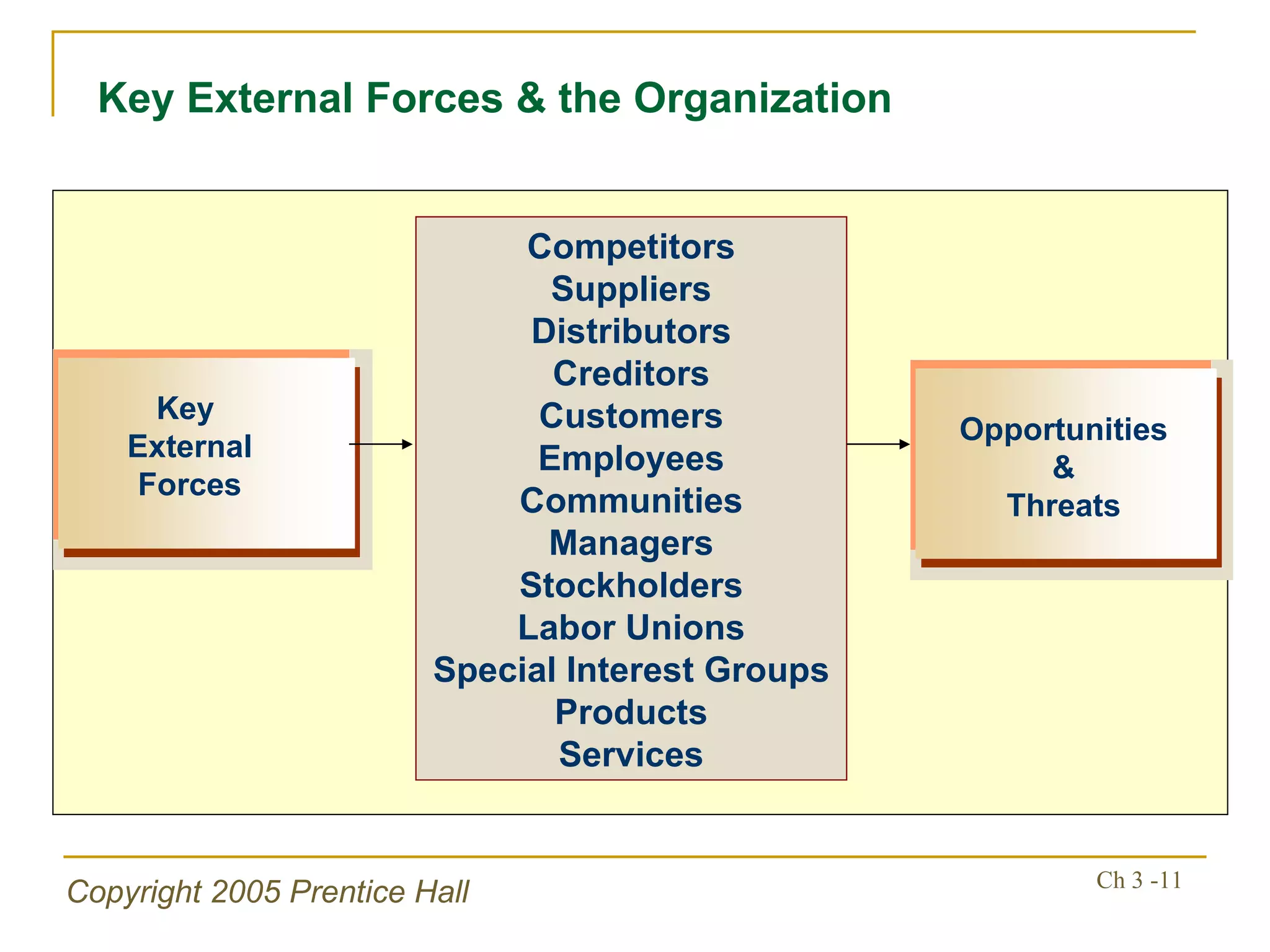
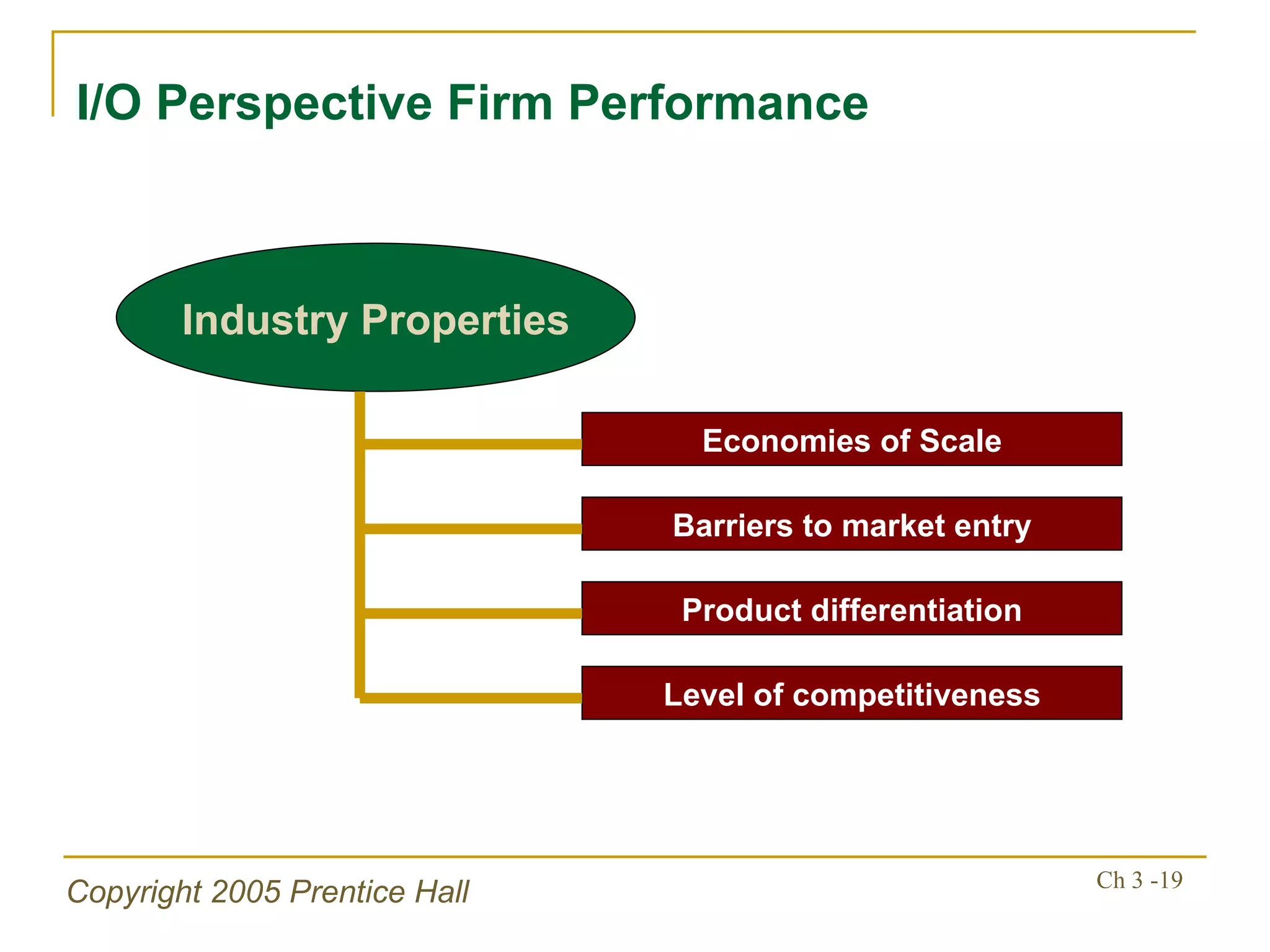
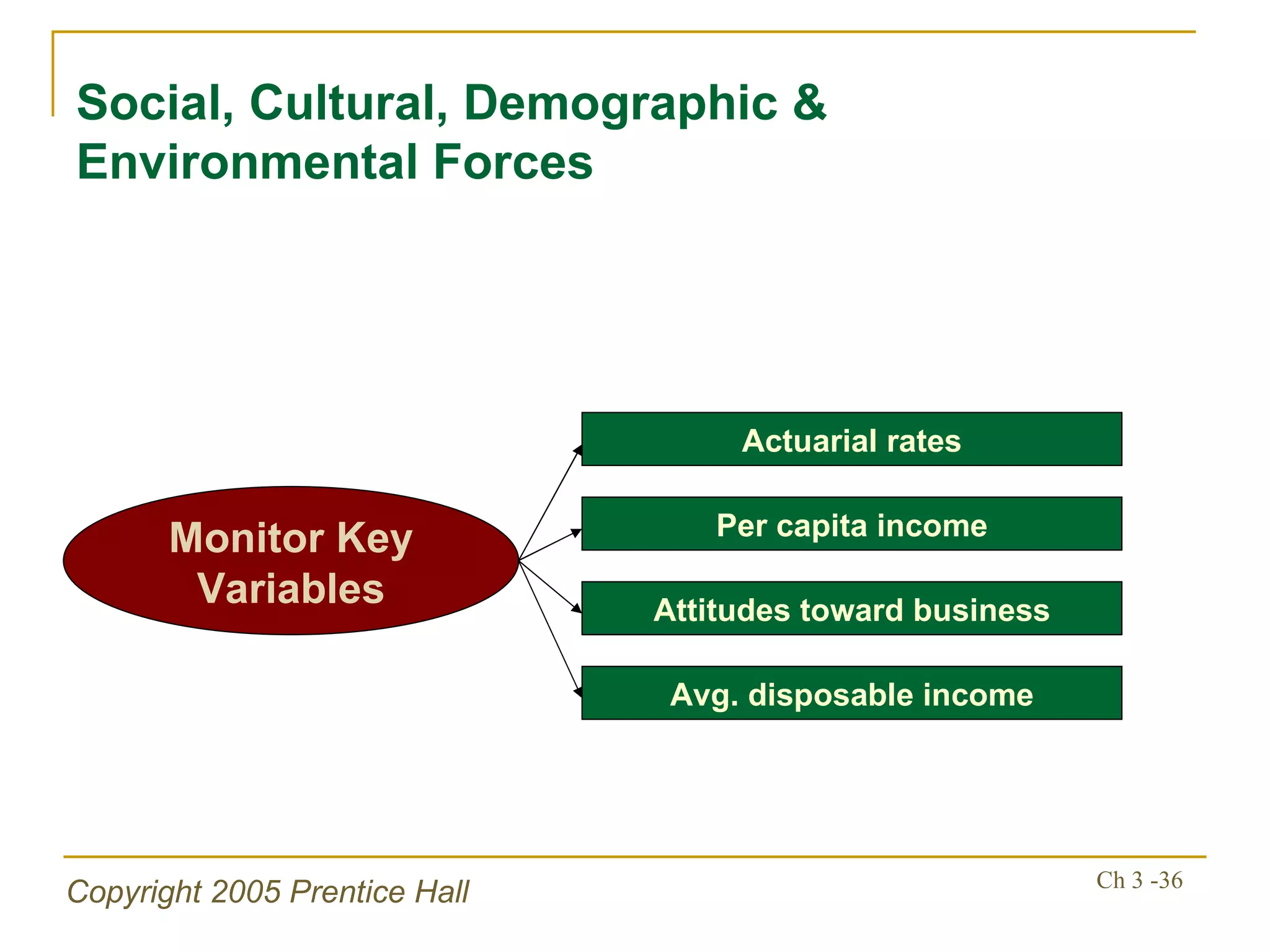
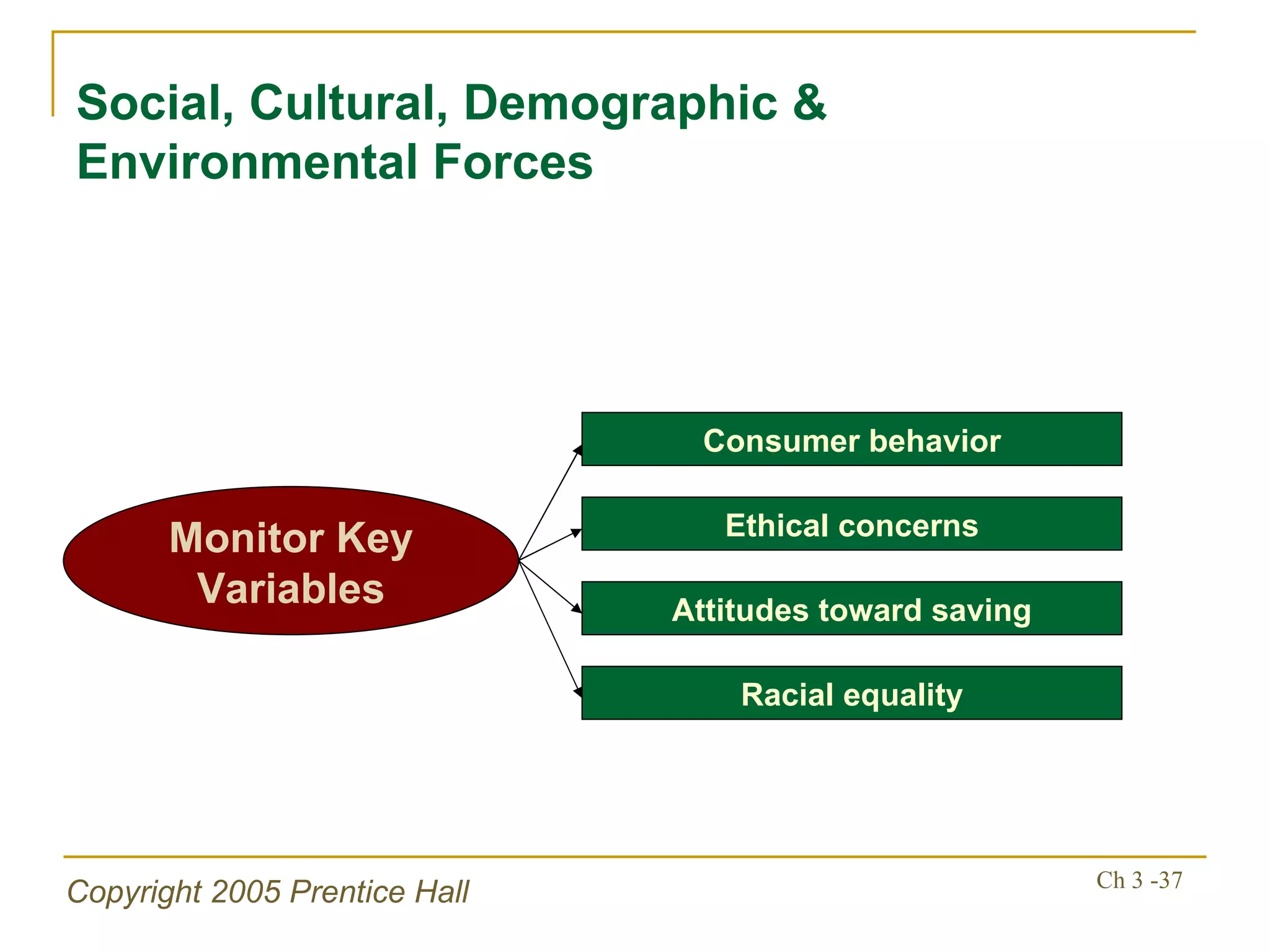
