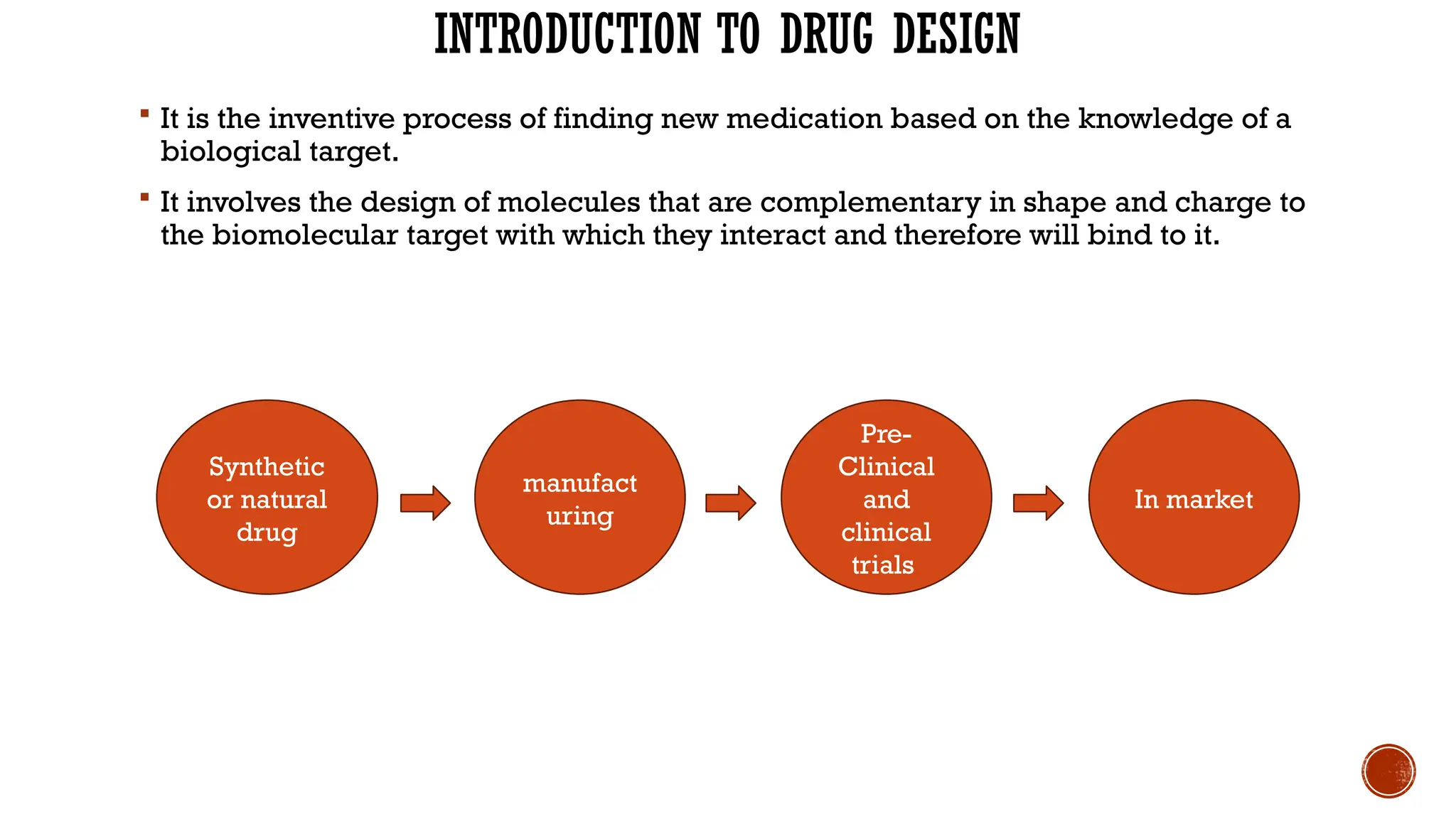
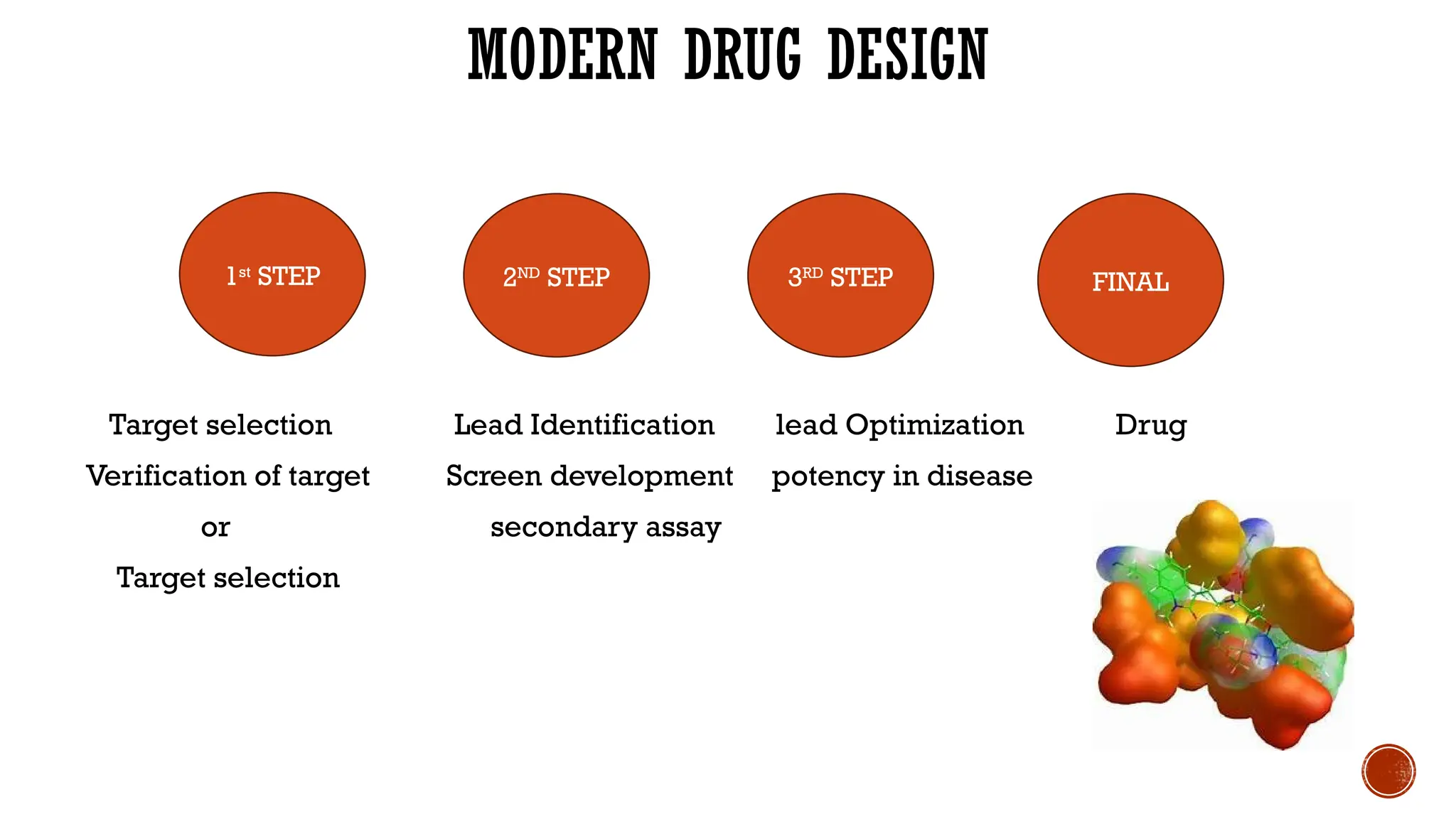
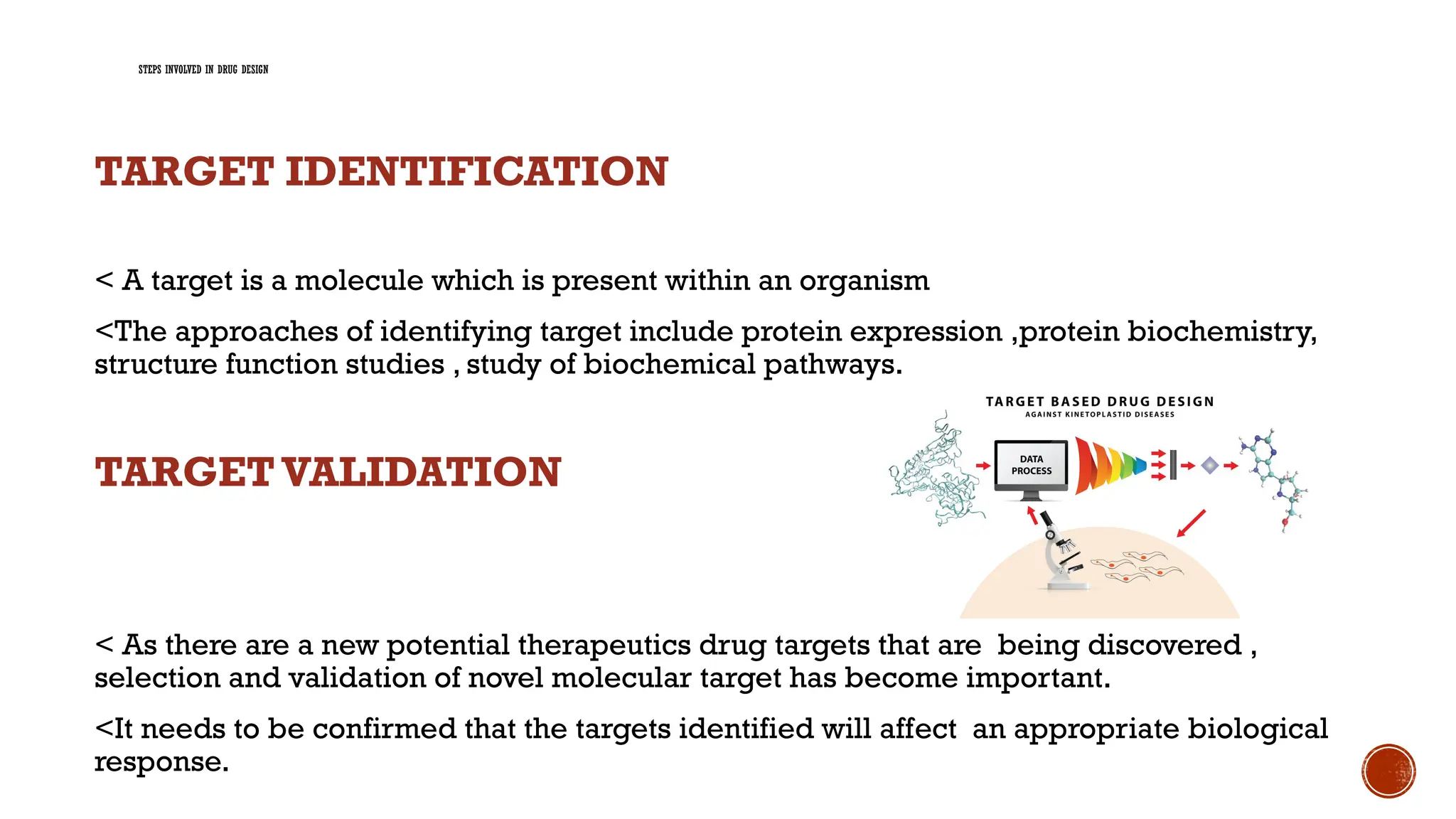
