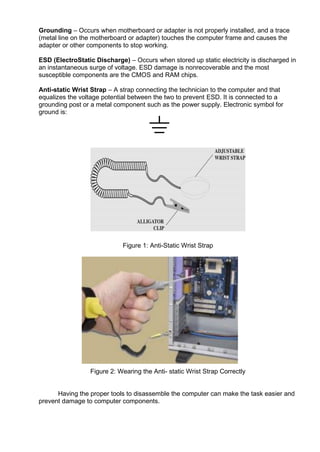
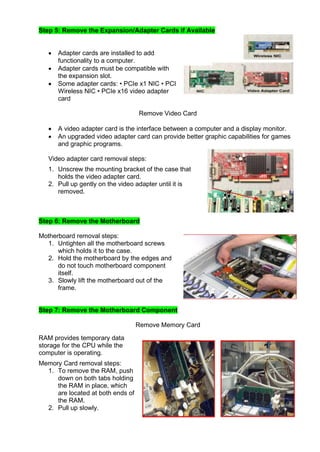
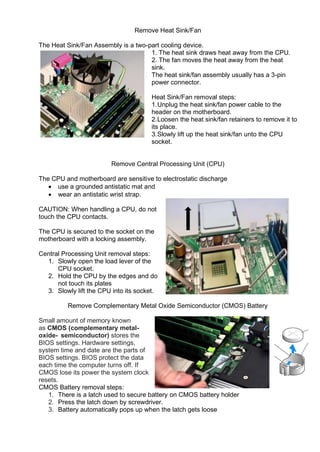
This document provides instructions for disassembling a desktop computer system unit as part of a learning activity. It lists the objectives of understanding how static electricity can damage computers and learning the proper procedure and tools for disassembly. The steps described include unplugging all cables, removing screws and side panels, taking out internal cables and components like hard drives, video cards, the motherboard, and the power supply unit. Precautions against electrostatic discharge are emphasized.