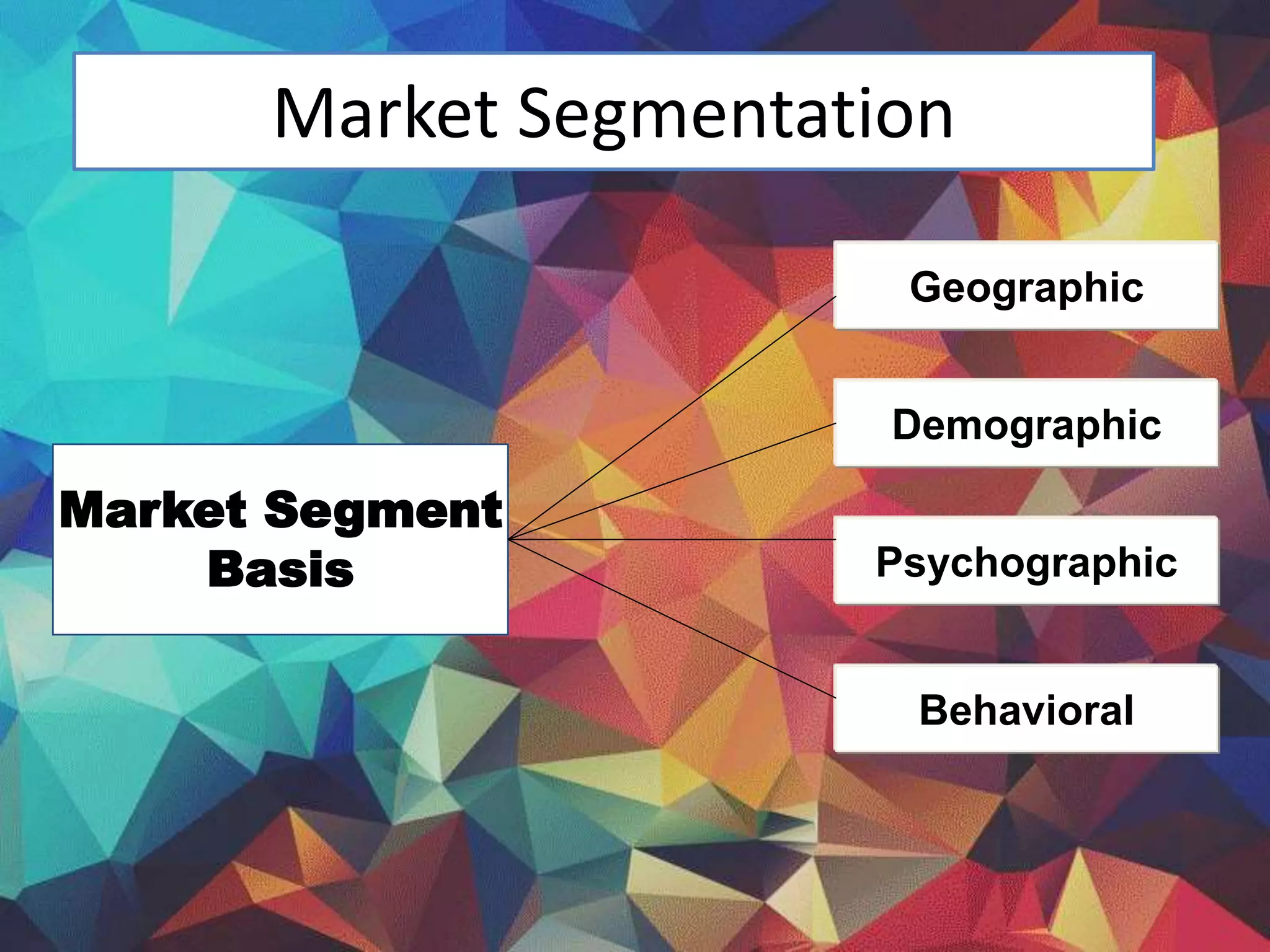
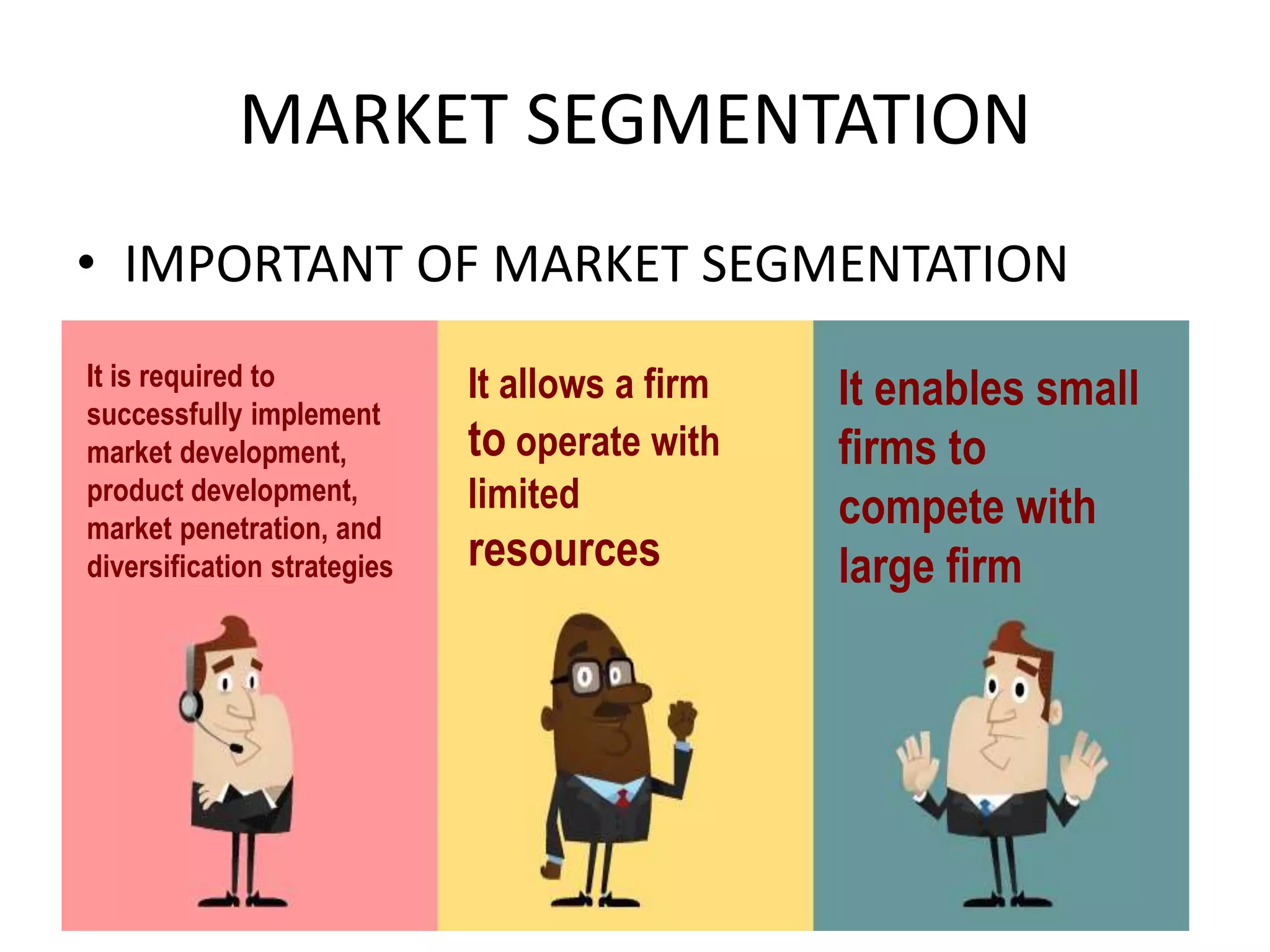
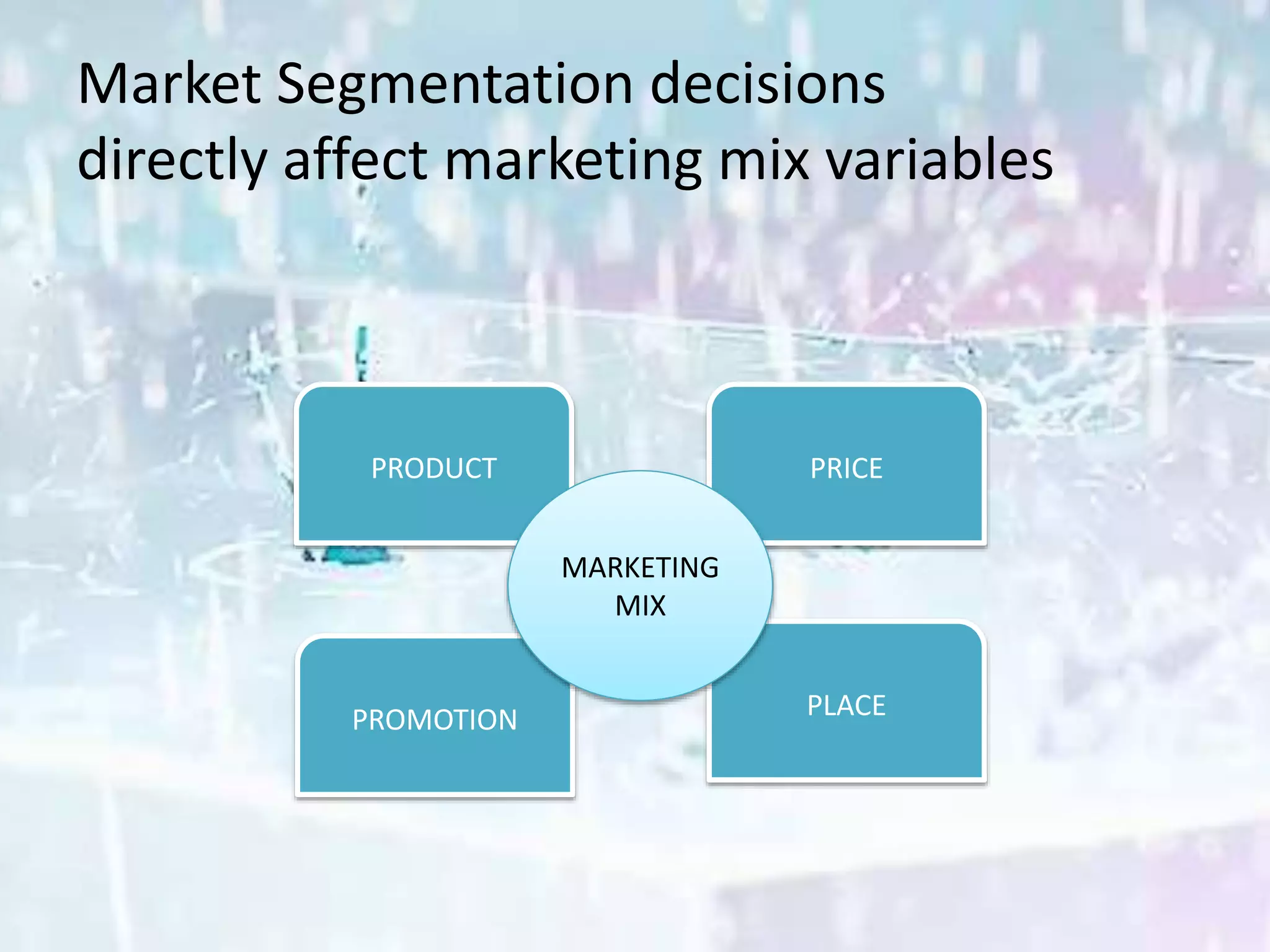
