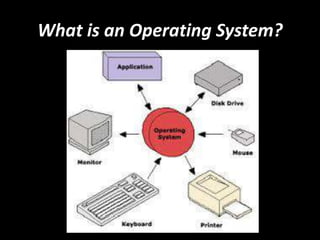
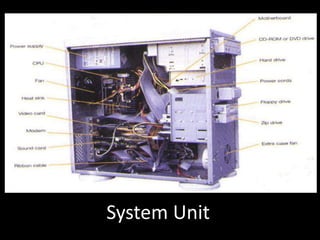
This document provides information about the key components of a computer system, including the operating system, central processing unit (CPU), memory, motherboard, power supply, storage devices, input devices, and output devices. It explains that the operating system coordinates all the components and allows for multi-user access and multi-tasking. Common input devices include keyboards, mice, scanners, and microphones, while output devices include monitors, printers, speakers, and projectors. The document provides examples and descriptions of each type of component to give an overview of a basic computer system.