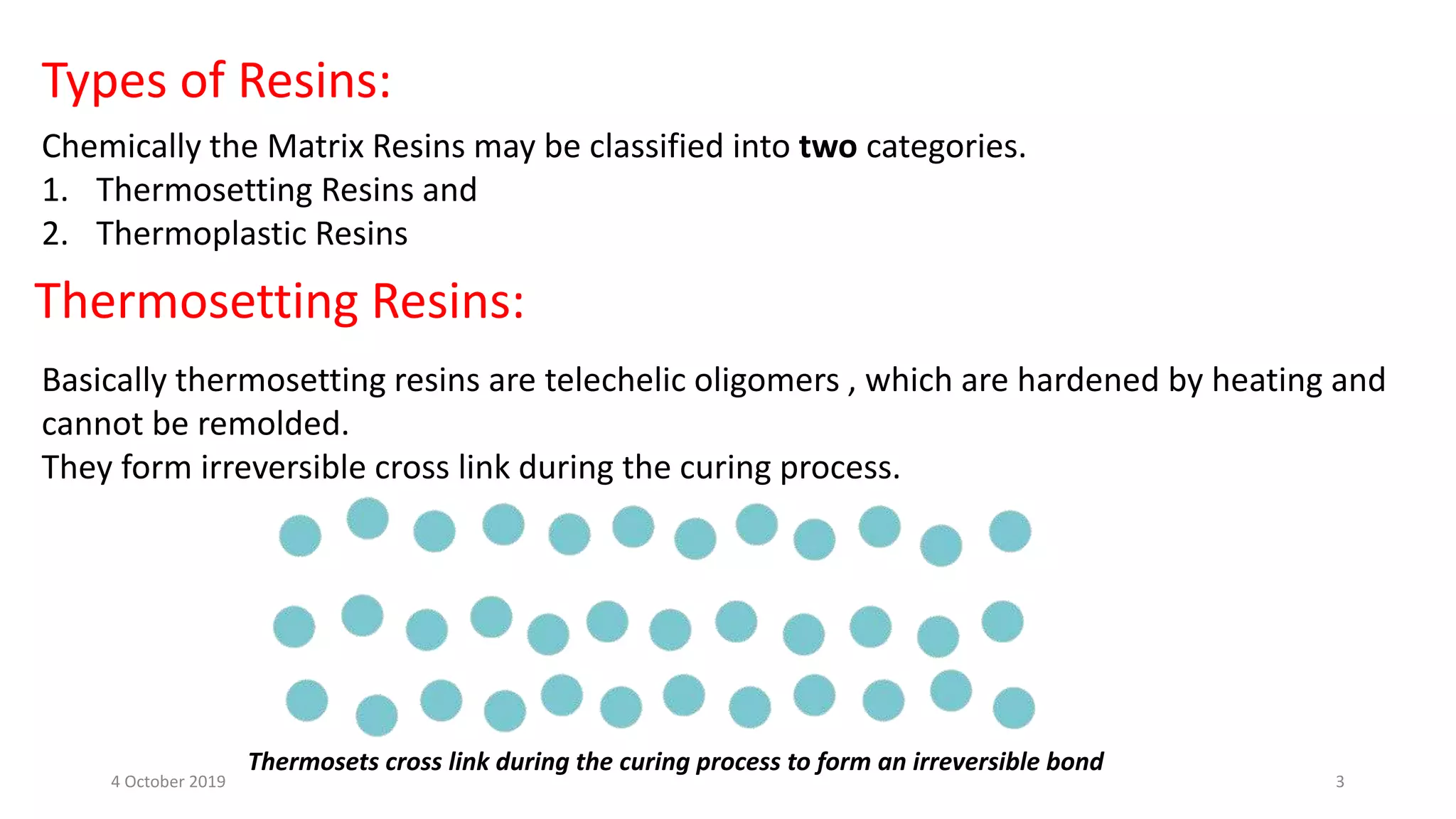
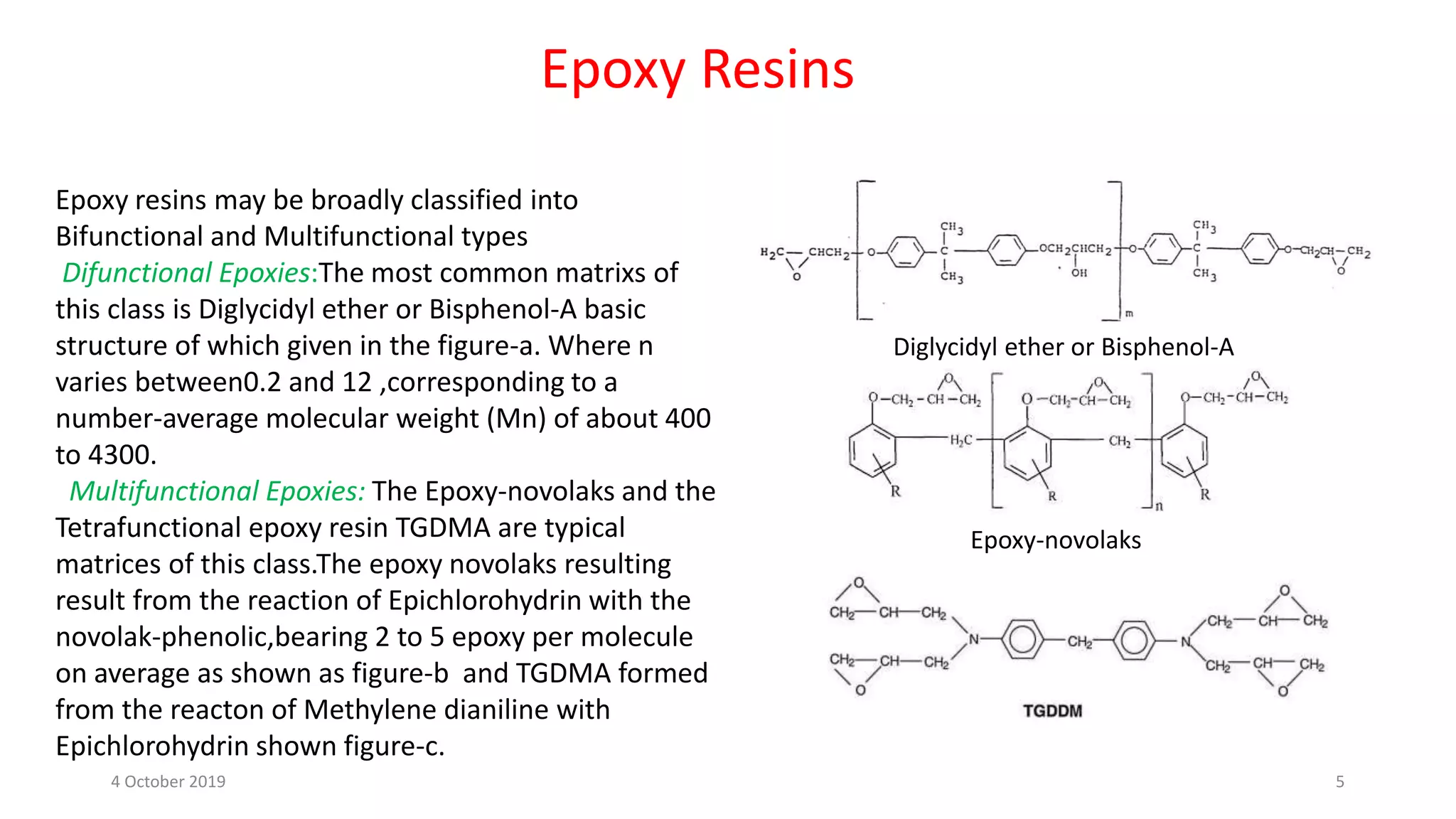
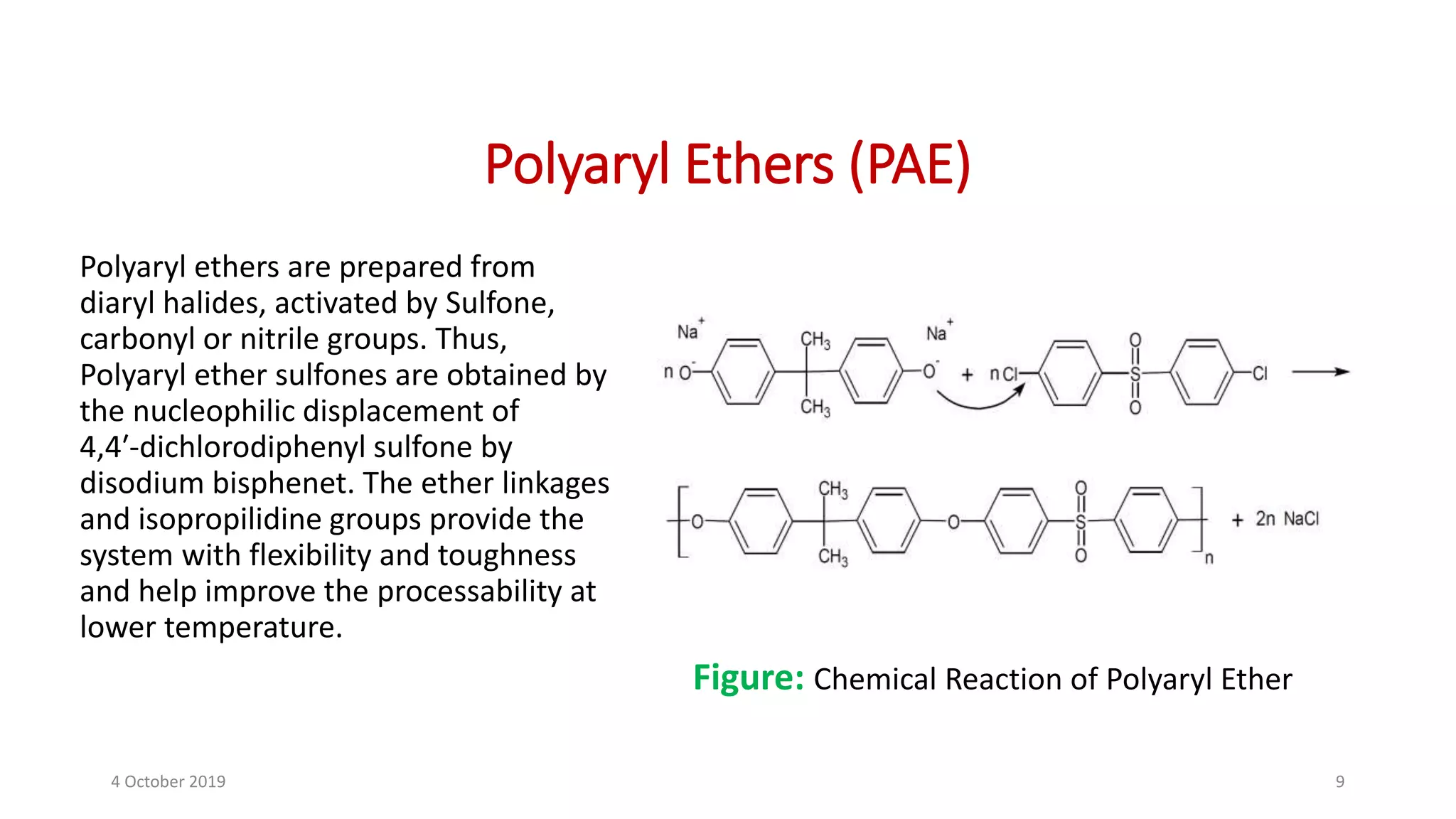
