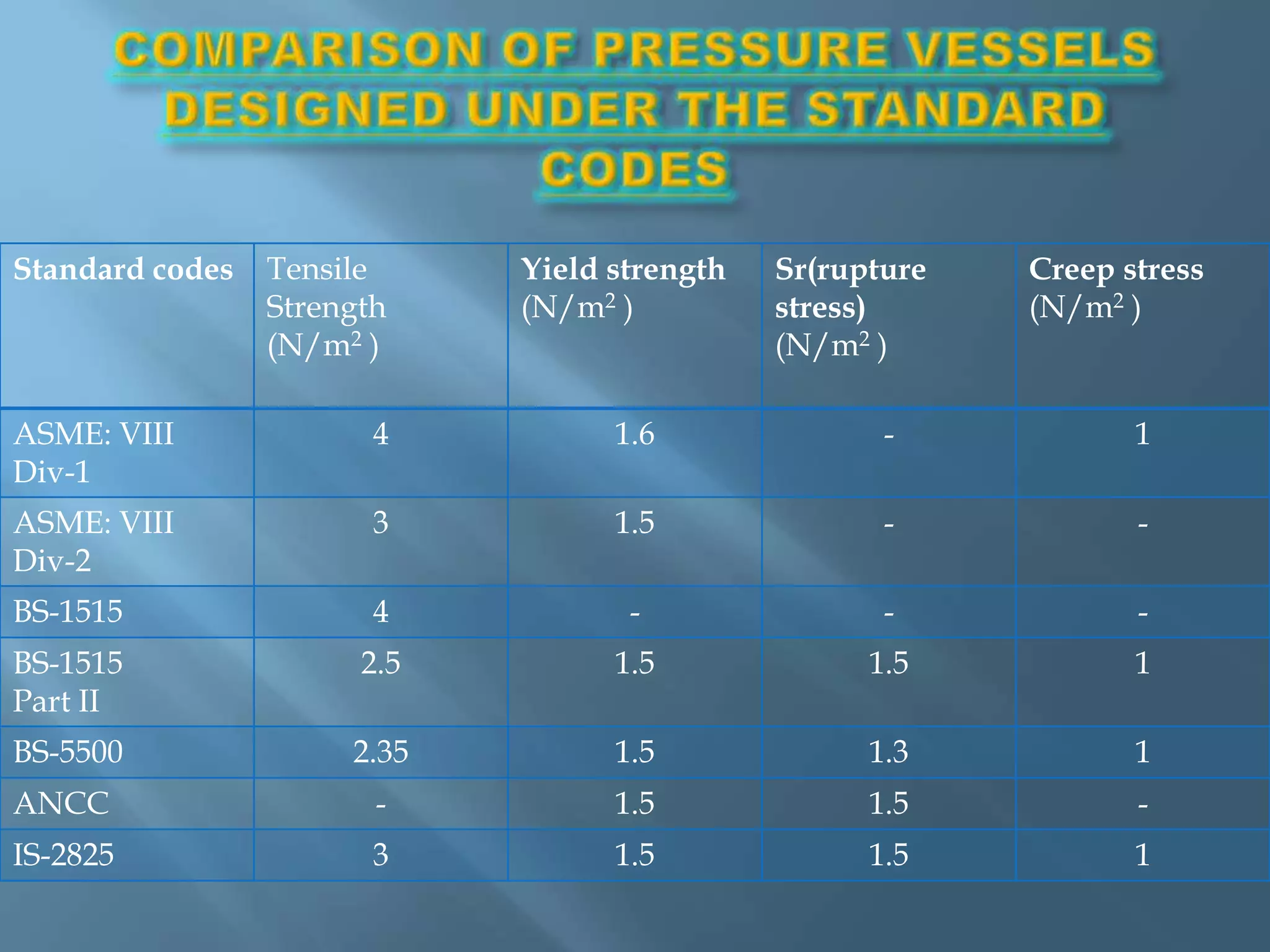
The document discusses pressure vessels, including their definitions, components, classifications, uses, applicable codes, design criteria, testing methods. It covers topics such as typical pressure vessel components, various classifications of pressure vessels, common uses of pressure vessels, design codes like ASME and materials qualification tests and leakage tests performed on pressure vessels.