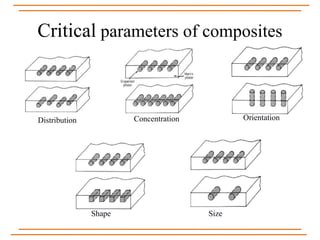
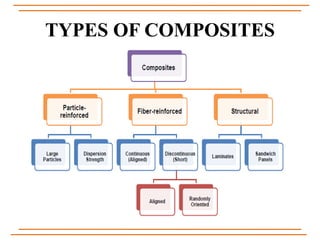
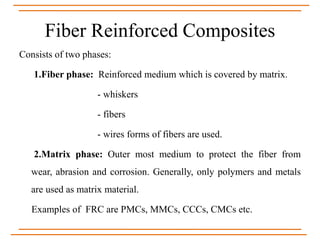
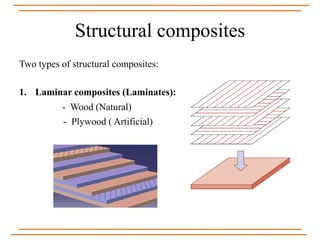
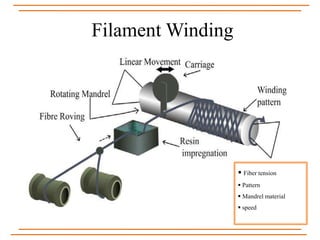
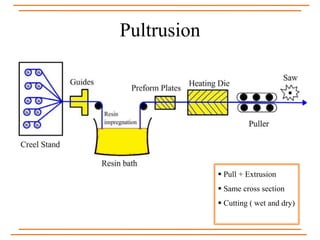
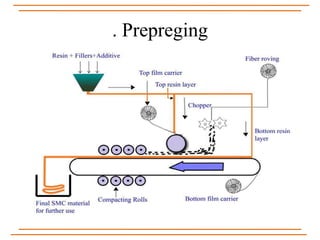
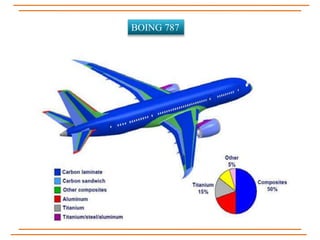
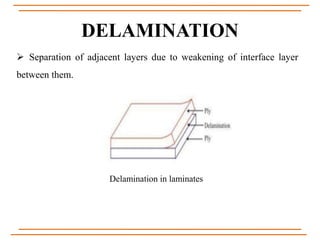
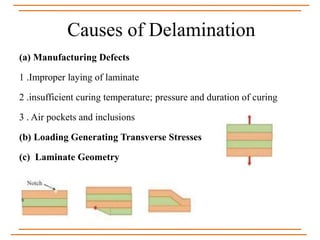
The document provides an overview of composite materials, detailing their definitions, types (natural and synthetic), and critical structural components. It discusses manufacturing processes such as filament winding, pultrusion, and prepreging, along with applications in aerospace, automotive, and various industries. Additionally, it addresses issues such as delamination, its causes, and impact on composite integrity.