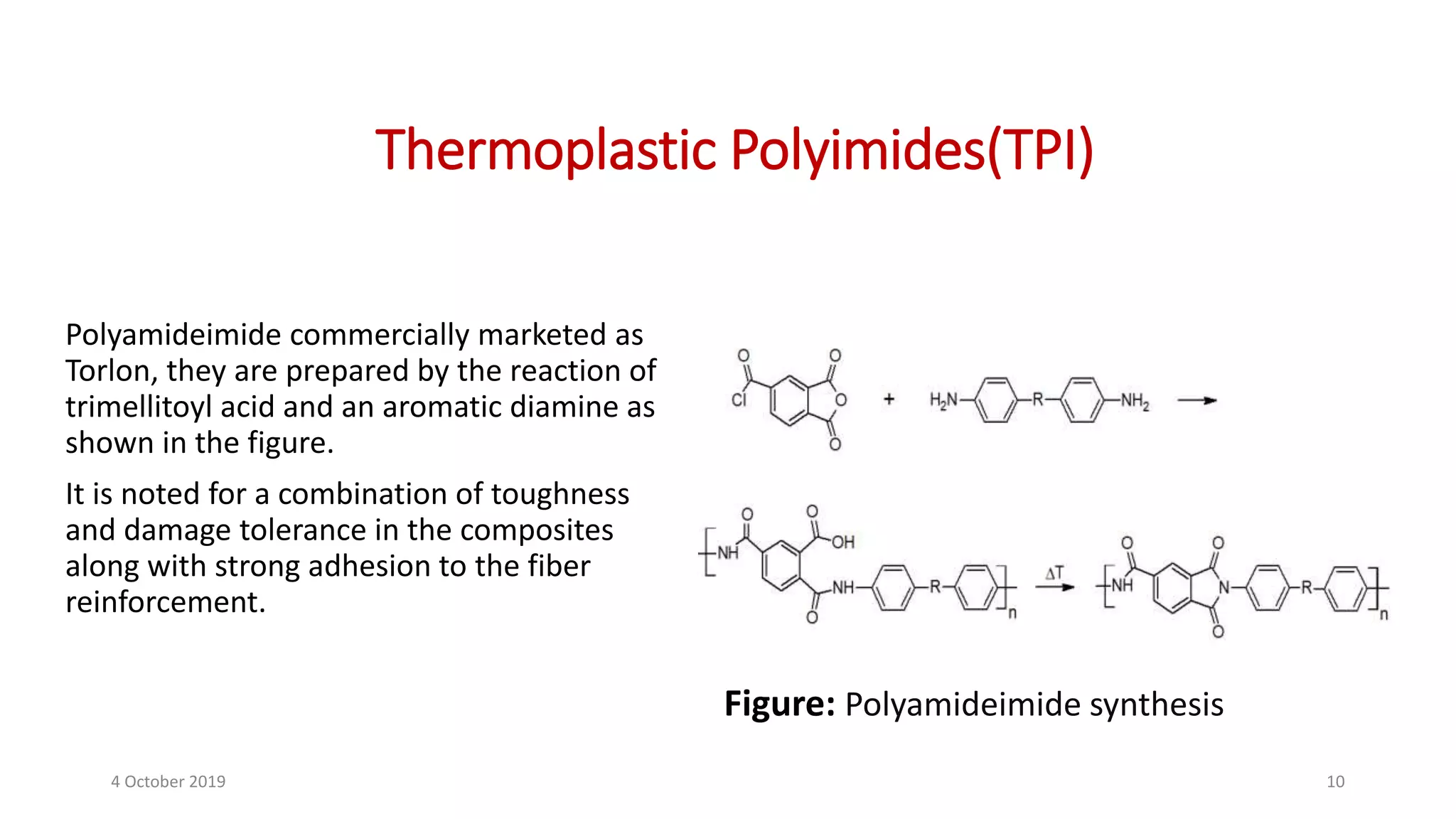
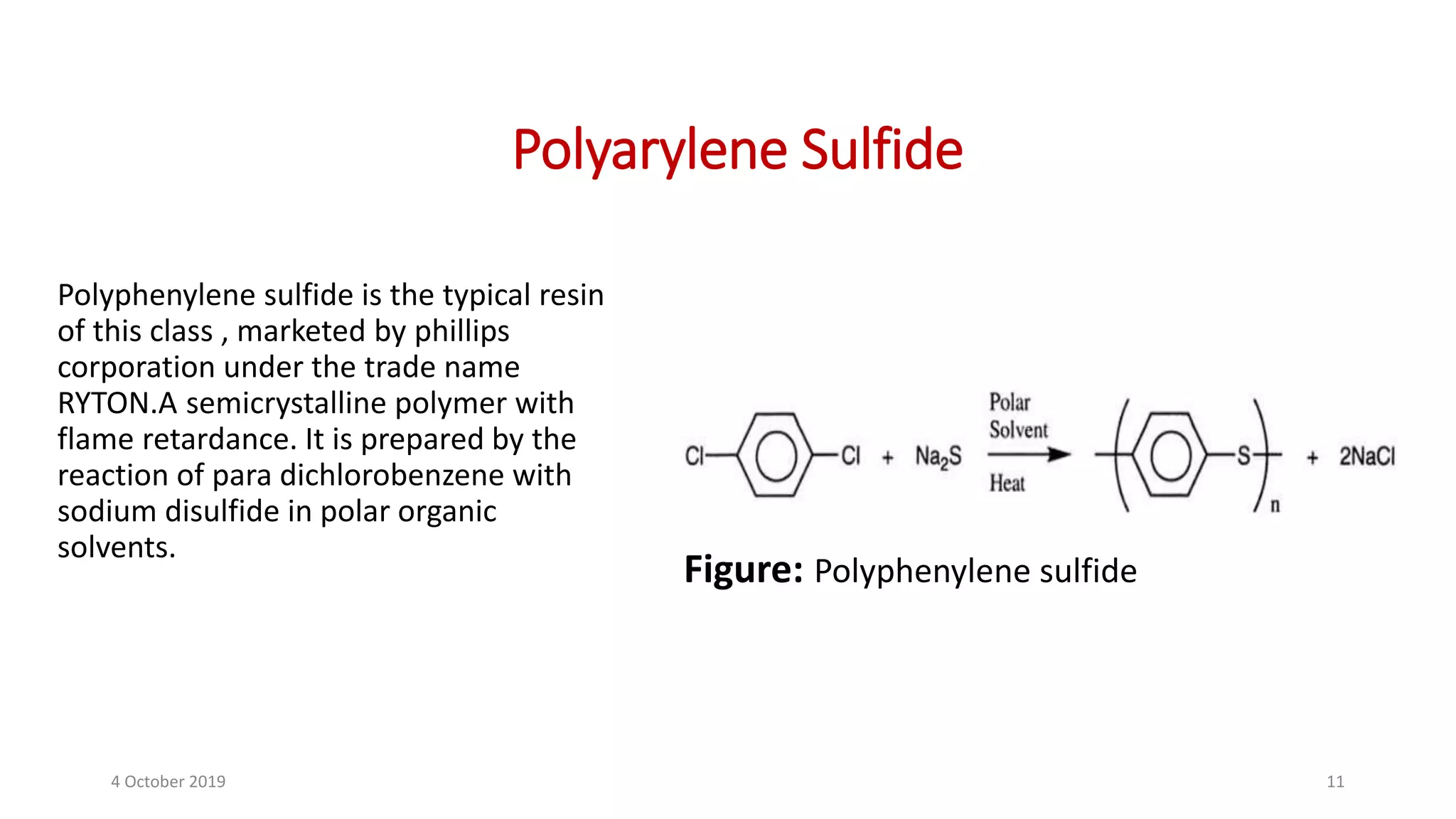
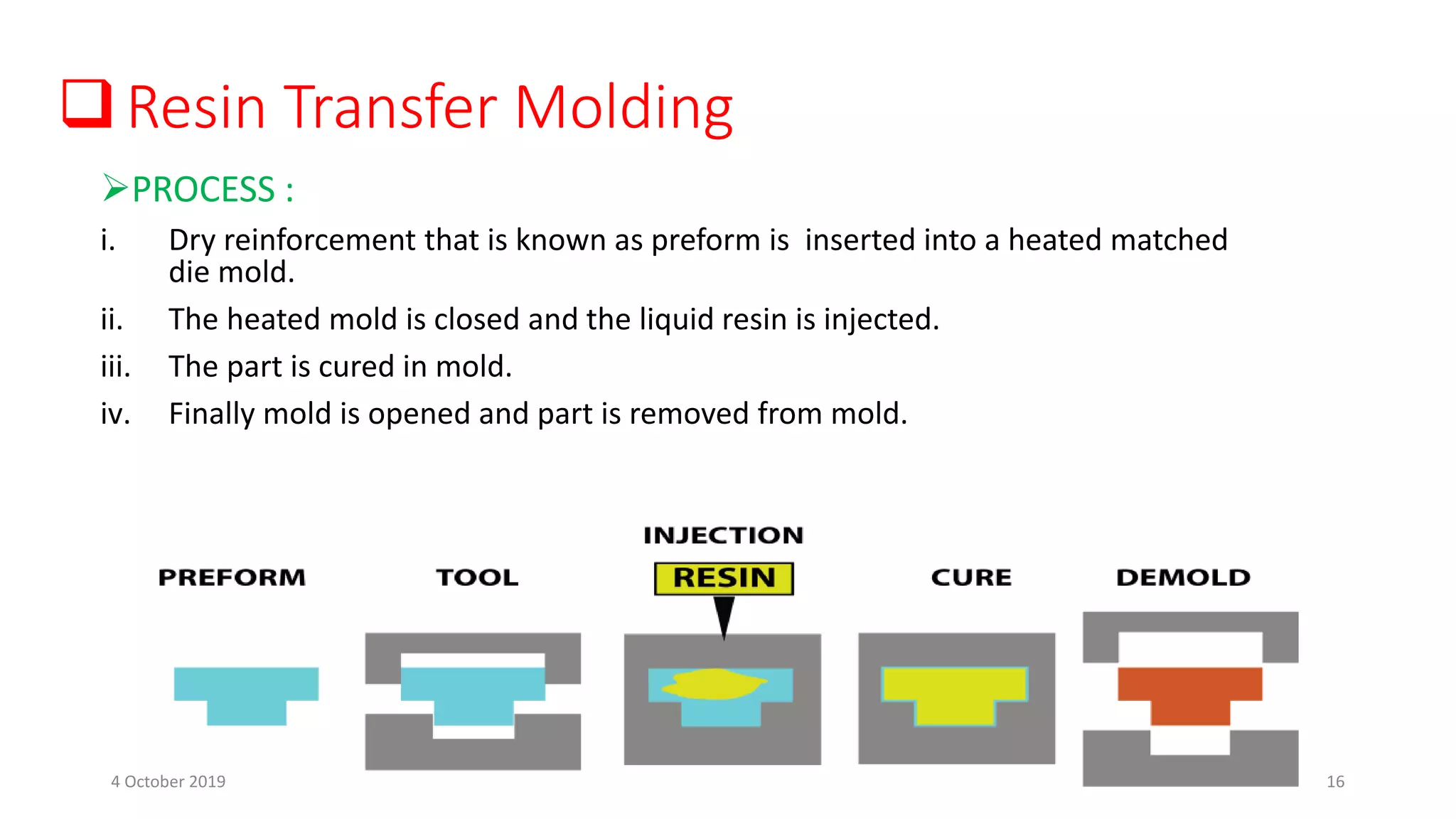
