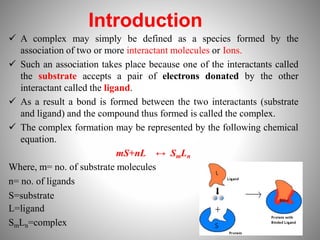
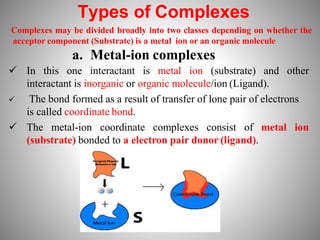
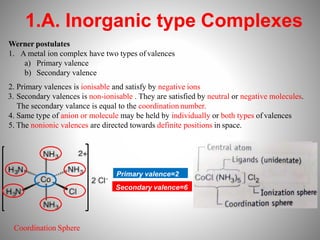
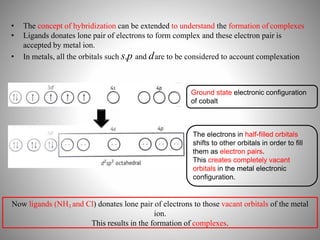
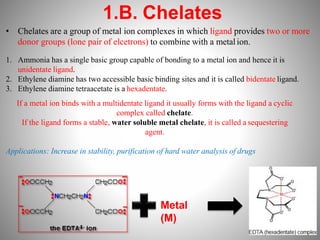
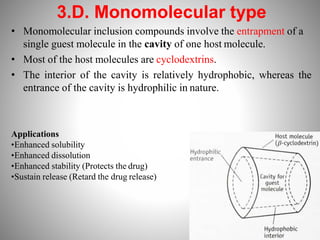
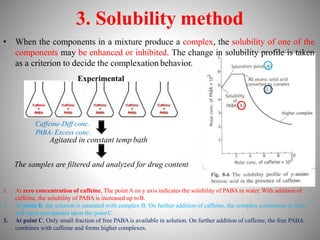
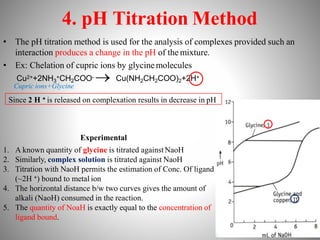
1. Complexation refers to the association of two or more interacting molecules or ions through coordinate bonding. This can occur between metal ions and ligands to form metal complexes, or between two organic molecules to form organic complexes.
2. Complexation has various applications in formulation such as improving physical state, reducing volatility, and enhancing solid state stability. It can also influence drug action by modifying properties like absorption, bioavailability, toxicity, and antibacterial activity.
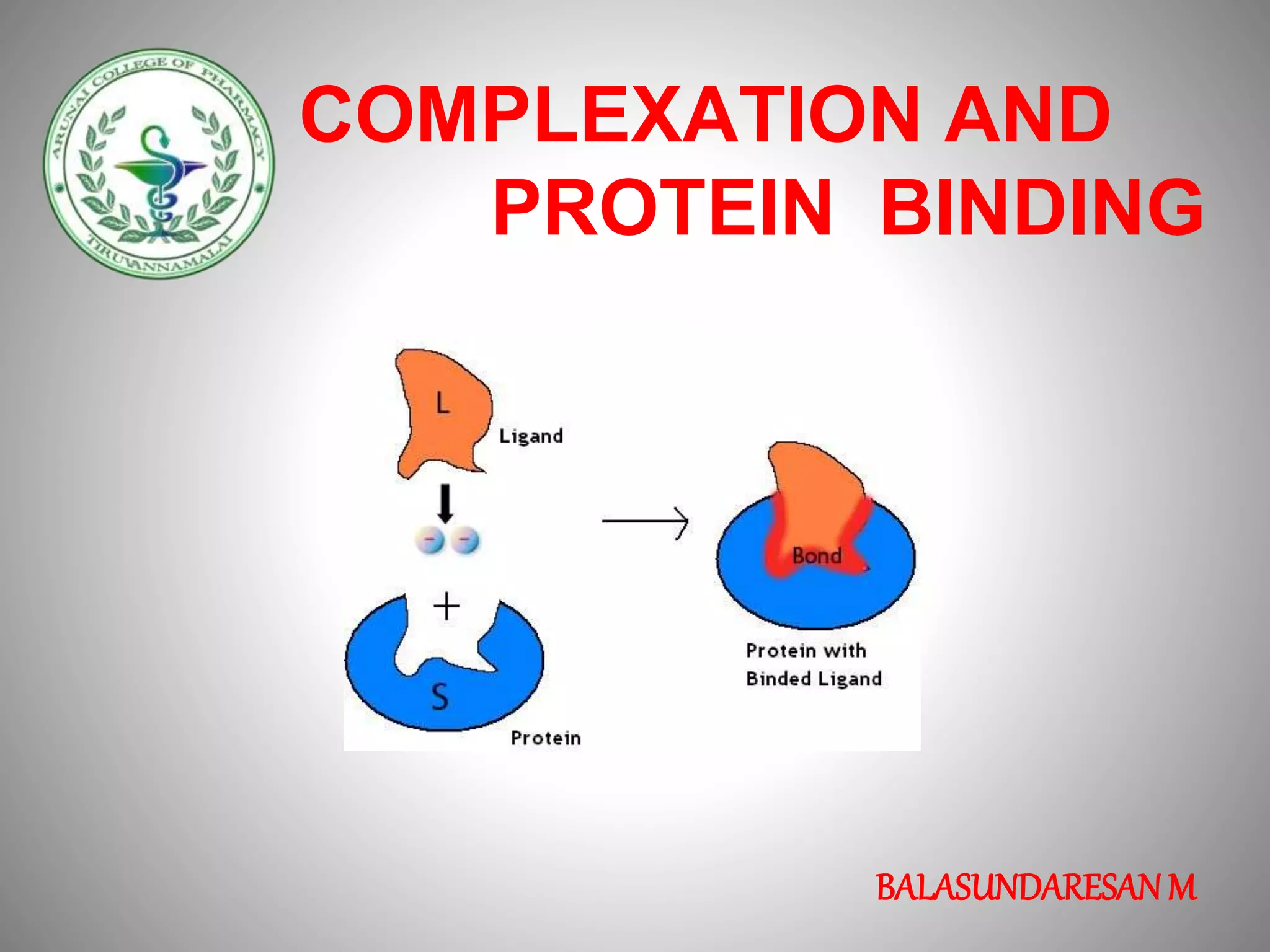
3. Protein binding refers specifically to the formation of complexes between drug molecules and blood proteins. This binding affects the amount of free or unbound drug available to produce pharmacological effects.








