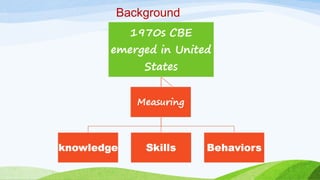
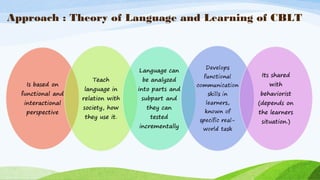
The document discusses competency-based language teaching (CBLT), which centers on skills and competencies rather than subject knowledge, emphasizing what students can do with language. It outlines the design elements of CBLT, including objectives, assessments, and the relationship between competencies and real-world job performance. The narrative concludes with a humorous anecdote illustrating the challenges language learners face, highlighting the importance of effective communication skills.