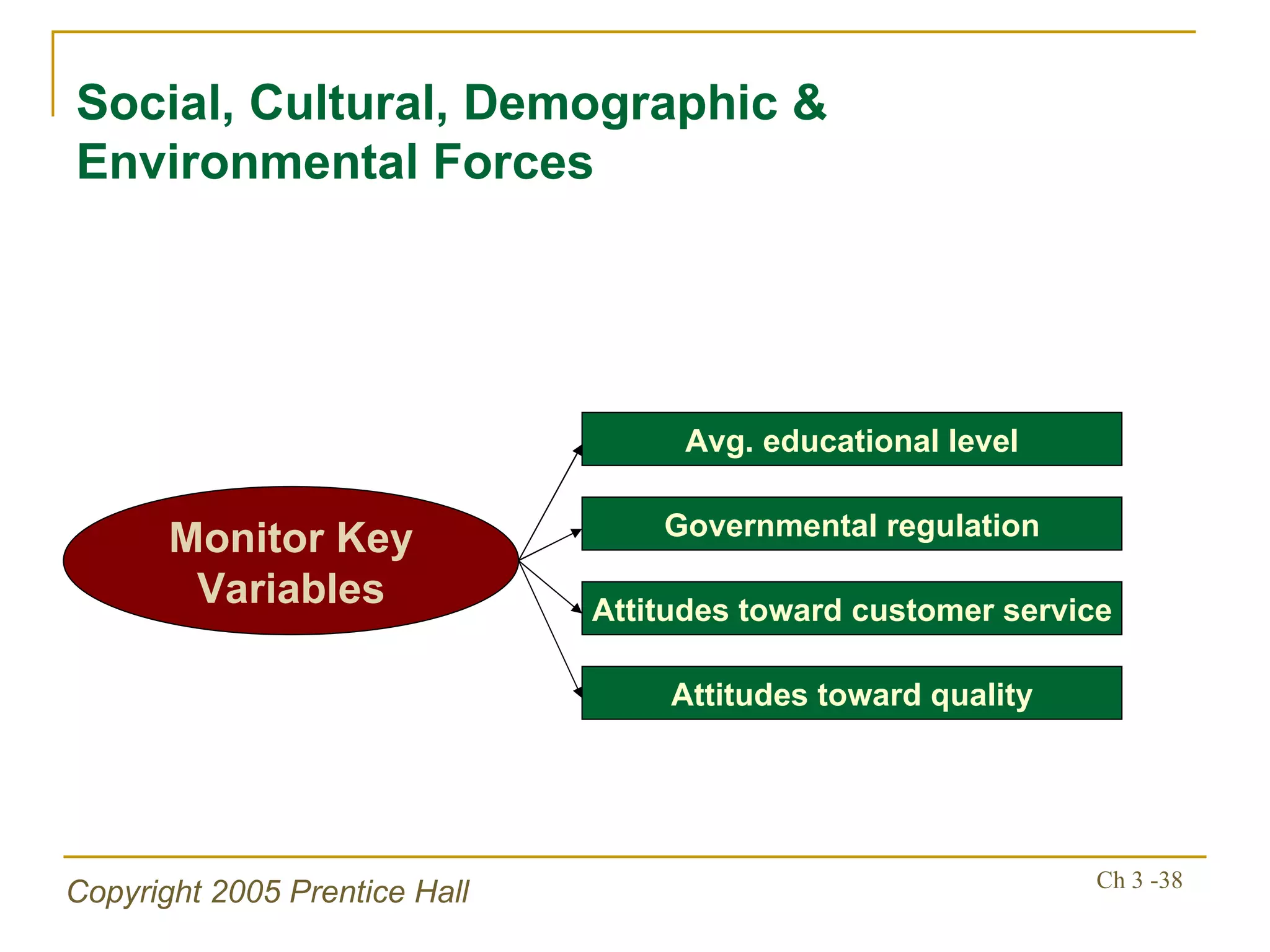
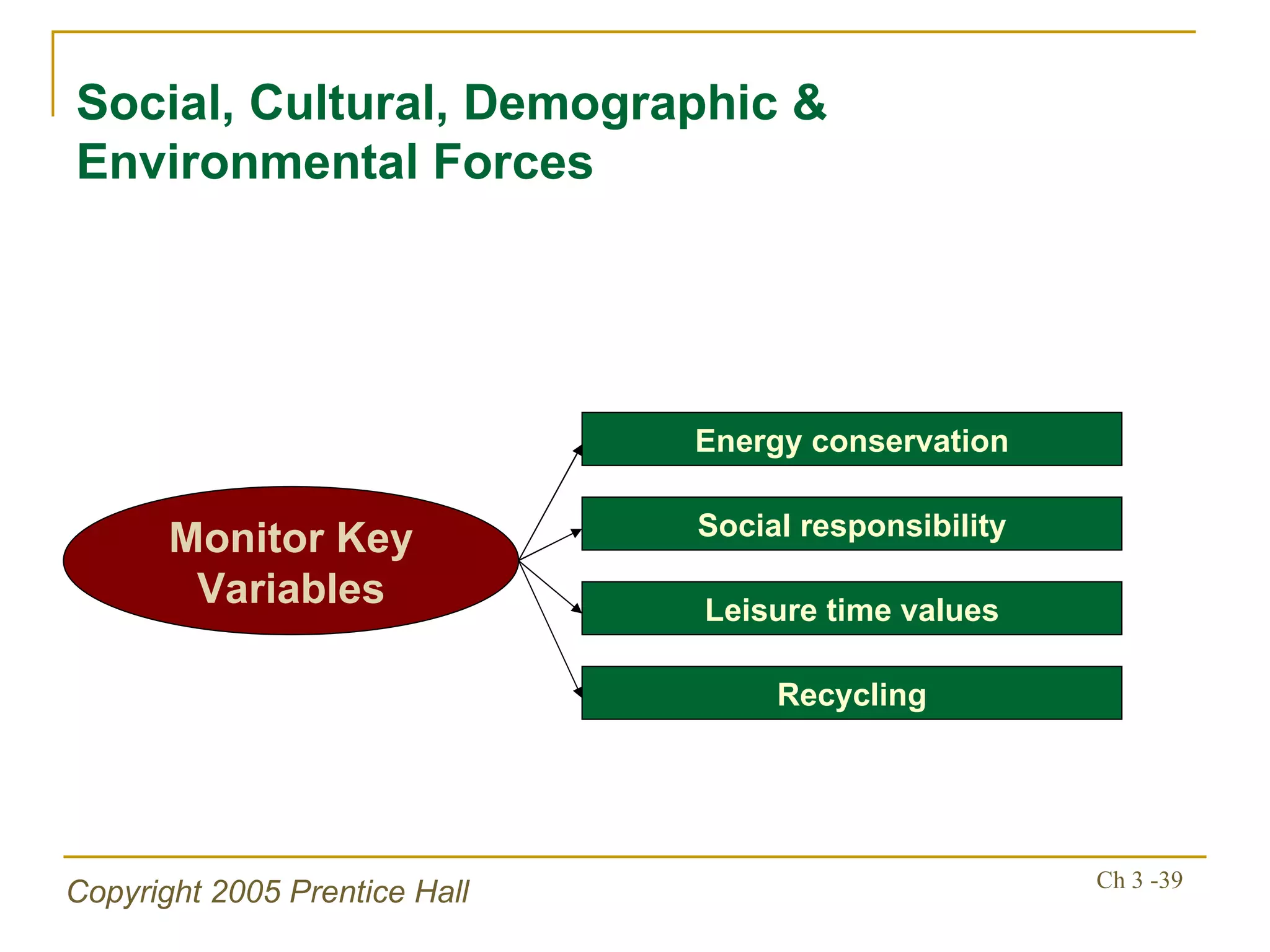
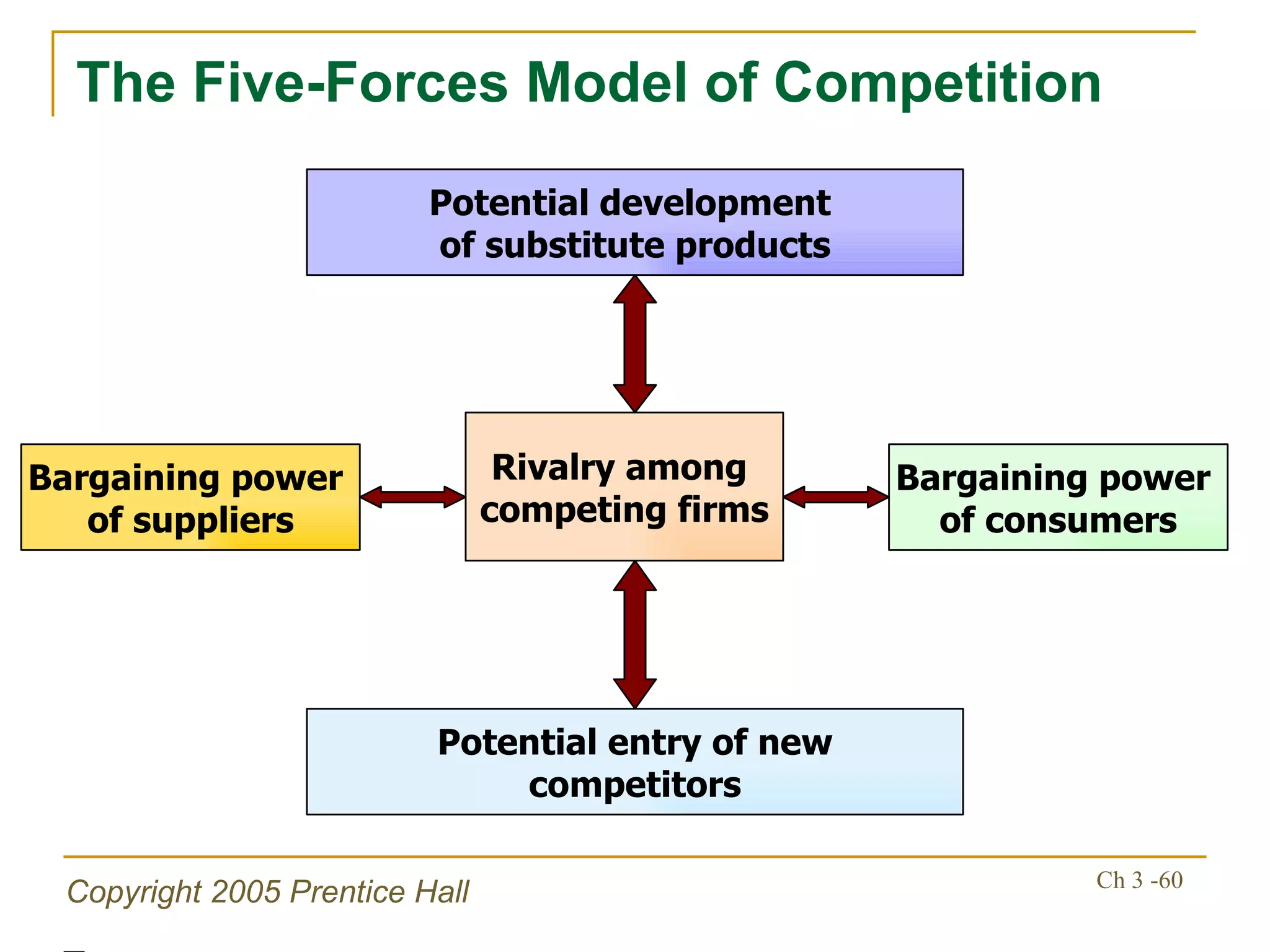
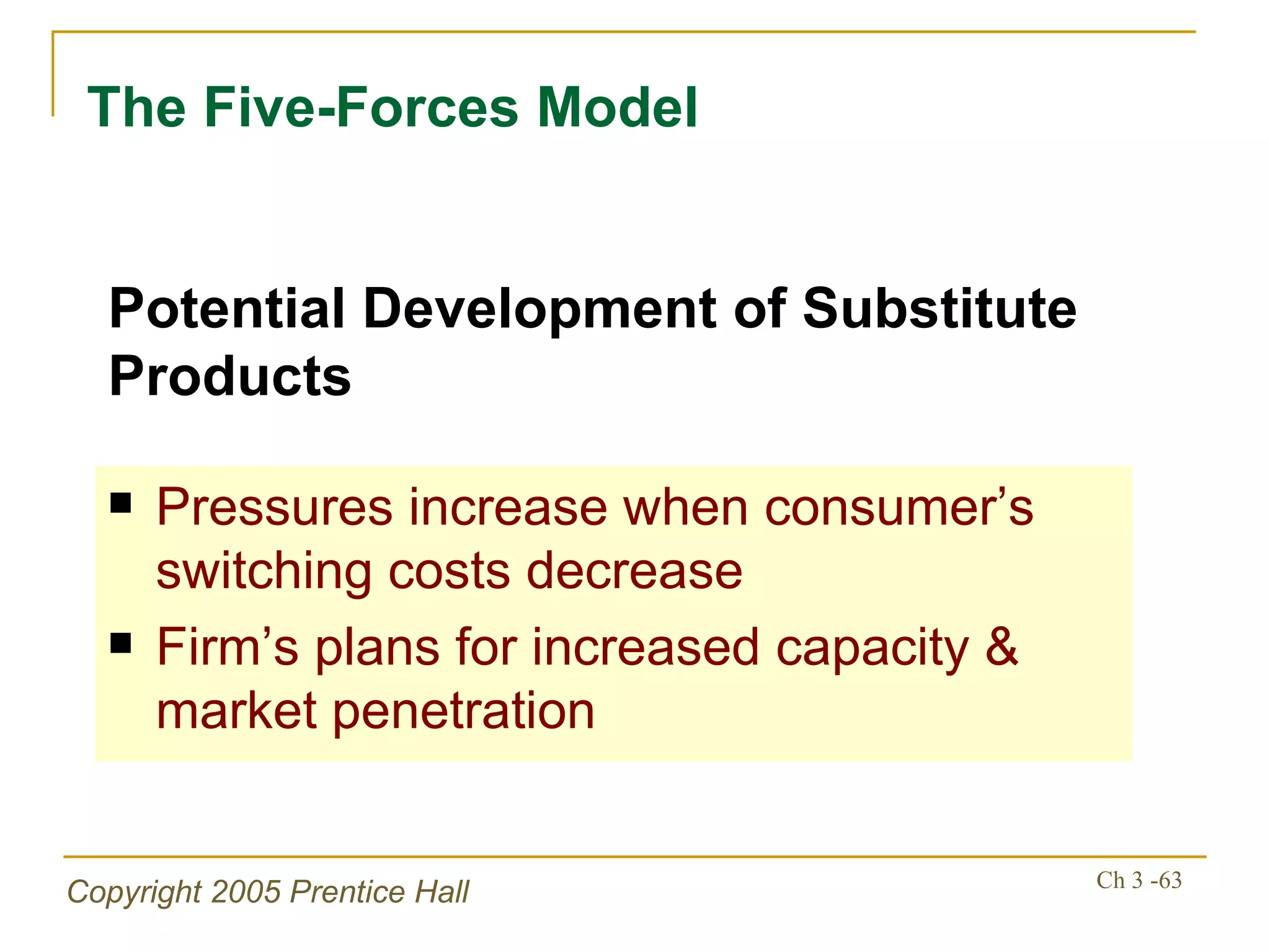
