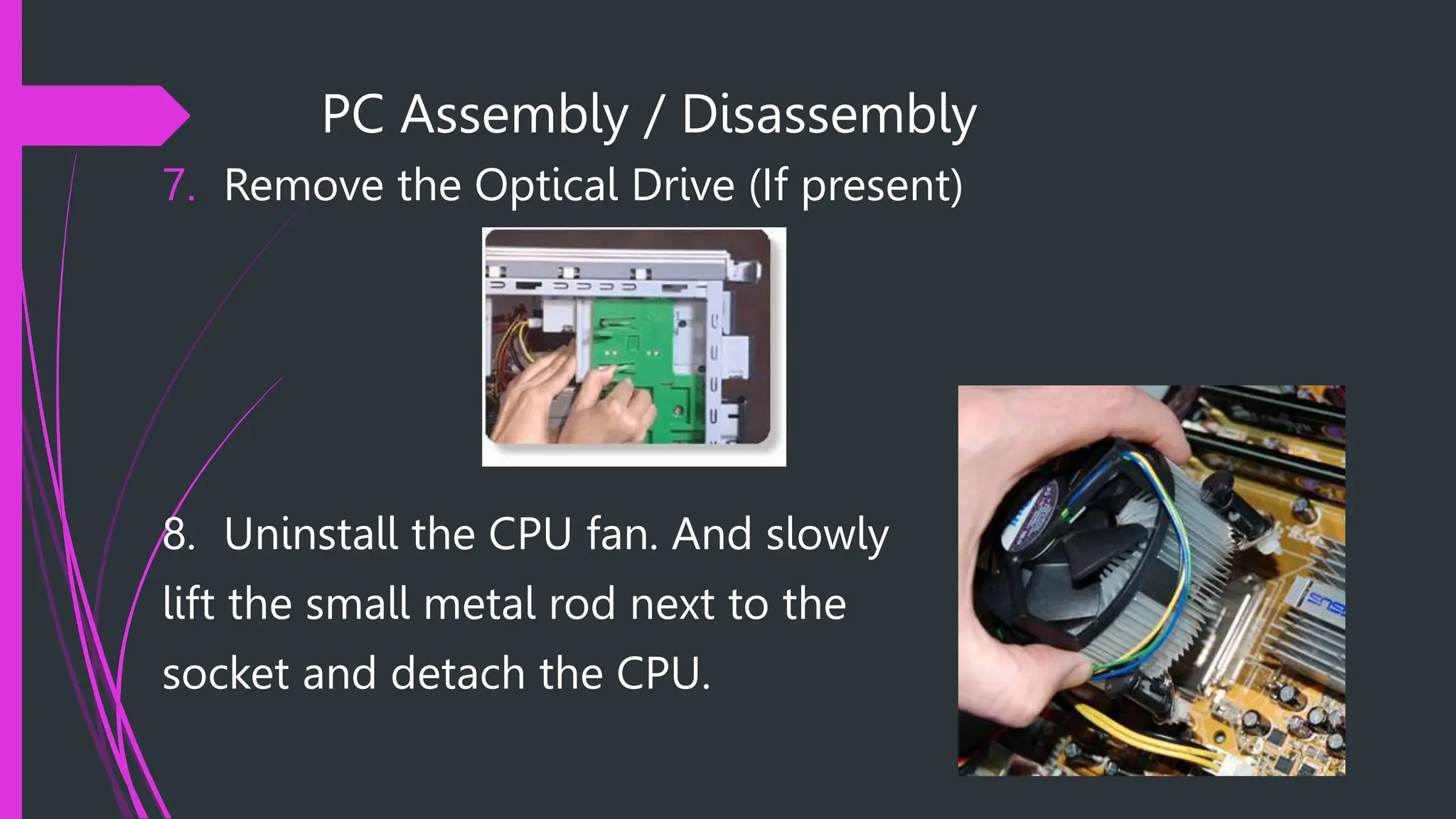
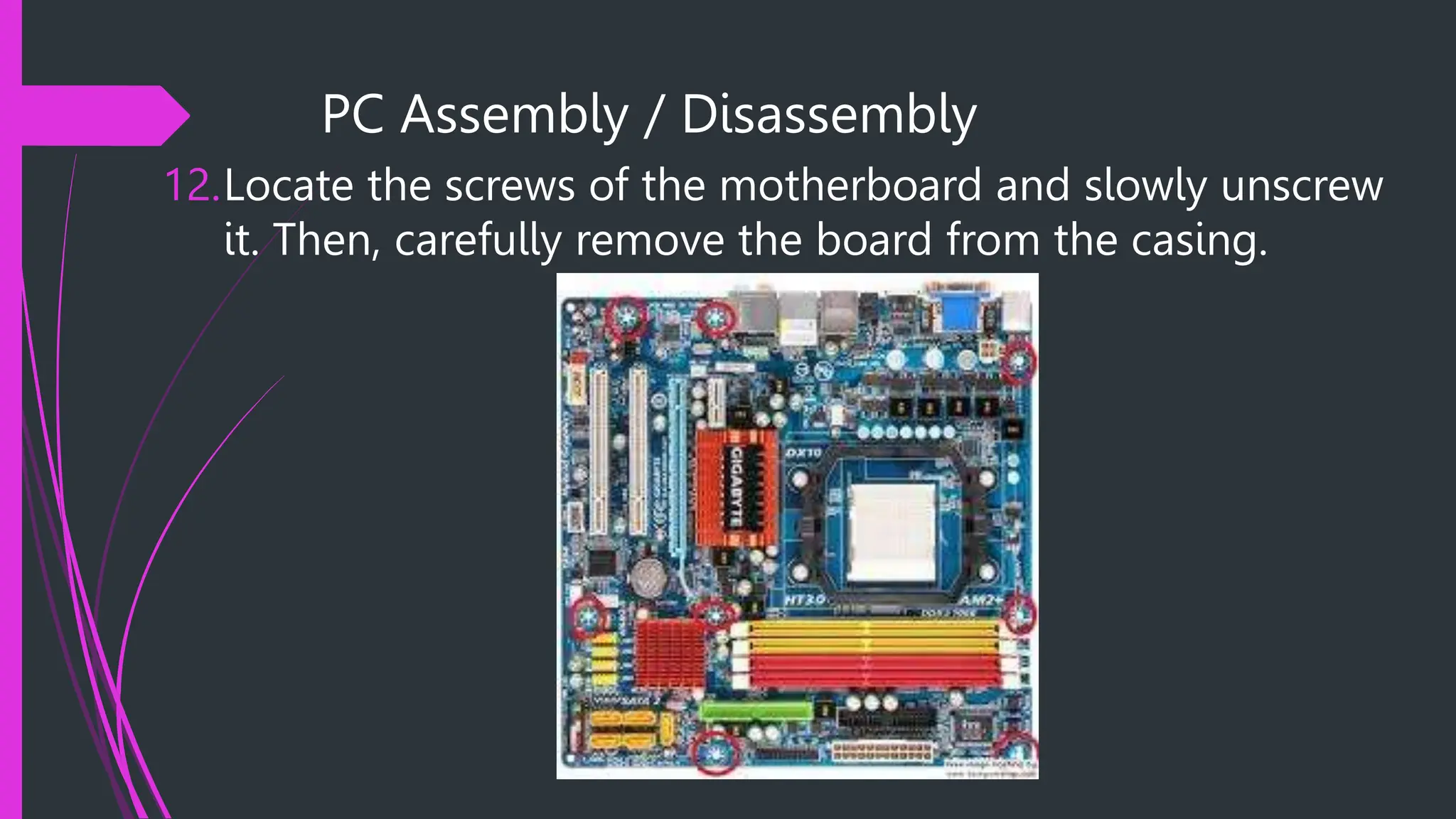
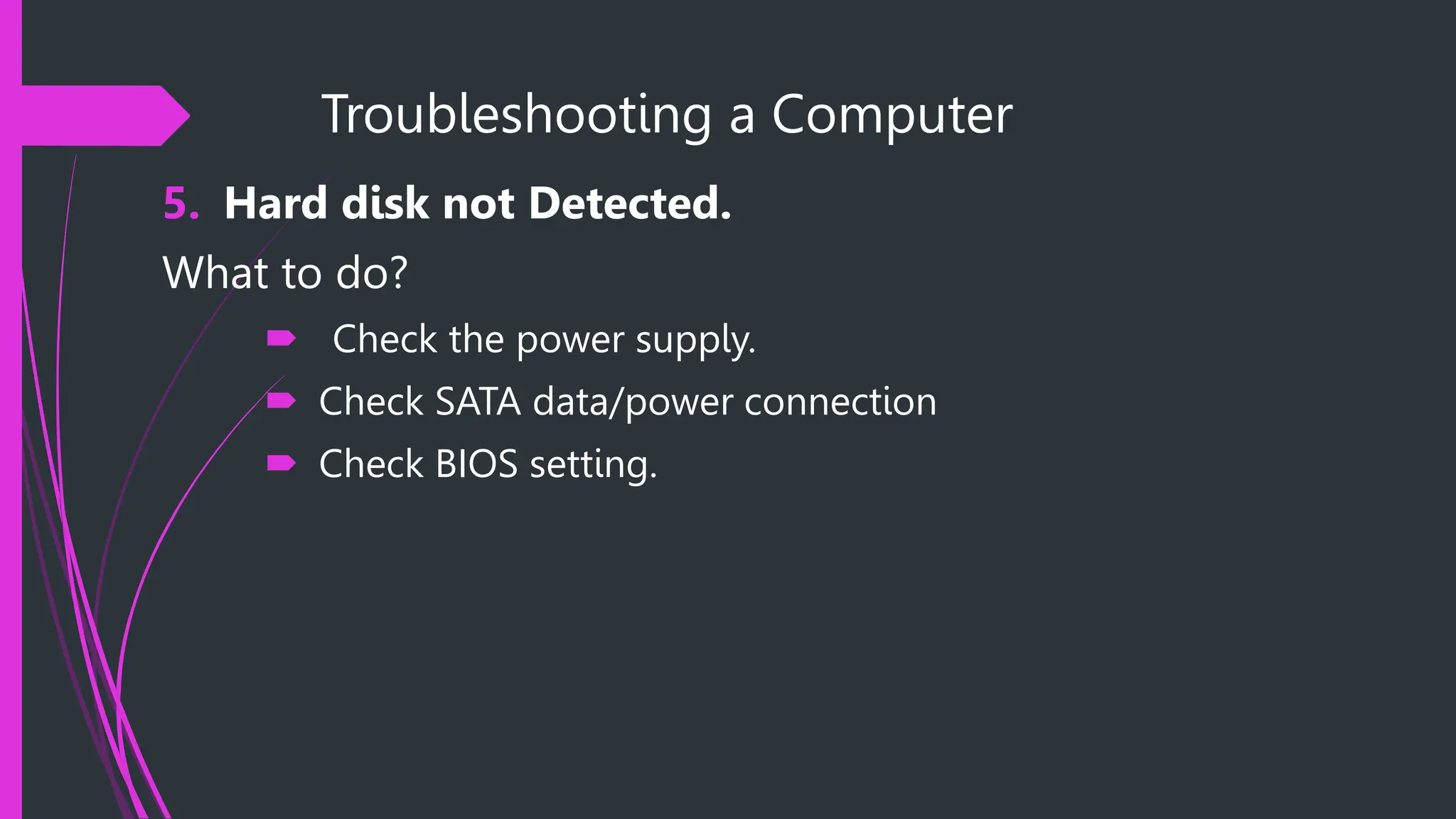
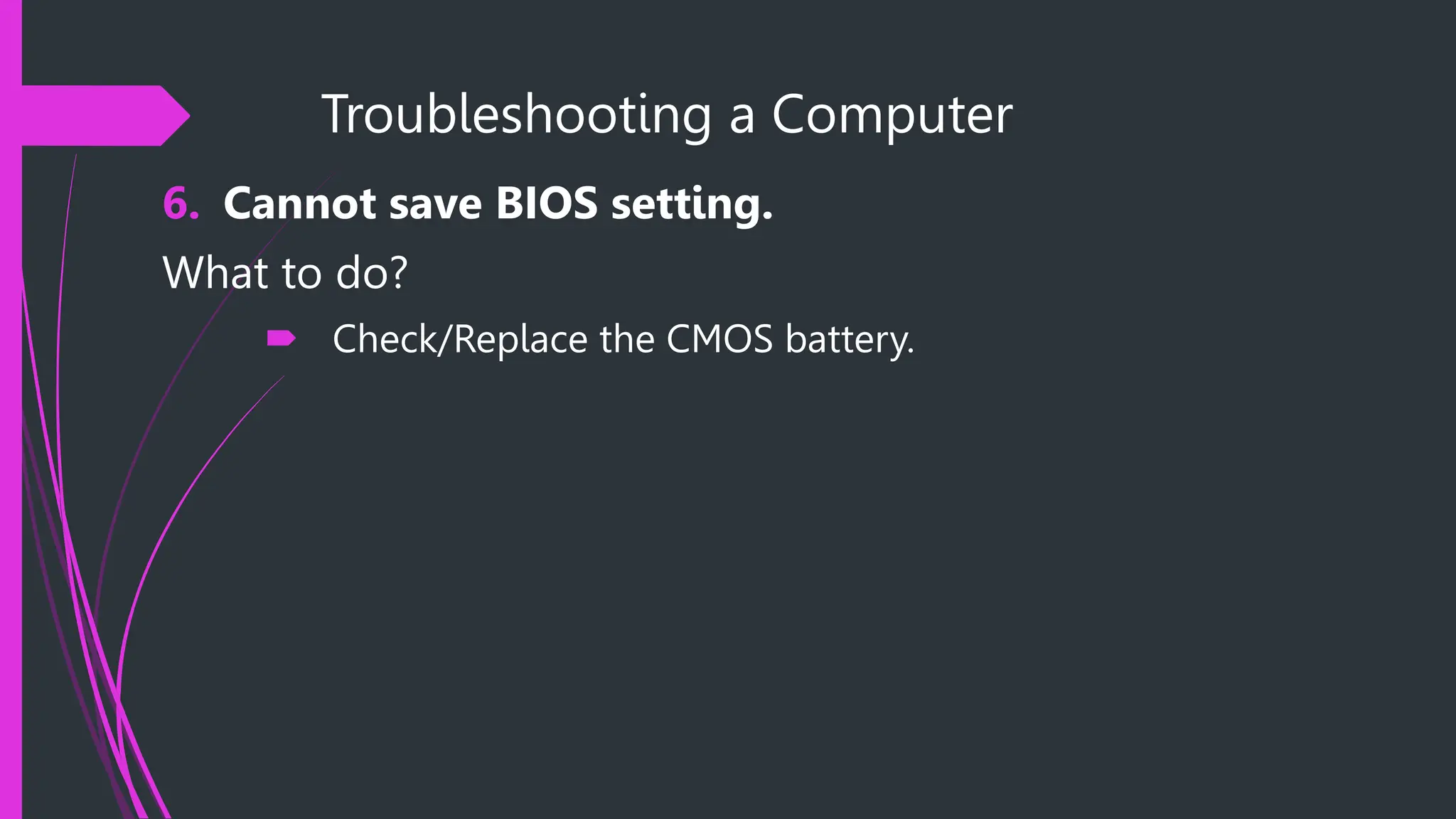
The document provides safety procedures and instructions for assembling and disassembling a computer. It lists several safety precautions like ensuring a clean workspace, wearing anti-static gloves and avoiding touching sensitive parts directly. The assembly process involves preparing necessary tools, disconnecting cables, uninstalling various components like the power supply, hard disk, CPU fan and motherboard in reverse order of their installation. The disassembly process is performed in the reverse order of assembly.