![2. Distribution method
• The distribution behavior of a solute b/w two immiscible liquids
is expressed as distribution coefficient or partition coefficient.
• When the solute forms complex with added substance the
distribution pattern changes depending on the nature of complex
(water soluble or insoluble)
Ex: I + K+I-
2
Iodine+Pottasium iodide
K+ I-
3
3
The equilibrium constant
K+ I-
[I2] [K+I-]
K=
Distribution coefficient of I2 b/w carbon disulfide and water= 625
Distribution coefficient of K+ I- Complex b/w carbon disulfide and water= 954
3
Iodine-Pottasium iodide complex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexationproteinbinding-220607131746-a36a8c1c/85/COMPLEXATION-PROTEIN-BINDING-pptx-25-320.jpg)




![• Binding is a function of the affinity of the protein
molecule for the drug molecules and also the
concentration of drugs and proteins. The
interaction between protein (P) and drug (D) for a
simple case of 1:1 protein drug complex can be
represented as follows:
P + D PD
Applying the law of mass action, the expression is
K=[PD]/[P] [D]
or, [PD] = K[P] [D]
Where, K= Association Constant
[P]= Concentration of unbound drug
[D]= Concentration of bound drug
[PD]= Concentration of protein drug complex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexationproteinbinding-220607131746-a36a8c1c/85/COMPLEXATION-PROTEIN-BINDING-pptx-32-320.jpg)

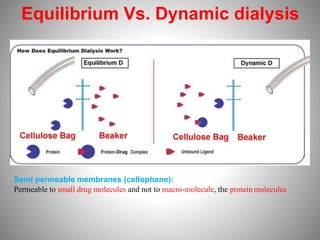
![Methods of determining
Protein Binding
b. Dynamic dialysis method
1. The dynamic dialysis method is based on the rate of
disappearance of the drug from a dialysis bag which is
proportional to the concentration of unbound drug.
2. The dialysis process follows the rate law
d[Dt]
k[Df ]
dt
Where, [Dt]= conc. of total drug. Mol/L
[Df]= conc. of free (unbound) drug in the bag, Mol/L
k= First order rate constant or permeability constant](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexationproteinbinding-220607131746-a36a8c1c/85/COMPLEXATION-PROTEIN-BINDING-pptx-34-320.jpg)