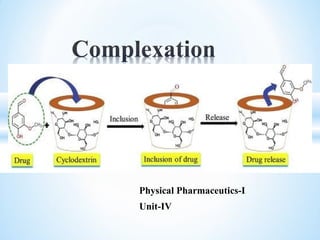
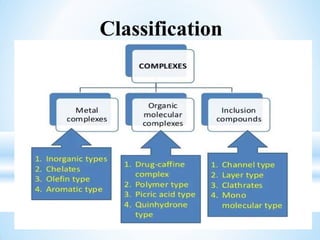
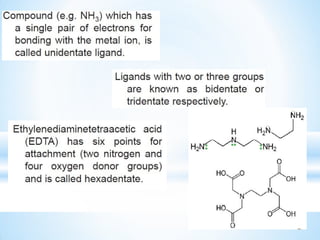
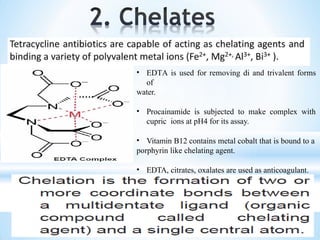
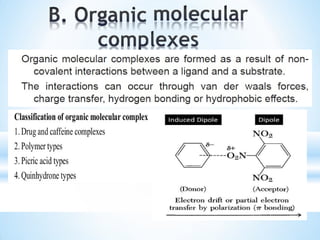
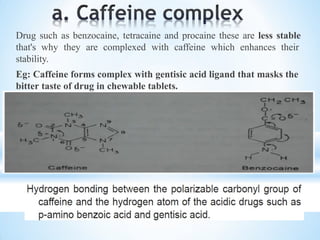
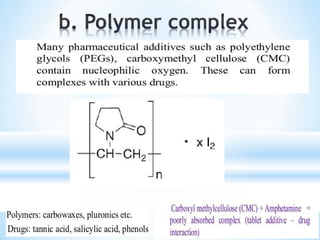
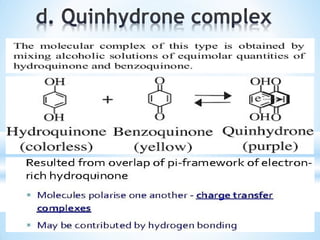
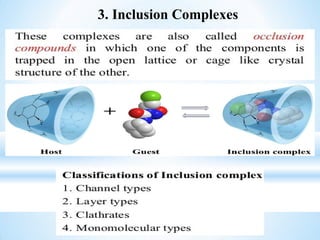
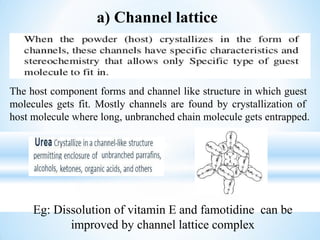
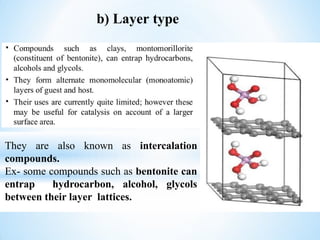
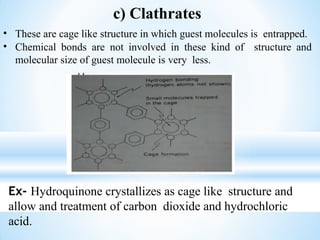
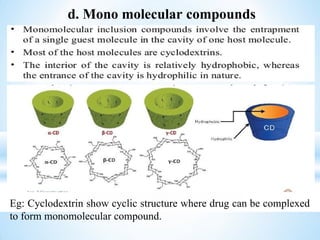
The document discusses the concepts of complexation in physical pharmaceutics, focusing on types of ligands (unidentate, bidentate, tridentate, hexadentate) and their roles in forming complexes with metal ions. Various examples are provided, including the use of EDTA and specific drugs like procainamide and vitamin B12, as well as the significance of aromatic and inclusion complexes. Additionally, it highlights the importance of these complexes in drug stability and bioactivity.