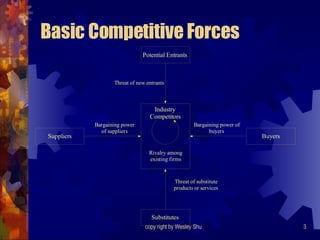
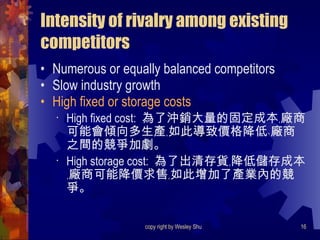
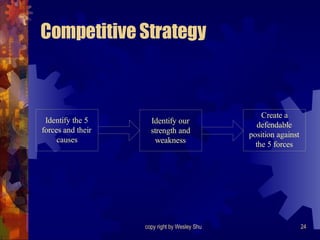
The document summarizes Michael Porter's framework for competitive strategy. It outlines the five competitive forces that determine the intensity of industry competition: threat of new entry, power of suppliers, power of buyers, threat of substitutes, and rivalry among existing competitors. It then discusses how firms can gain a competitive advantage by positioning themselves in the industry where these forces are weakest or by influencing the competitive balance through strategic changes. The document also covers Porter's generic strategies of cost leadership, differentiation, and focus.