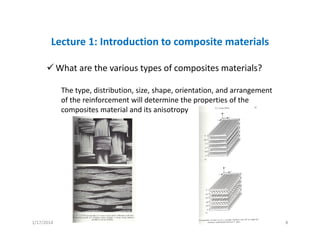
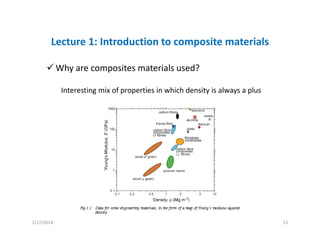
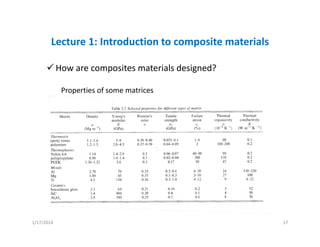
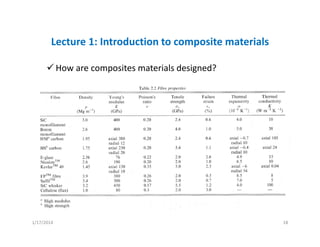
This document provides an overview of a lecture on composite materials. It defines composites as materials made of two or more constituents and discusses the various types of composite materials in terms of their matrices (such as polymer, metal, ceramic) and reinforcements (such as fibers, particles, flakes). The document also explains that composites are used because they offer advantages like lower density, higher strength, and versatility through tailored design. Finally, it states that composites are designed by comparing matrix and reinforcement properties to meet the specifications for a material's intended usage.