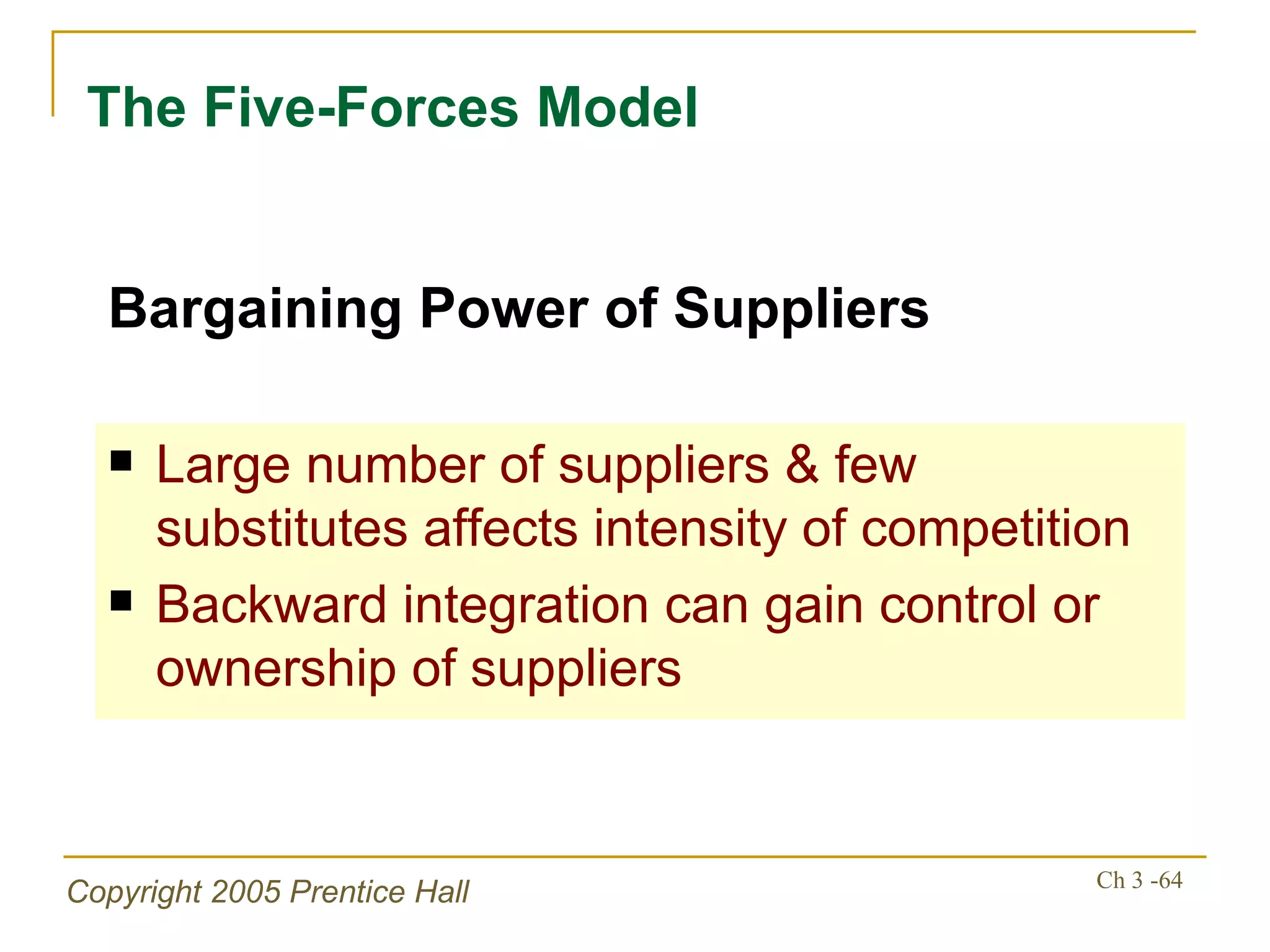
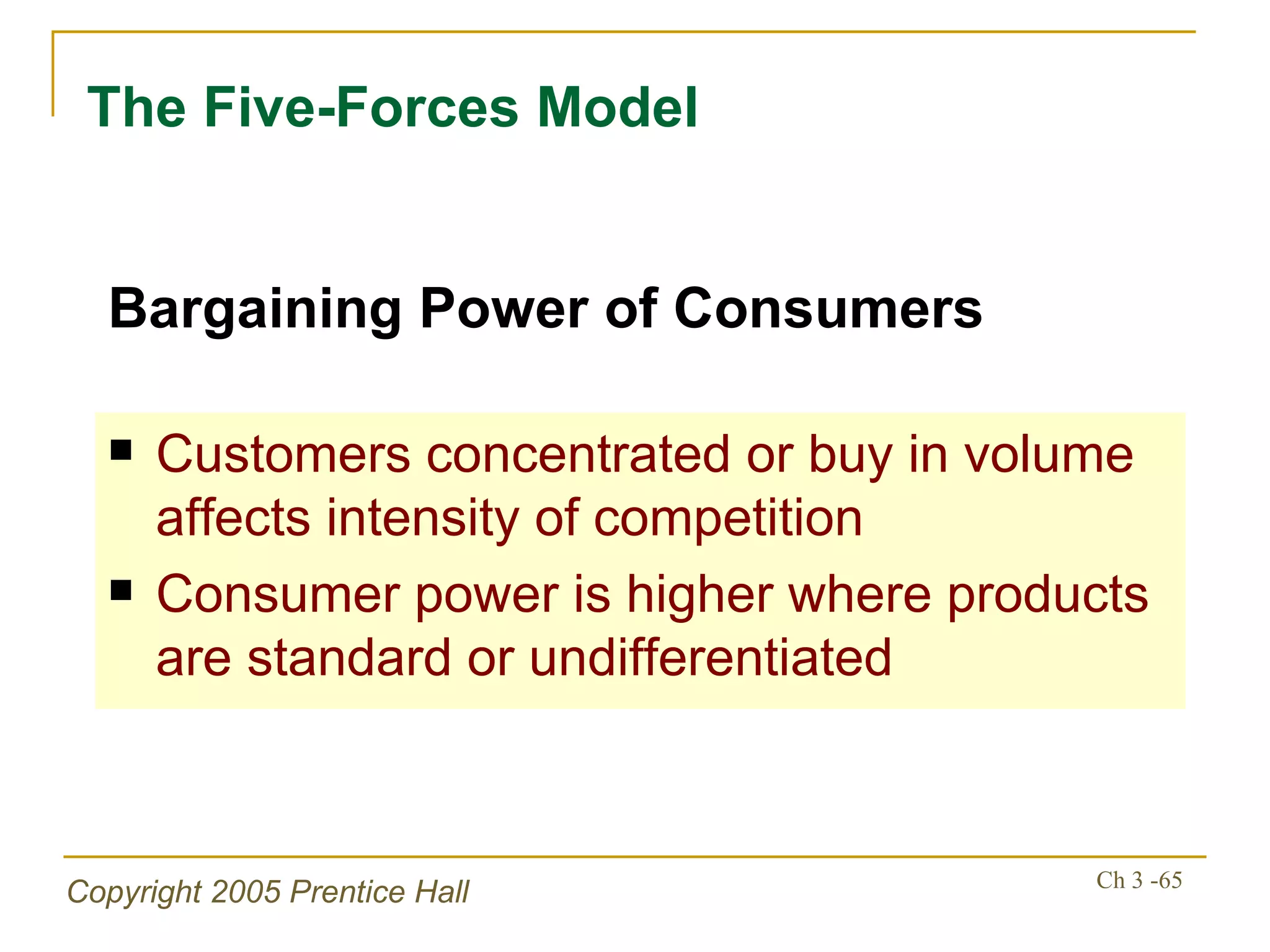
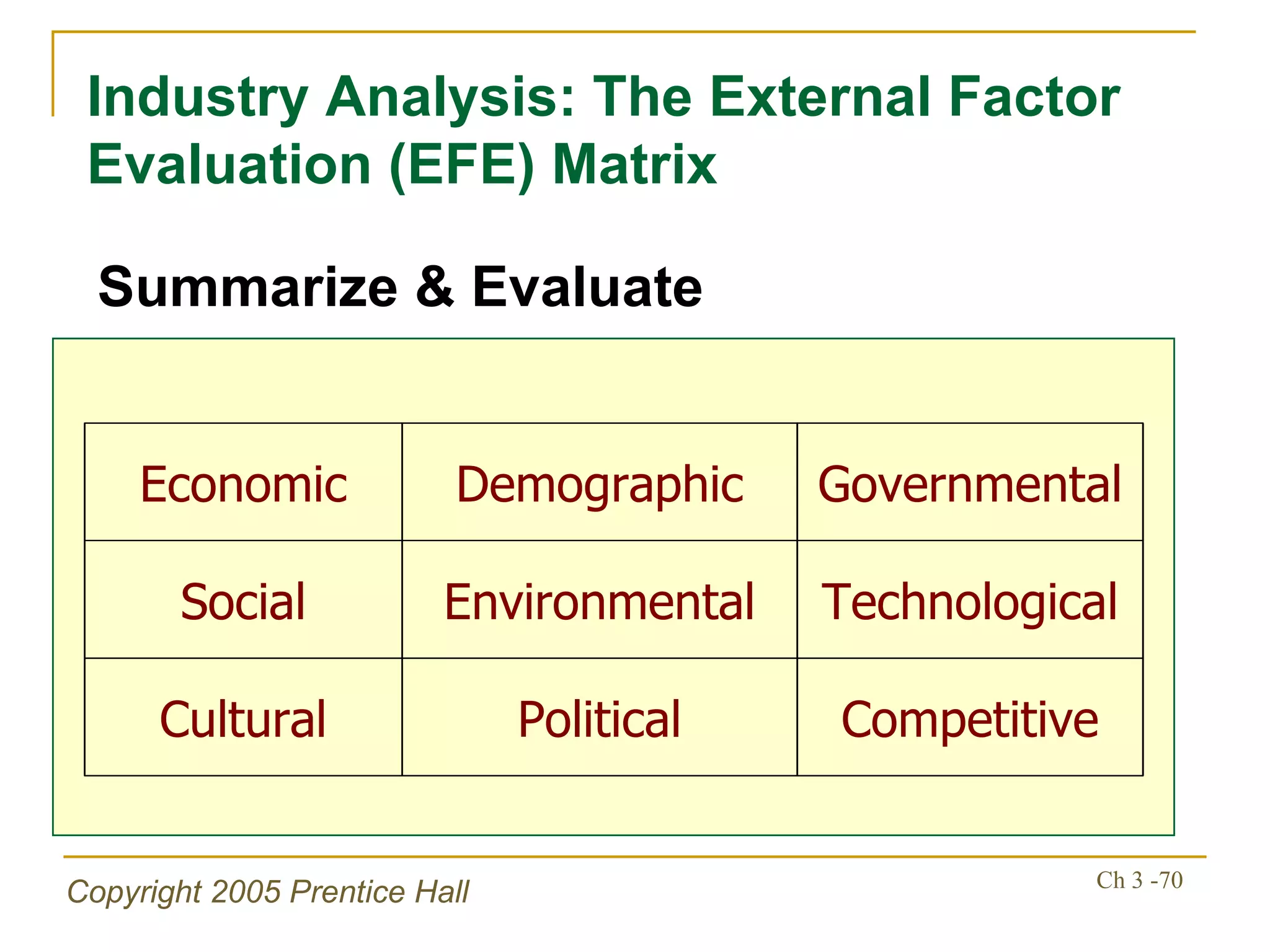
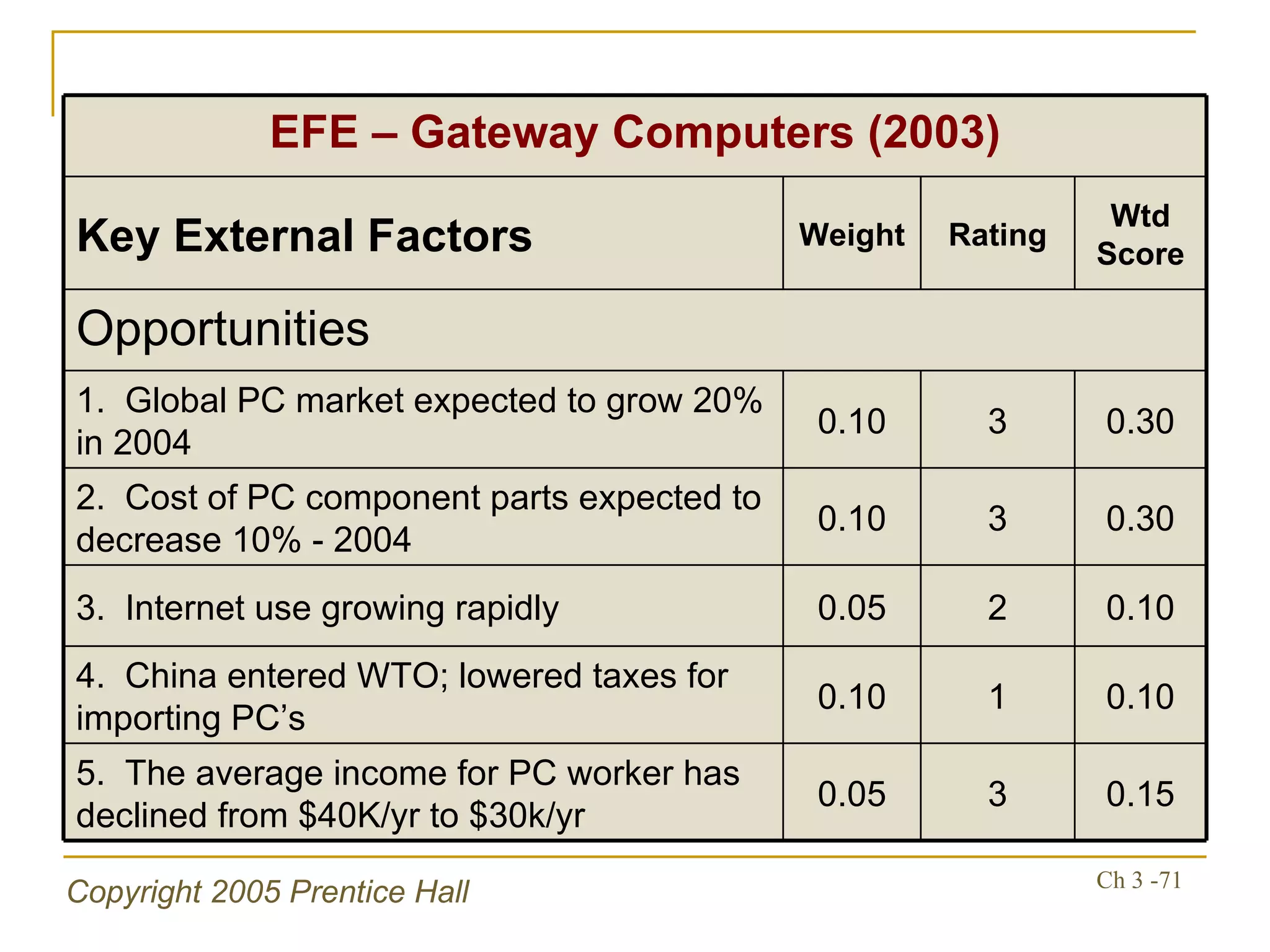
