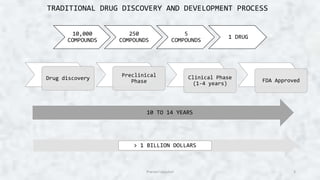
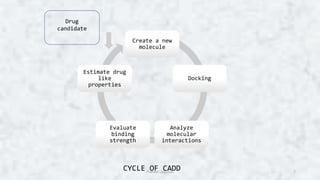
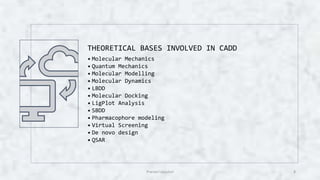
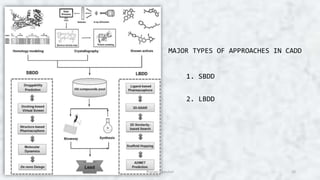
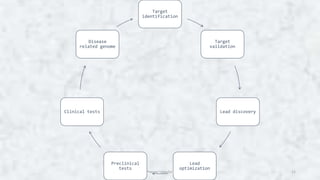
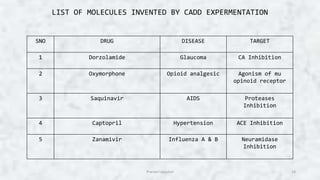
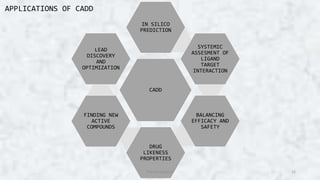
Computer aided drug design (CADD) uses computational tools to aid in the drug discovery and development process. It relies on digital repositories to study how potential drug compounds may interact with biological targets. CADD methods can screen thousands of compounds simultaneously, increase the odds of identifying compounds with desired characteristics, and help speed up the drug development process from hit to lead. Some key applications of CADD include lead discovery and optimization, predicting ligand-target interactions, and assessing drug-like properties of compounds.