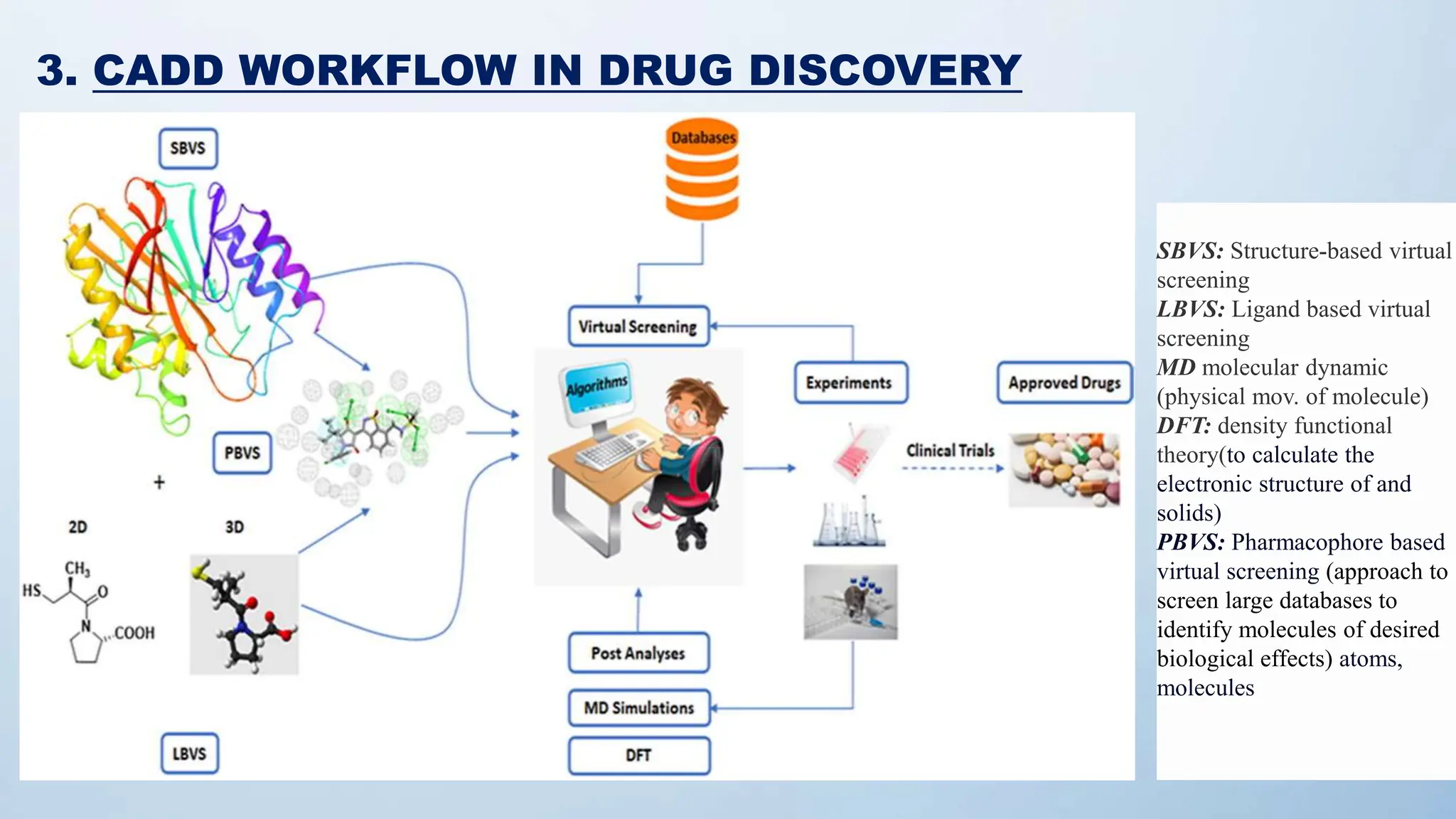
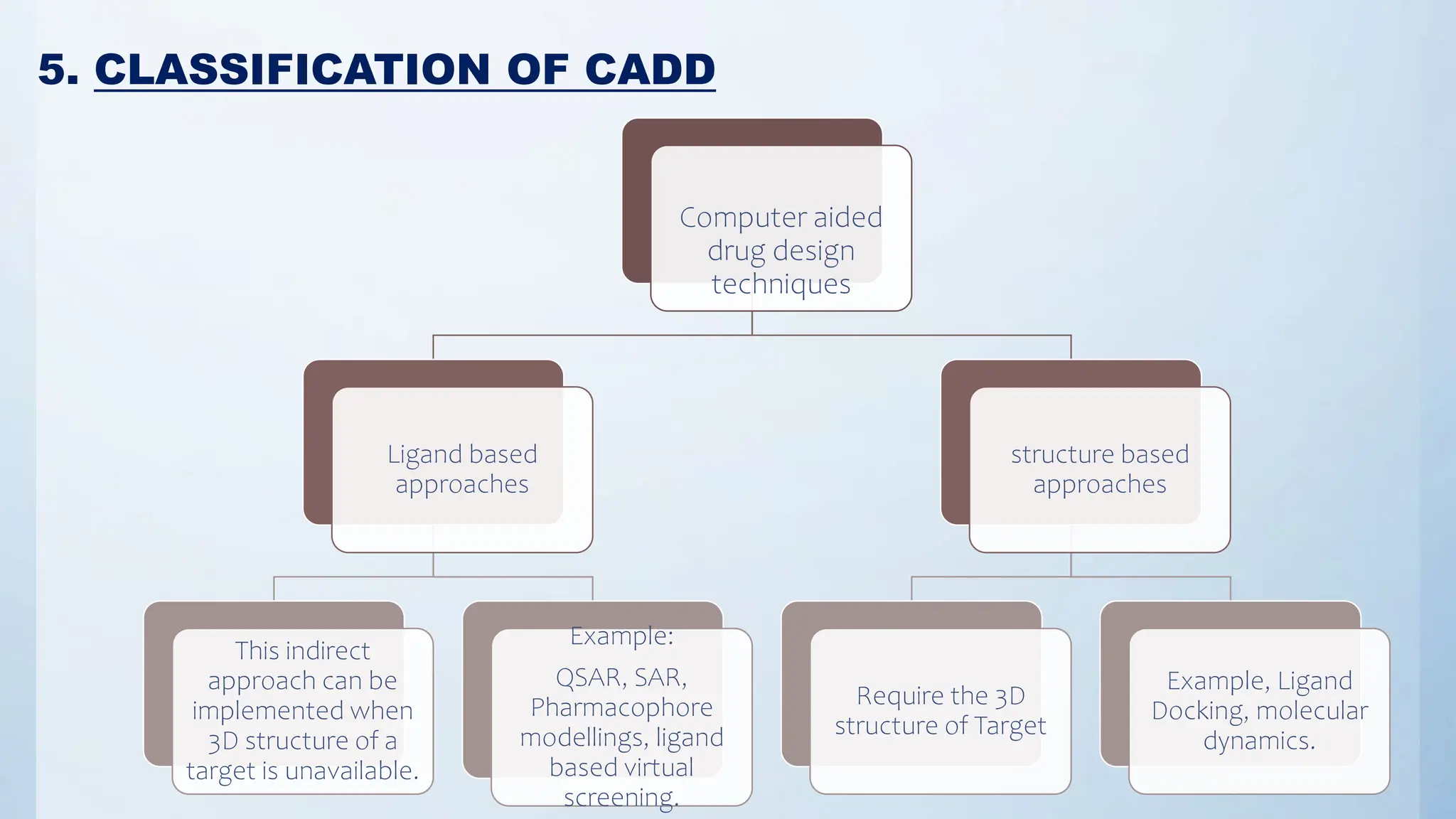
Computer-Aided Drug Design (CADD) is a computational methodology utilized for drug discovery and development, integrating techniques like molecular docking, QSAR, and pharmacophore modeling. It expedites the identification, evaluation, and optimization of pharmaceutical compounds, significantly improving the hit rate for novel drugs. Despite the lengthy and complex nature of drug development, advancements in CADD techniques offer promising strategies to enhance the efficiency and success of bringing new drugs to market.