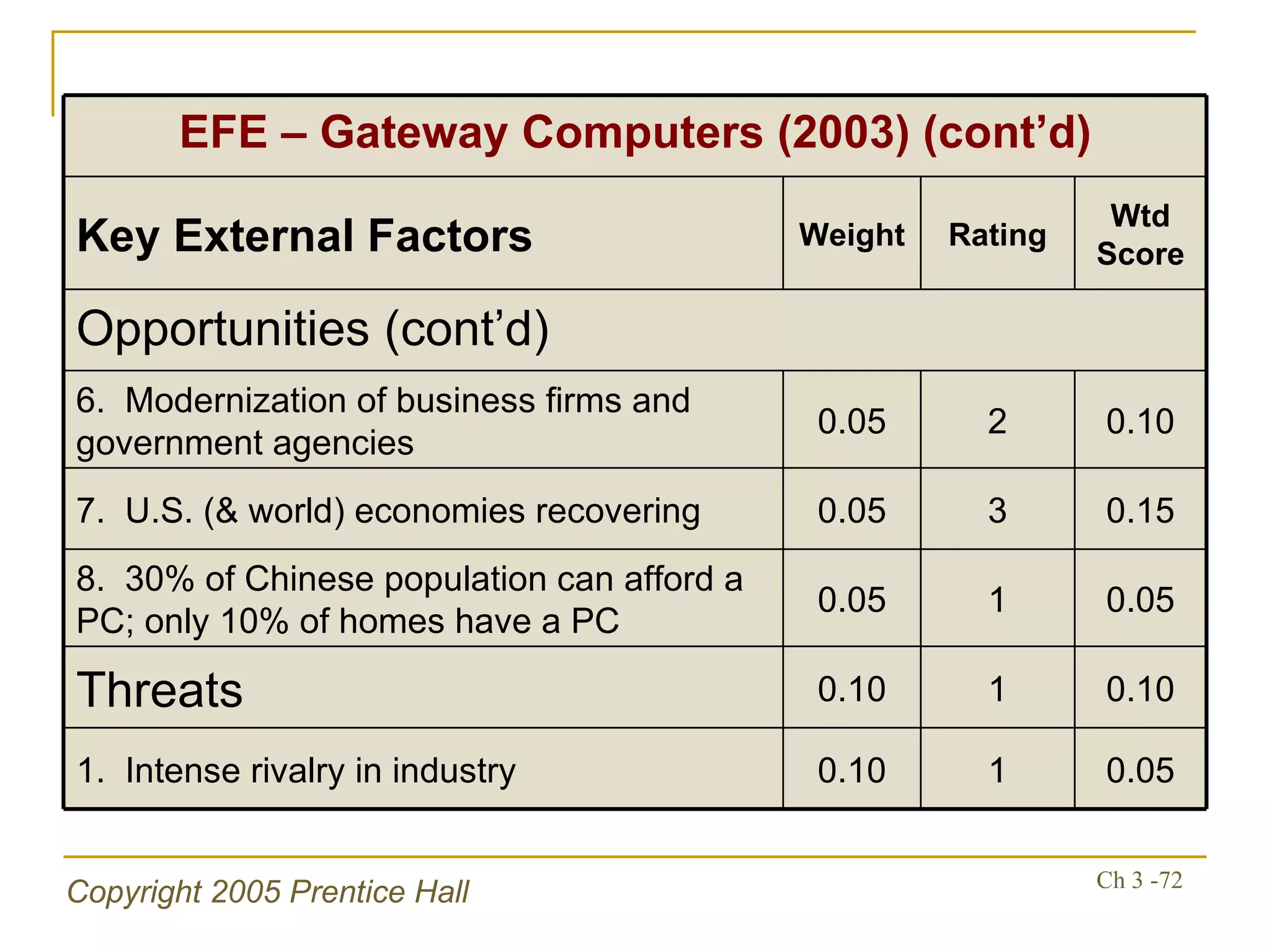
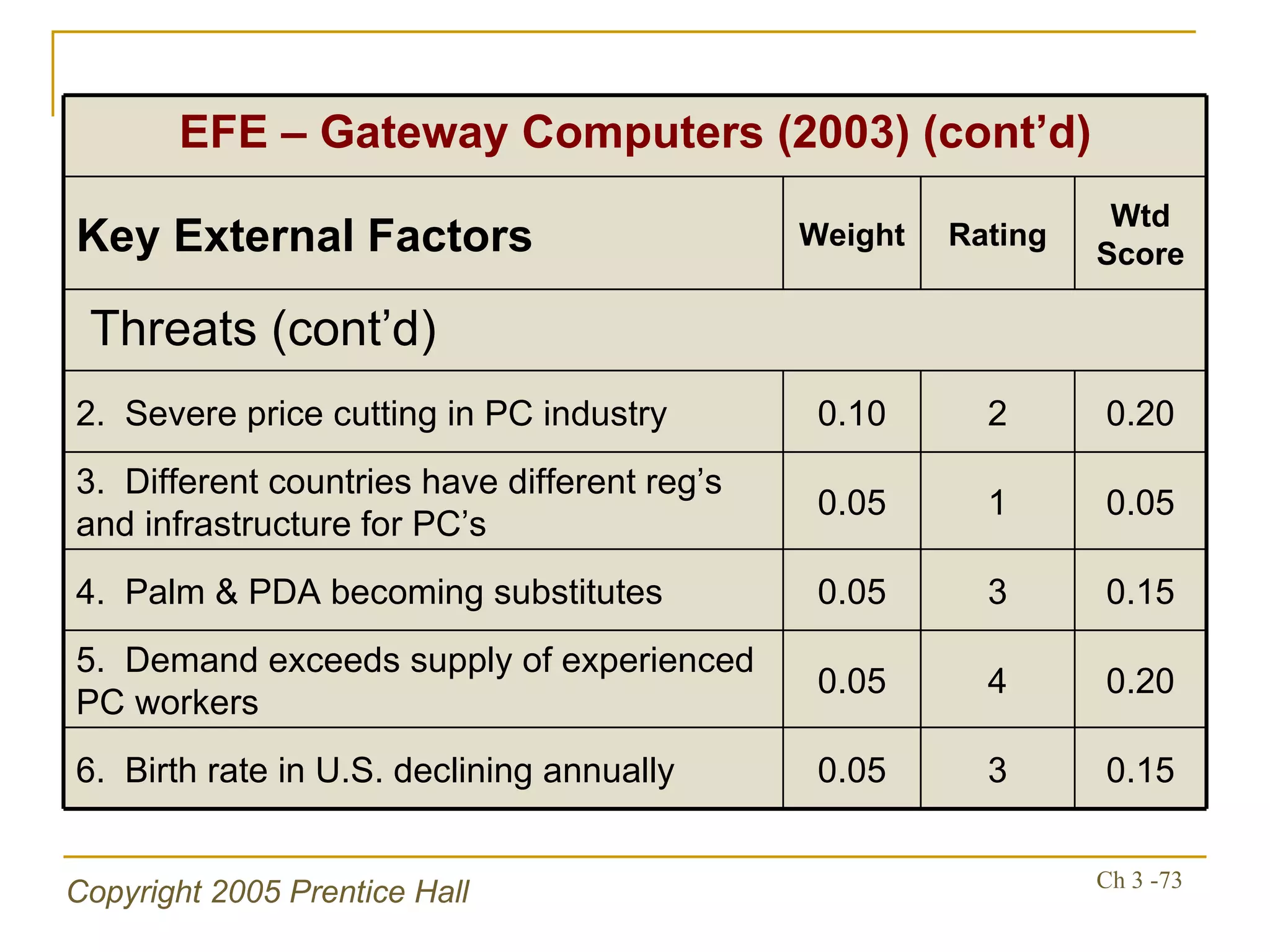
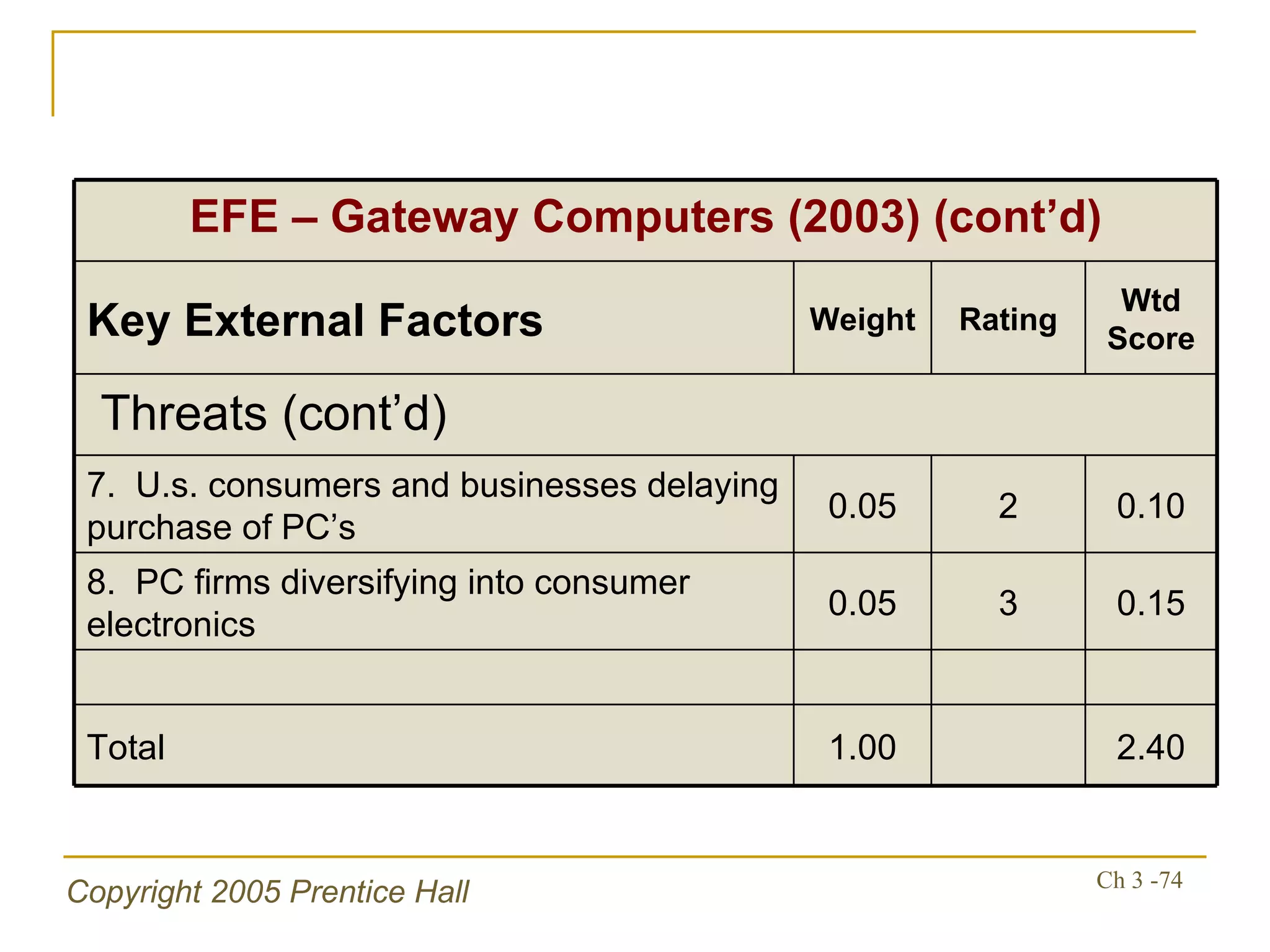