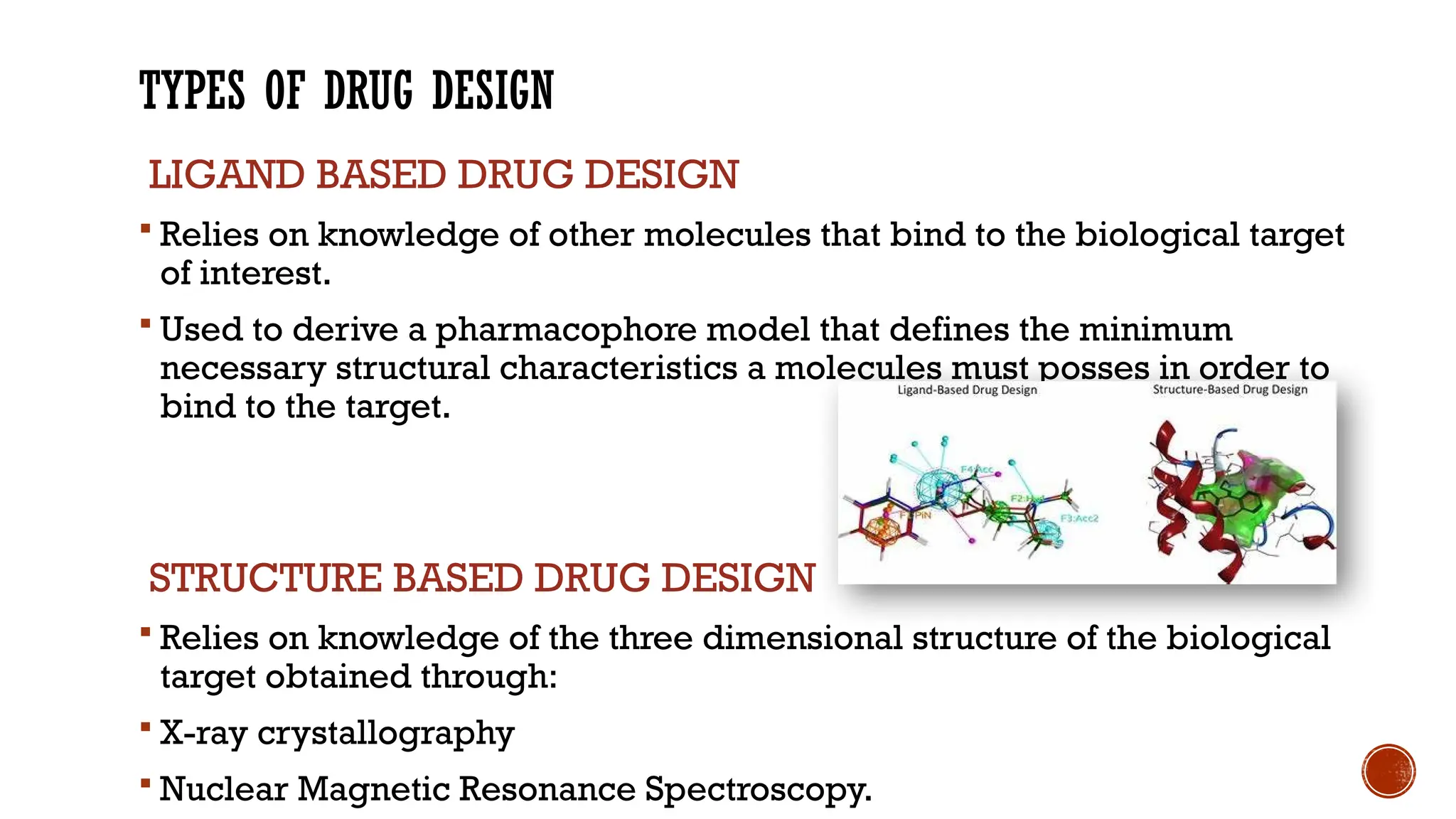
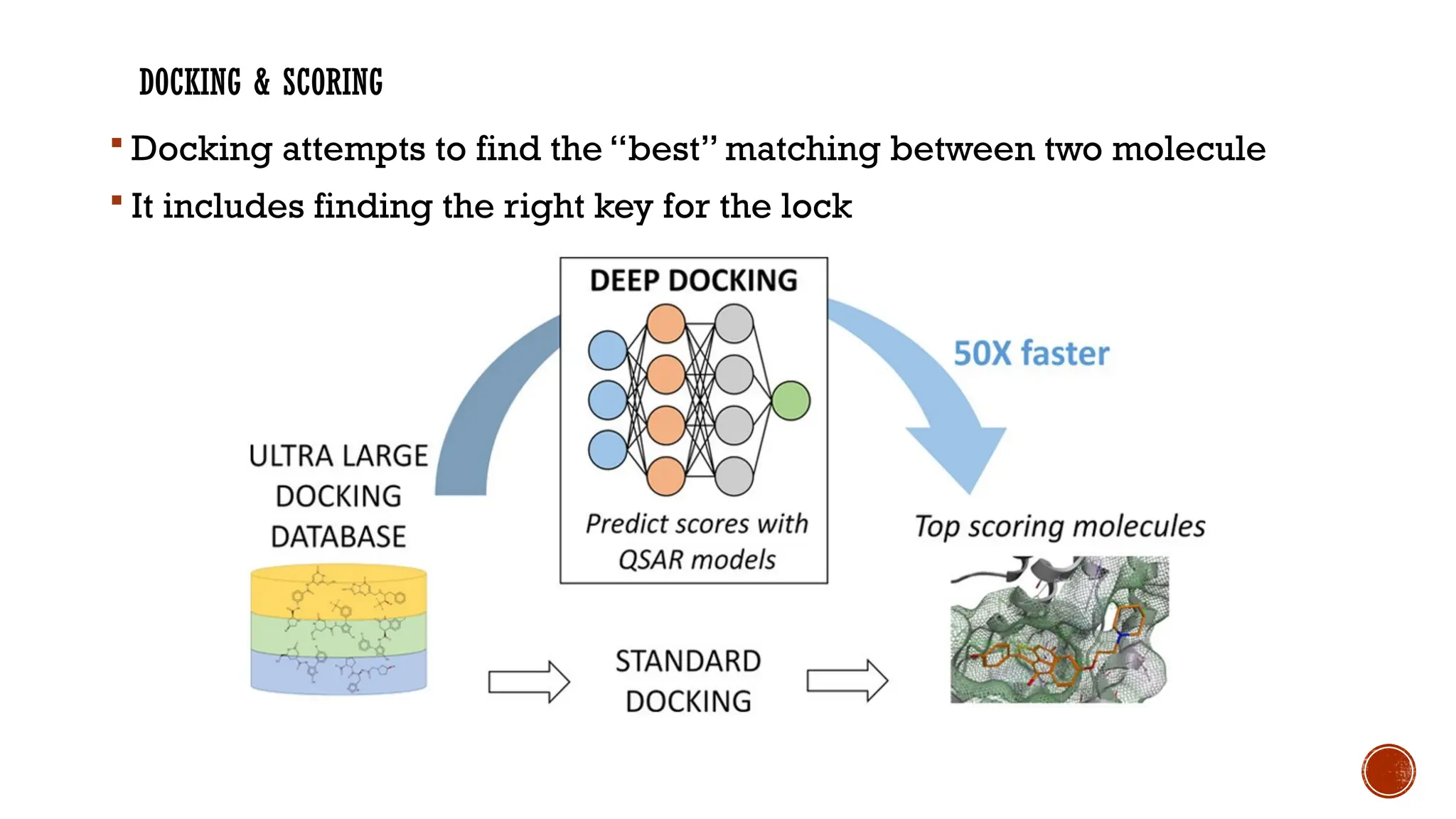
The document covers a presentation on computer-aided drug design (CADD), exploring its history, processes, types, and advantages. It emphasizes the role of CADD in drug discovery, detailing methods like virtual screening and de novo design, and the importance of target identification and validation. Key tools and software for drug design are also discussed, along with the benefits of CADD in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness.