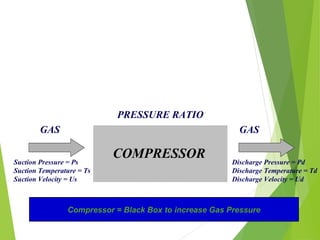
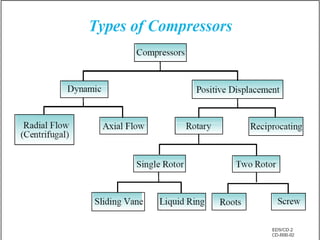
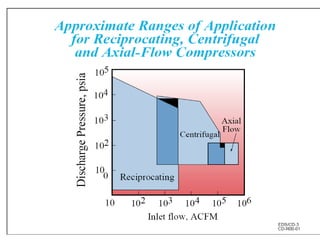
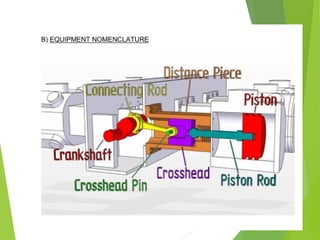
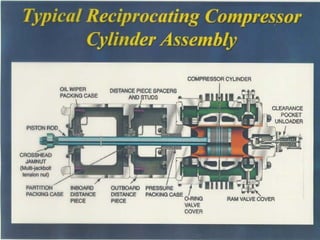
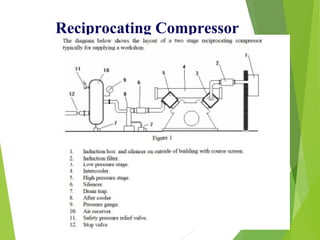
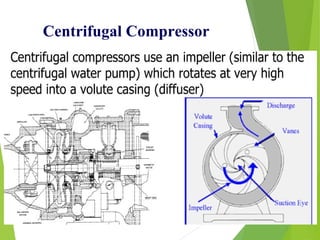
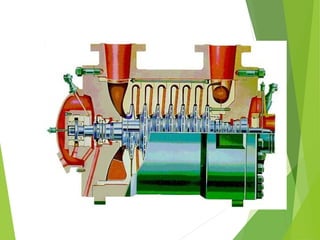
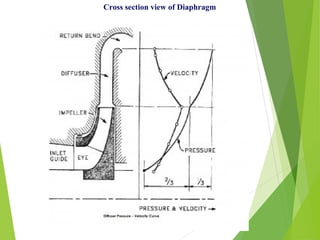
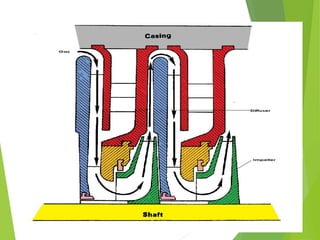
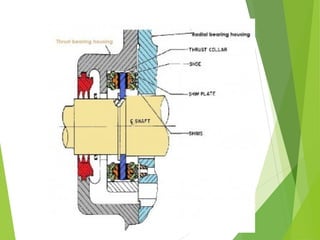
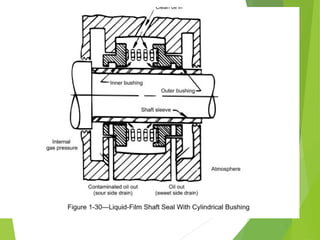
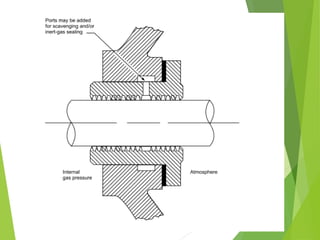
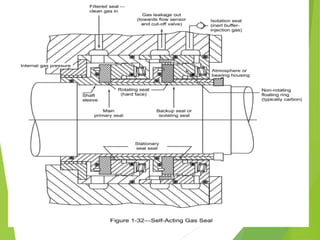
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a compressible fluid like air or gas by reducing its volume. It works similarly to a pump but for gases, which are compressible, rather than liquids. There are several types of compressors including reciprocating, rotary, centrifugal, and axial. Centrifugal compressors use rotary impellers to increase the velocity and pressure of a gas by pulling it through a curved casing. Key components include impellers, diffusers, bearings, seals, and casings. Compressors are selected based on various parameters like the gas handled, flow rates, pressures, and temperature.