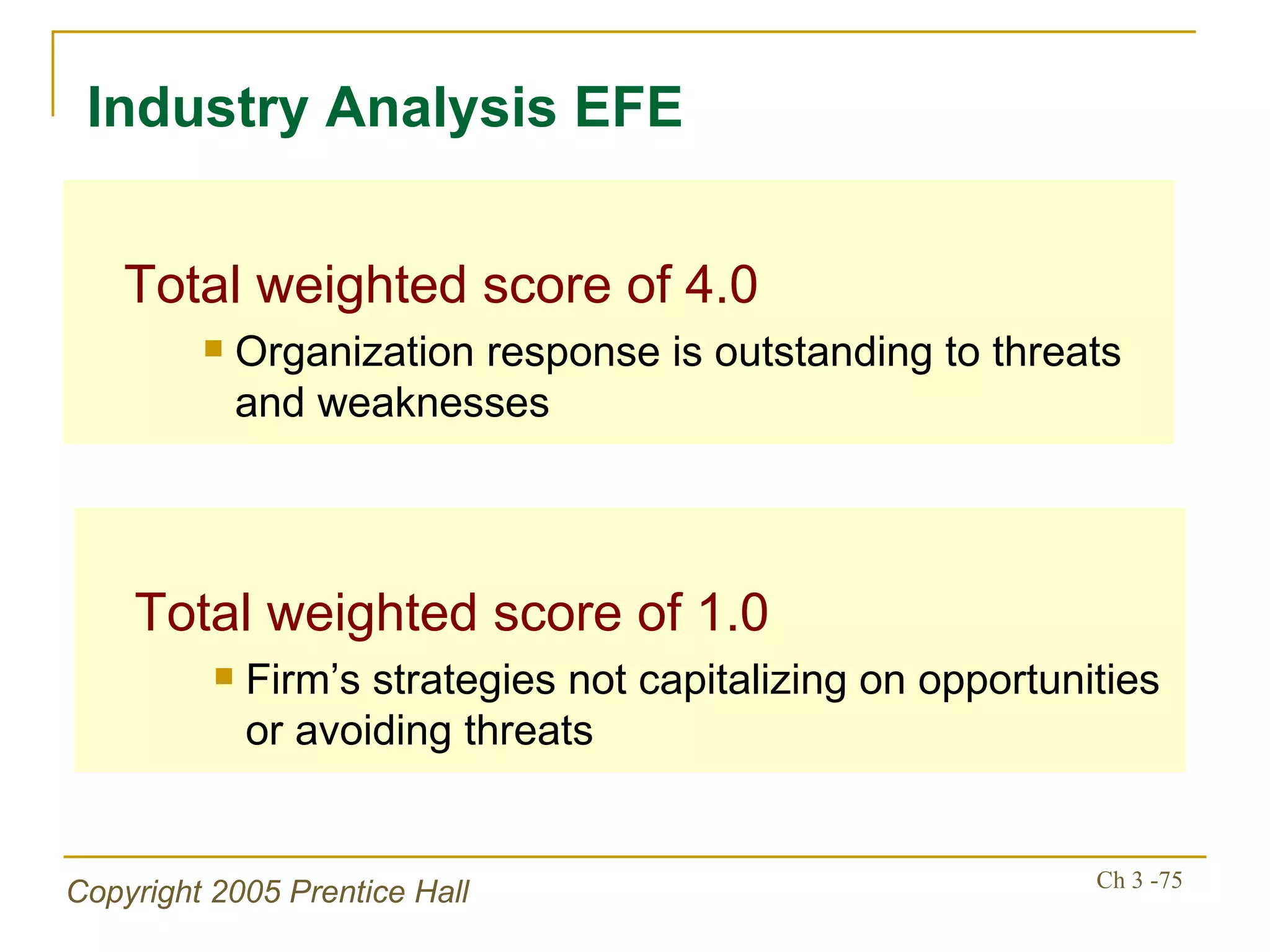
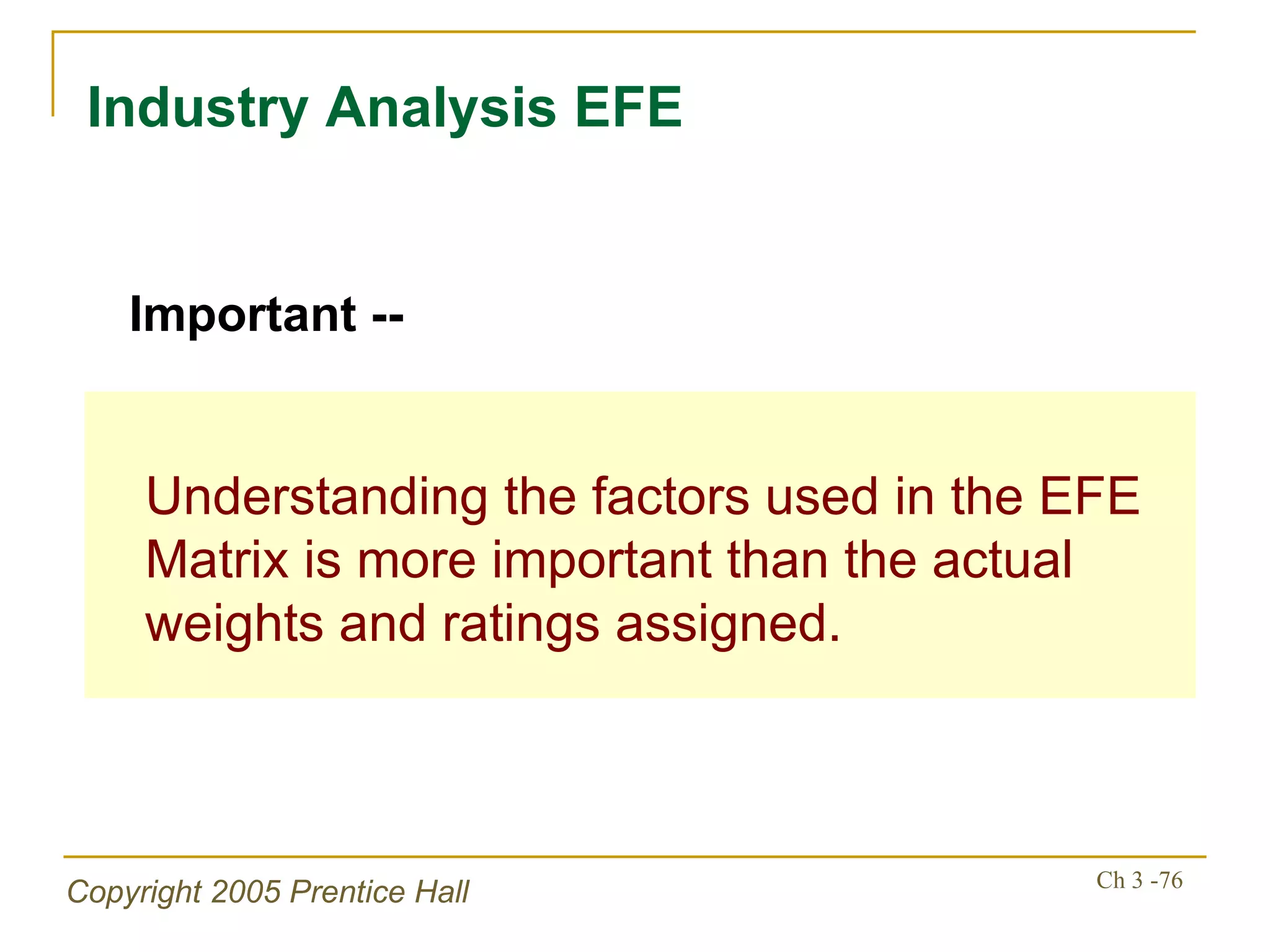
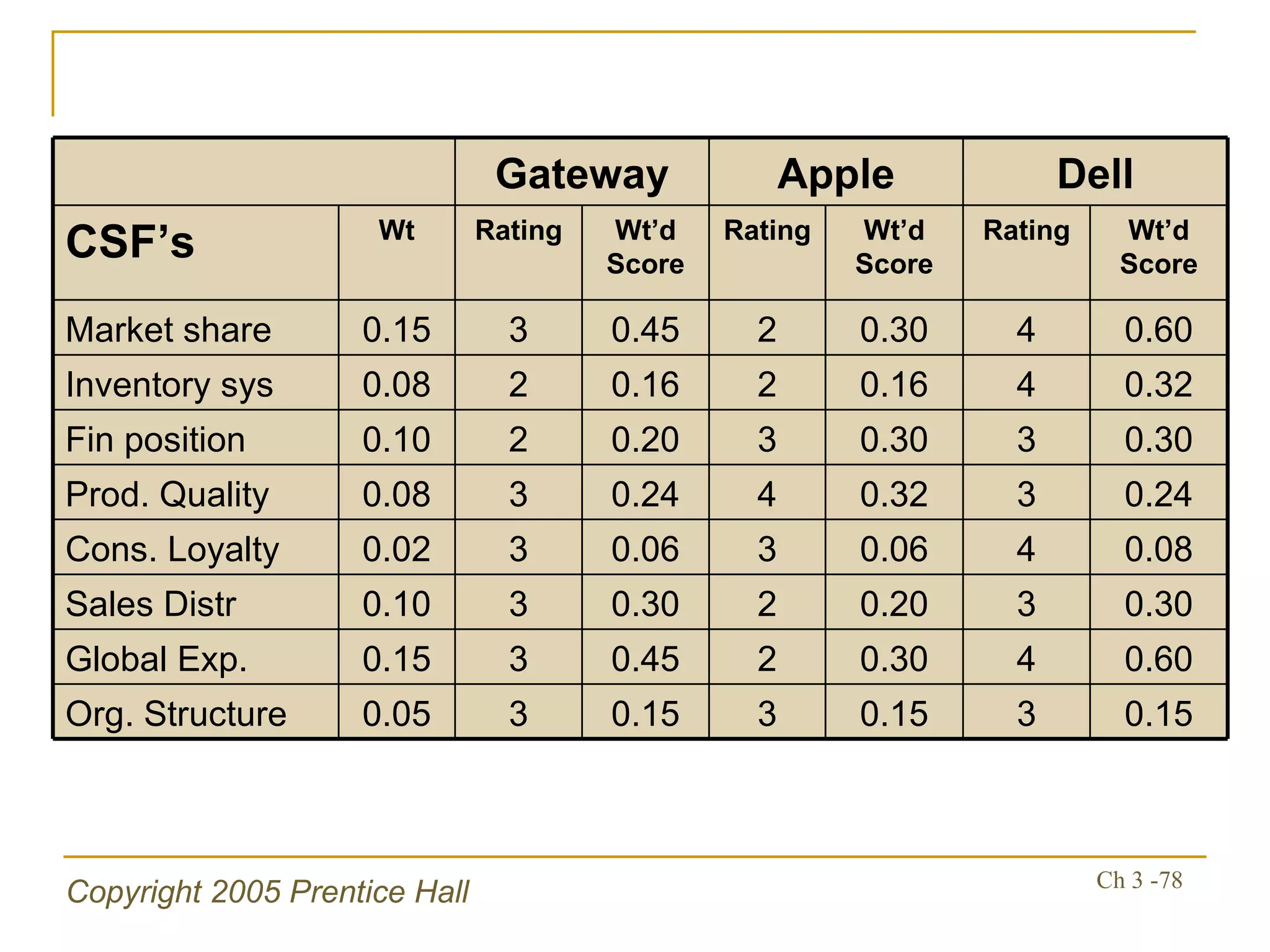
The document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 3 of a strategic management textbook. It outlines the external assessment process, including analyzing industrial organization forces, social/demographic trends, economic/political factors, technological changes, and competitive forces using models like Porter's Five Forces. Key steps are identifying opportunities/threats, performing an external audit using various sources, and creating matrices like the EFE and CPM to evaluate external factors and competitors.