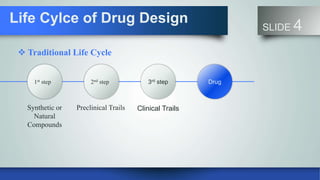
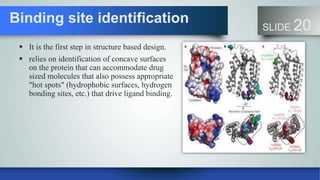
Computer aided drug design uses computational methods to facilitate the design and discovery of new therapeutic solutions. There are two main types of drug design - ligand-based which relies on knowledge of molecules that bind to the target, and structure-based which relies on the 3D structure of the target. The main steps in structure-based design are target selection, binding site identification, molecular docking to predict how ligands bind to the target, and scoring to evaluate interactions. Computational tools are used for databases, molecular modeling, docking, screening, and predicting absorption and toxicity properties. These tools help speed up the drug design process and make it more efficient.