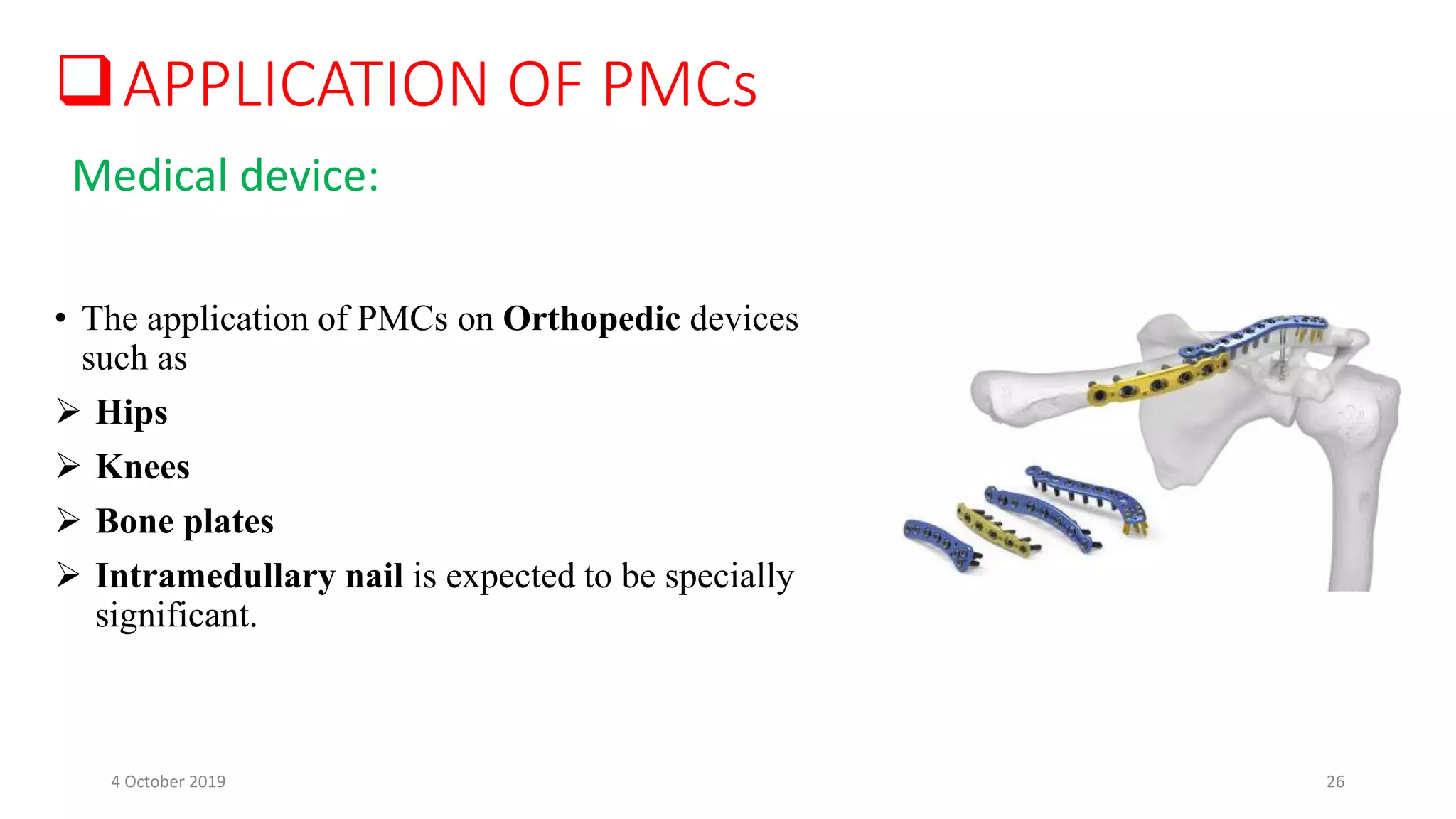
This document discusses polymer matrix composites (PMCs), which consist of a polymer resin matrix reinforced with fibers. It defines resin as a solid or viscous material that forms a polymer after curing. The document discusses the types and advantages of resin matrices, including thermosetting and thermoplastic resins such as epoxy, phenolic, and polyimide resins. It also describes PMC manufacturing methods like resin transfer molding and injection molding and applications of PMCs in aerospace, automotive, construction, and medical industries due to benefits like high strength and stiffness to weight ratios.