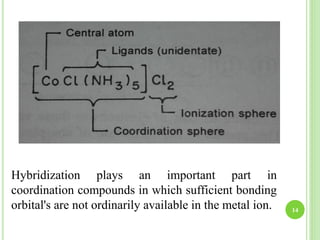
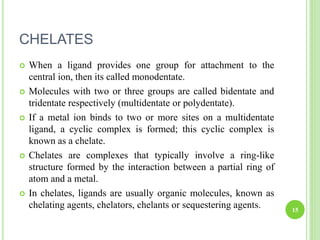
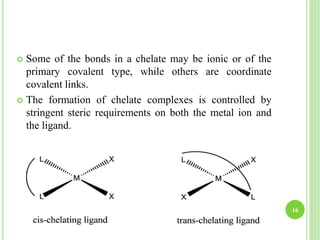
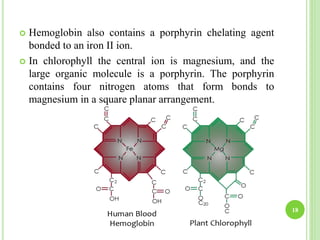
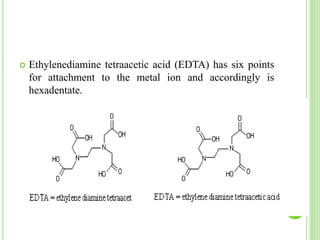
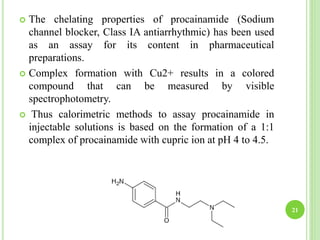
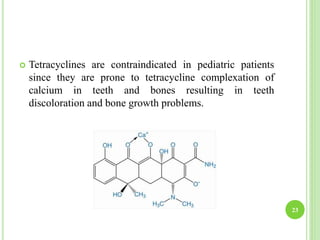
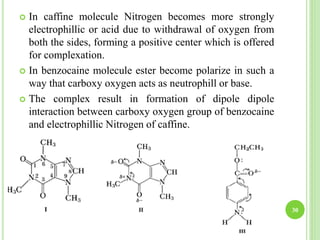
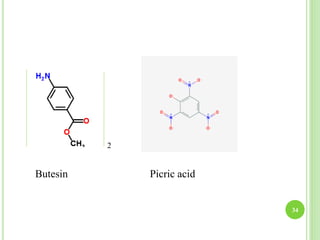
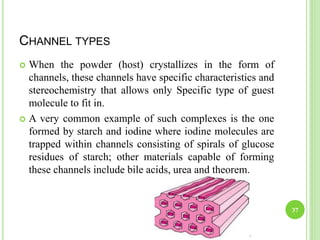
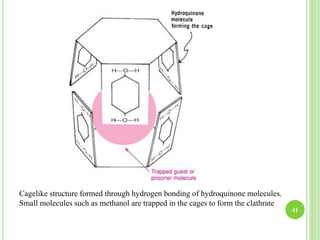
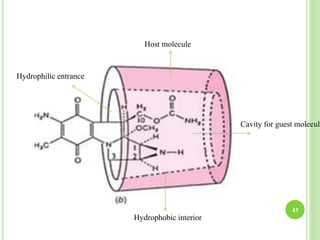
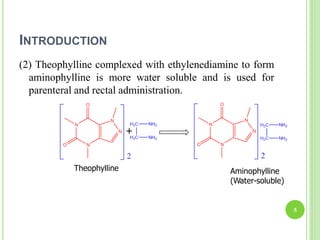
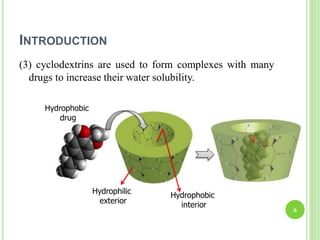
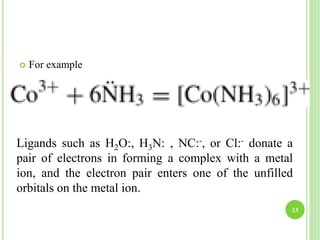This document provides definitions and classifications of complex compounds. It defines complexes as molecules where most bonding structures can be described by classical theories but one or more bonds are anomalous. Complexes result from donor-acceptor reactions between Lewis acids and bases. They are divided into metal ion complexes, organic molecular complexes, and inclusion complexes. Metal complexes involve coordination between metal ions and ligands. Chelates form cyclic structures with multidentate ligands. Organic complexes involve weaker interactions like hydrogen bonding. Inclusion complexes entrap guest molecules in host structures like channels, layers, or cavities. Common examples of complexes and their properties are discussed.








![INORGANIC COMPLEXES
The ammonia molecules in hexamminecobalt (III)
chloride, as the compound [Co(NH3)6] 3+ Cl3 - is
called, as the ligands and are said to be coordinated to
the cobalt ion.
The coordination number of the cobalt ion, or number of
ammonia groups coordinated to the metal ions, is six.
Other complex ions belonging to the inorganic group
include [Ag(NH3)2] + , [Fe(CN)6] 4-, and [Cr(H2O)6]
3+ .
Each ligand donates a pair of electrons to form a
coordinate covalent link between itself and the central
ion having an incomplete electron shell. 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complex-190118092410/85/Complex-12-320.jpg)