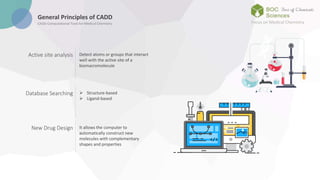
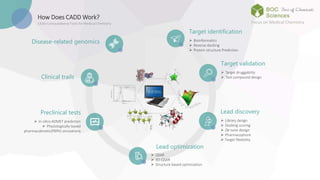
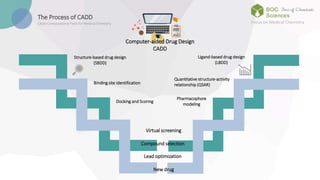
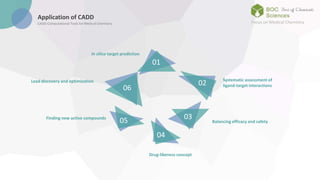
The document discusses computer-aided drug design (CADD), a technology that employs computational tools to design, manage, and analyze drug compounds. It emphasizes the benefits of CADD, including increased efficiency in drug discovery and optimization processes, cost savings, and the ability to predict drug interactions. The text outlines the historical development of CADD and its applications in identifying lead compounds and facilitating clinical research.