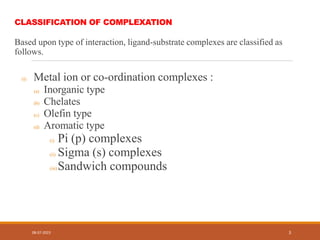
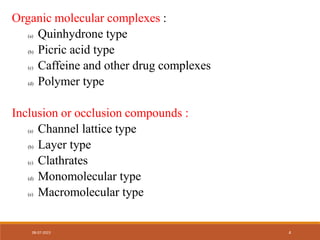
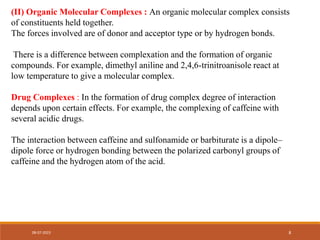
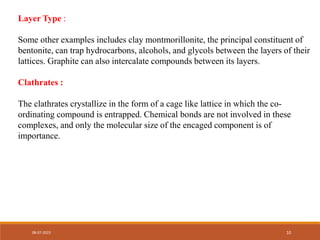
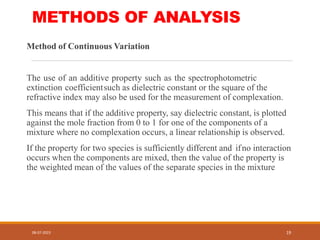
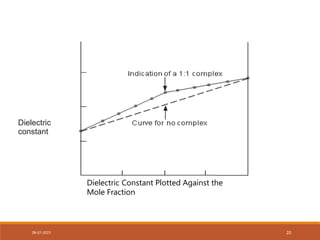
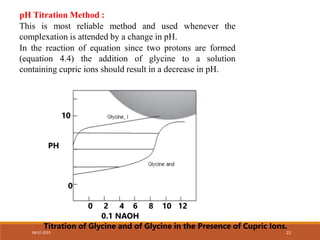
This document discusses complexation and protein binding. It defines complexation as interactions between two or more compounds capable of independent existence via covalent or non-covalent bonds. Complexes are classified as metal ion complexes or organic molecular complexes. Metal ion complexes include inorganic complexes, chelates, and aromatic complexes. Organic molecular complexes involve donor-acceptor interactions or hydrogen bonds. Complexation can enhance drug solubility, bioavailability, and modify drug properties. It is used in diagnosis, as a therapeutic tool, and to treat poisoning by facilitating removal of toxic substances from the body.















![PROTEIN BINDING
A complete analysis of protein binding, including the multiple equilibria below.
We write the interaction between a group or free receptor P in a protein and a
drugmolecule D as
P + D º PD
The equilibrium constant,disregarding the difference between activities and
concentrations, is
K [P] [Df] = [PD]
K is the association constant,
[P] is the concentration of the protein in terms of free binding sites,
[Df] is the concentration of free drug (in moles),
08-07-2023 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexationandproteinbinding-230708103340-437a18a4/85/COMPLEXATION-AND-PROTEIN-BINDING-27-320.jpg)