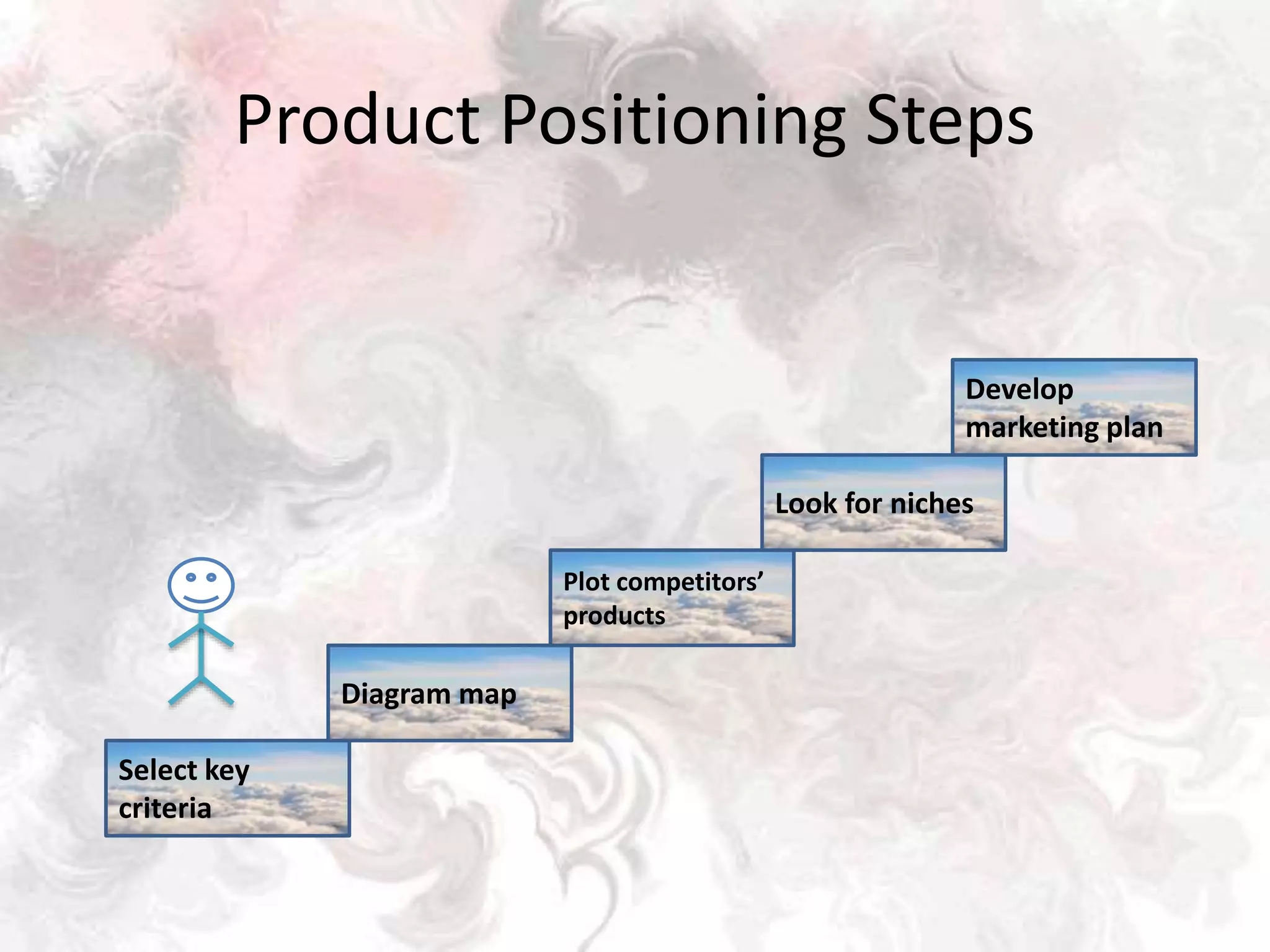
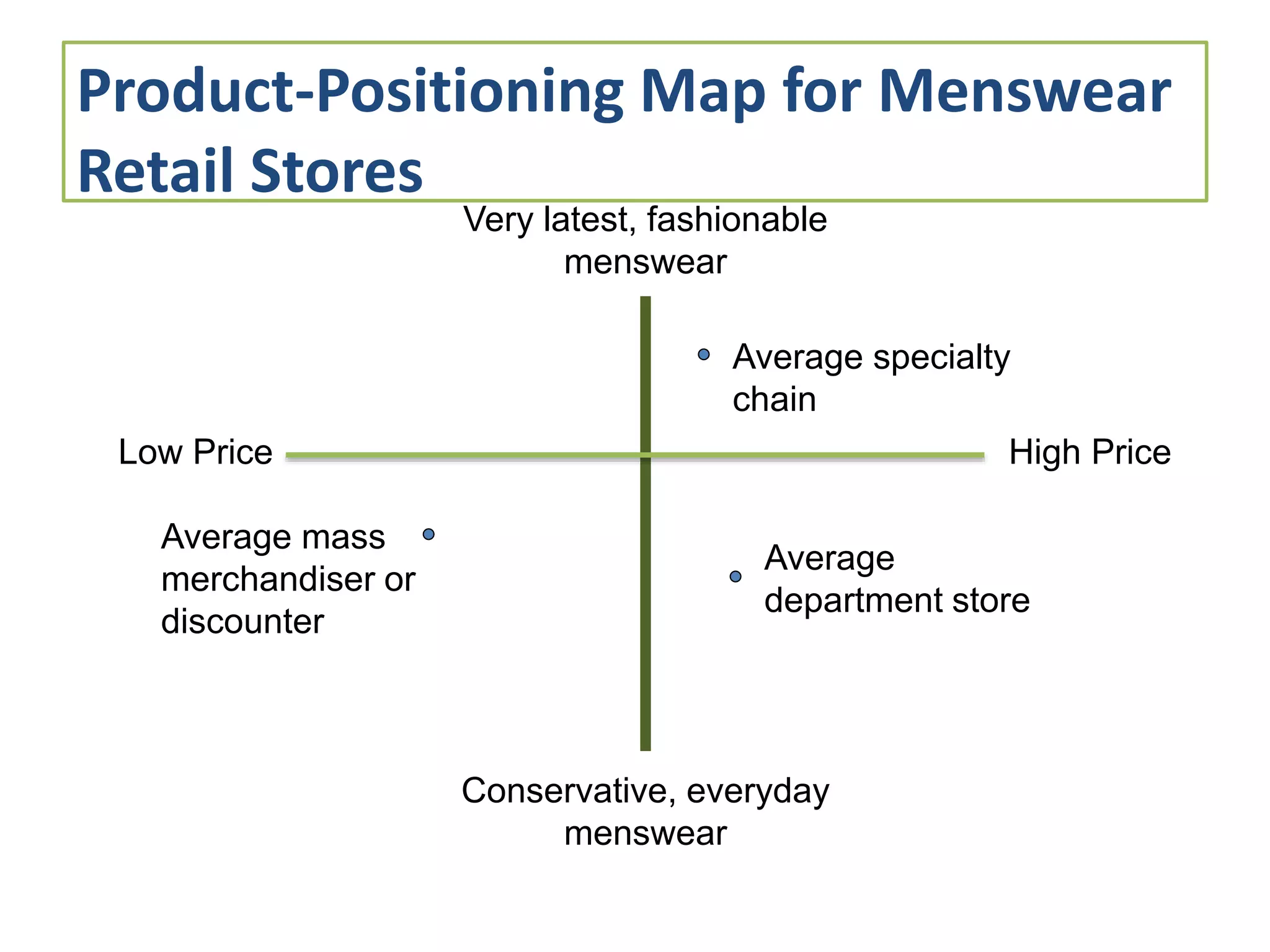
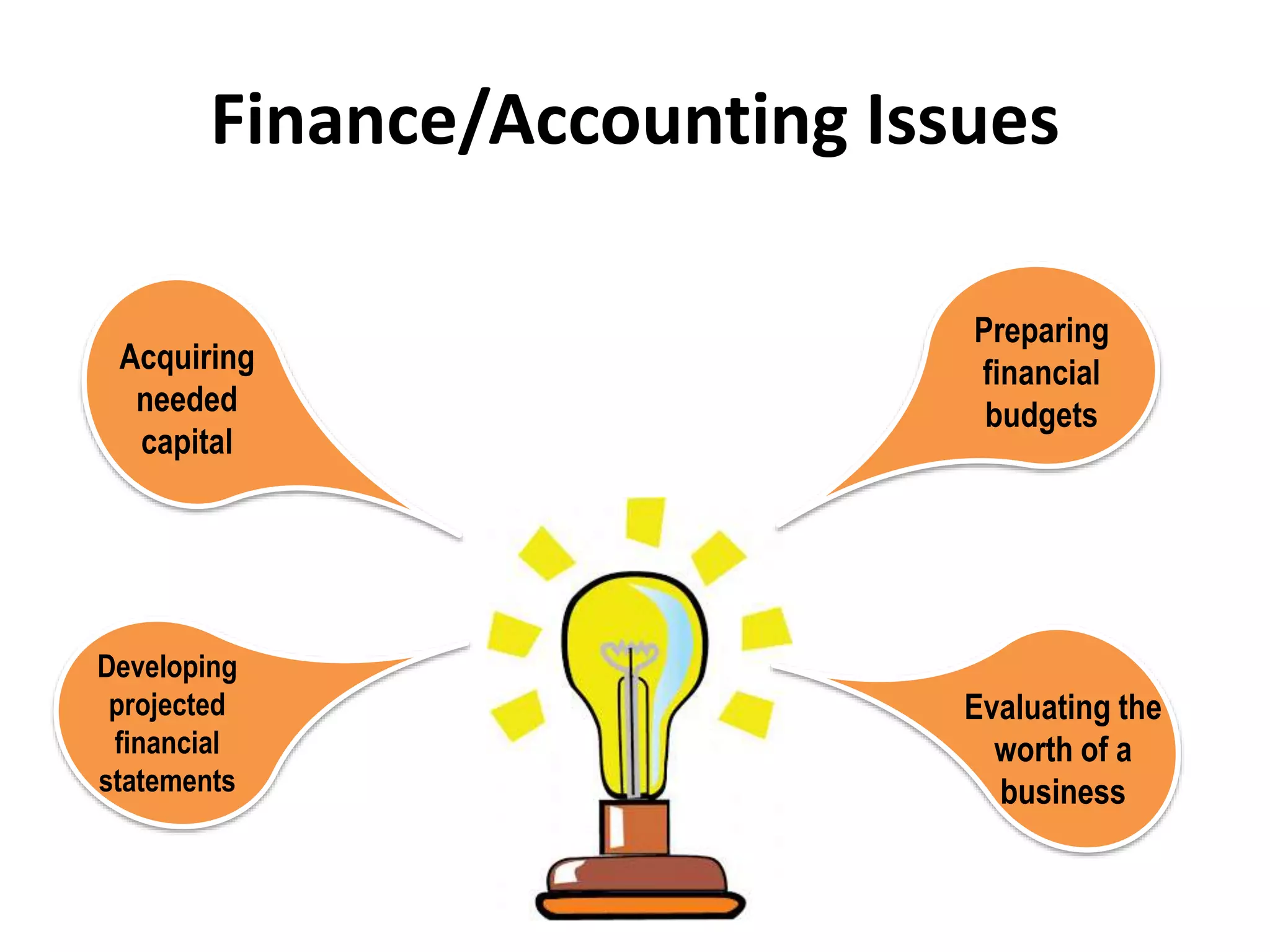
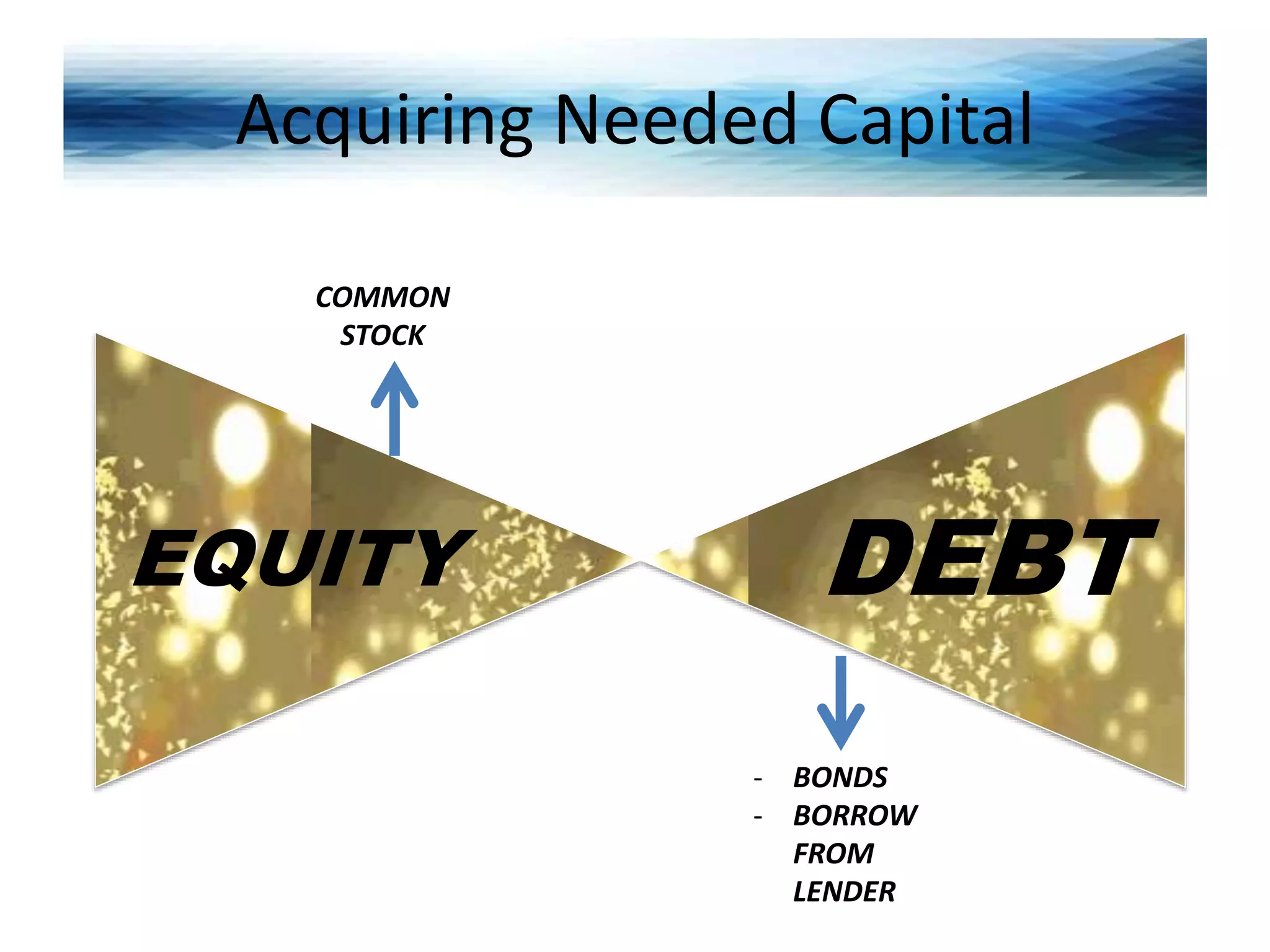
