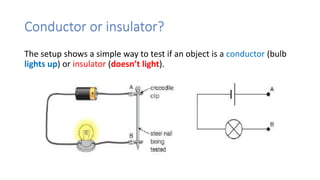
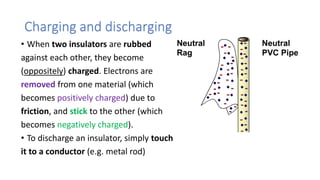
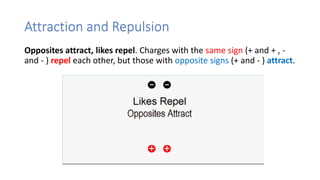
This document discusses electric charge and static electricity. It explains that conductors allow electric current to flow through them while insulators do not. When two insulators are rubbed together, they become oppositely charged due to friction. It also describes how charged objects can attract or repel each other depending on whether their charges are opposite or the same. Some applications of static electricity mentioned include electrostatic paint spraying, inkjet printers, and electrostatic precipitators which remove particles from smoke. The document concludes with safety precautions for dissipating built-up static charges.

![Charging by (electrostatic) induction
When a charged object is held close to an uncharged one, charge of
the opposite sign is induced on the side of the uncharged object
closest to the charged one. Then the two objects attract each other.
A good demonstration of this is the
gold leaf experiment [details in
book]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igcseelectriccharge-220828084730-13d38c1a/85/IGCSE-Electric-Charge-pptx-5-320.jpg)






