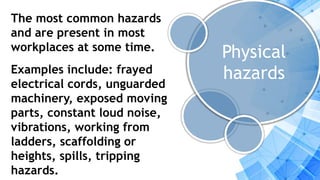
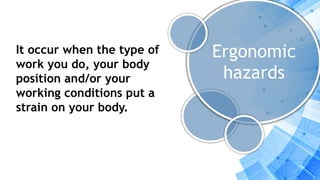
This document discusses occupational health and safety (OHS) procedures for computer system servicing. It outlines four objectives for understanding and applying OHS policies when assembling computers. These include understanding what OHS procedures are, applying OHS in assembly, identifying tools for assembly/disassembly, and understanding tools, materials and equipment. The document provides examples of 12 OHS procedures to follow in a computer laboratory, such as powering off computers before working, wearing protective equipment, and recognizing emergency procedures. It also outlines four main types of workplace hazards: physical, ergonomic, chemical and biological hazards.