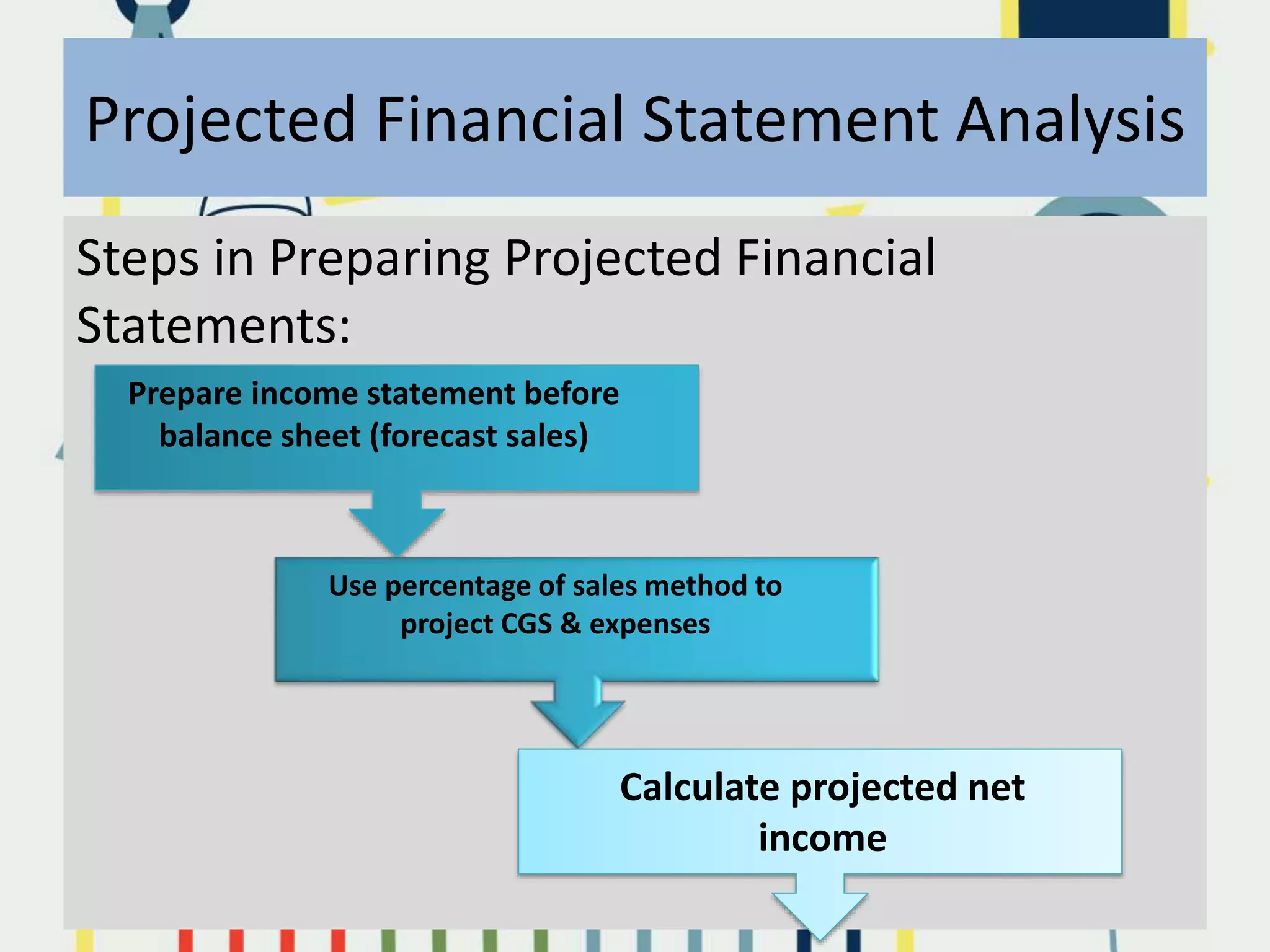
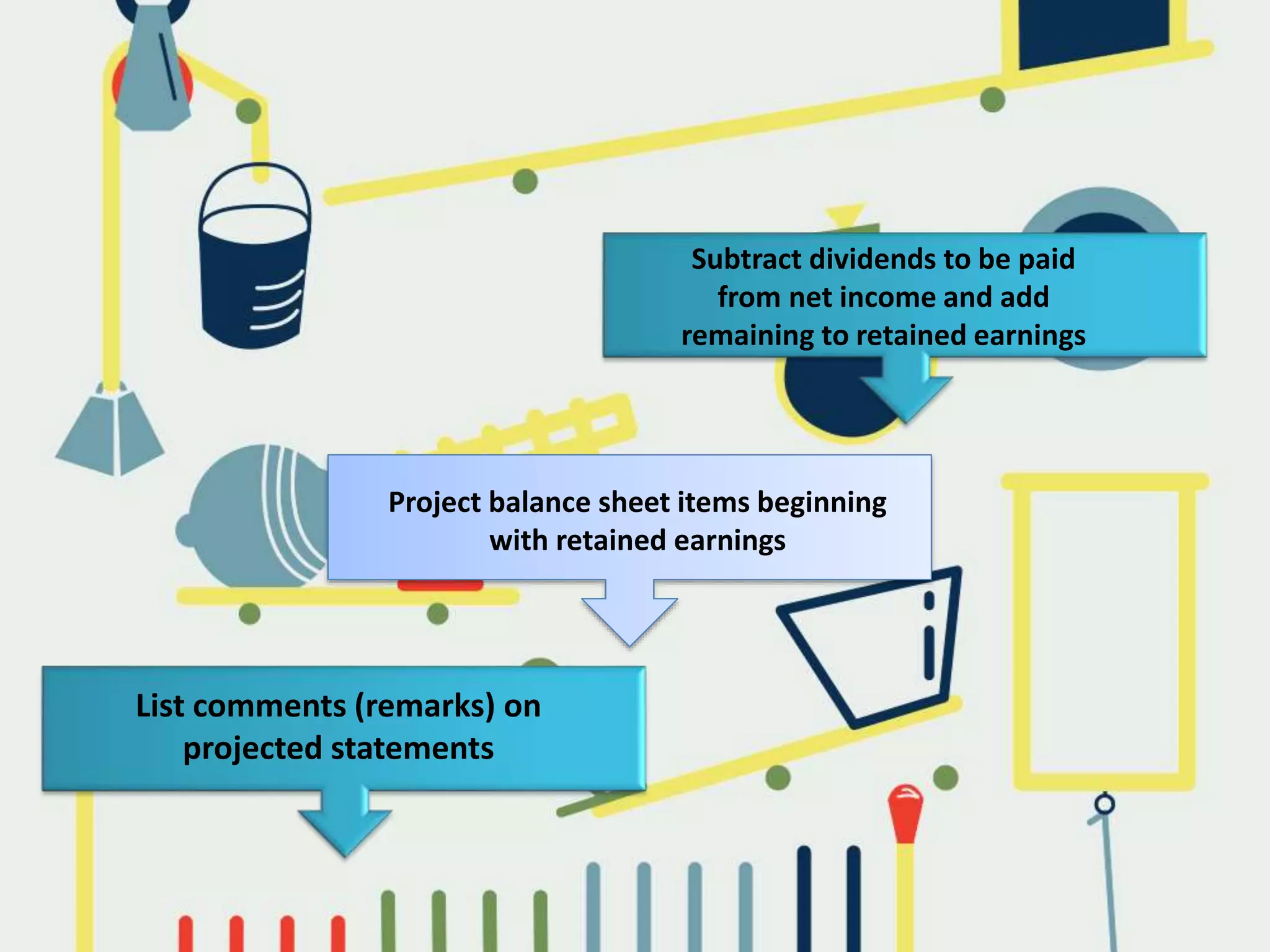
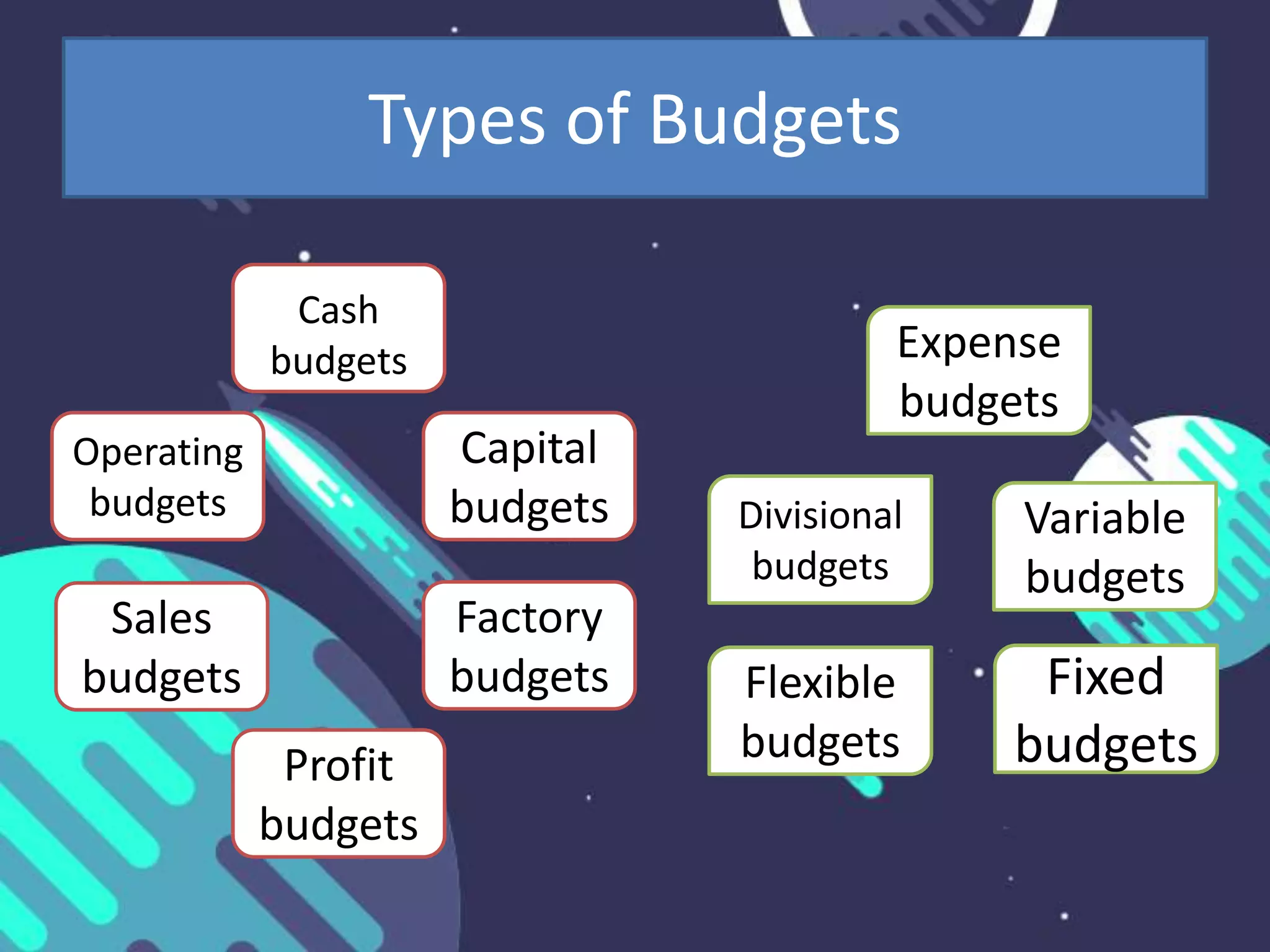
This document discusses key issues in implementing strategies related to marketing, finance/accounting, research and development (R&D), and management information systems (MIS). It explains that market segmentation and product positioning are important tools for implementing strategies. It also discusses determining a business's worth, developing projected financial statements, acquiring needed capital through equity or debt, and using budgets. The document notes that R&D approaches can allow firms to be first-to-market or low-cost producers. Finally, it states that an effective MIS system can help differentiate successful firms by collecting, storing, and sharing important information.