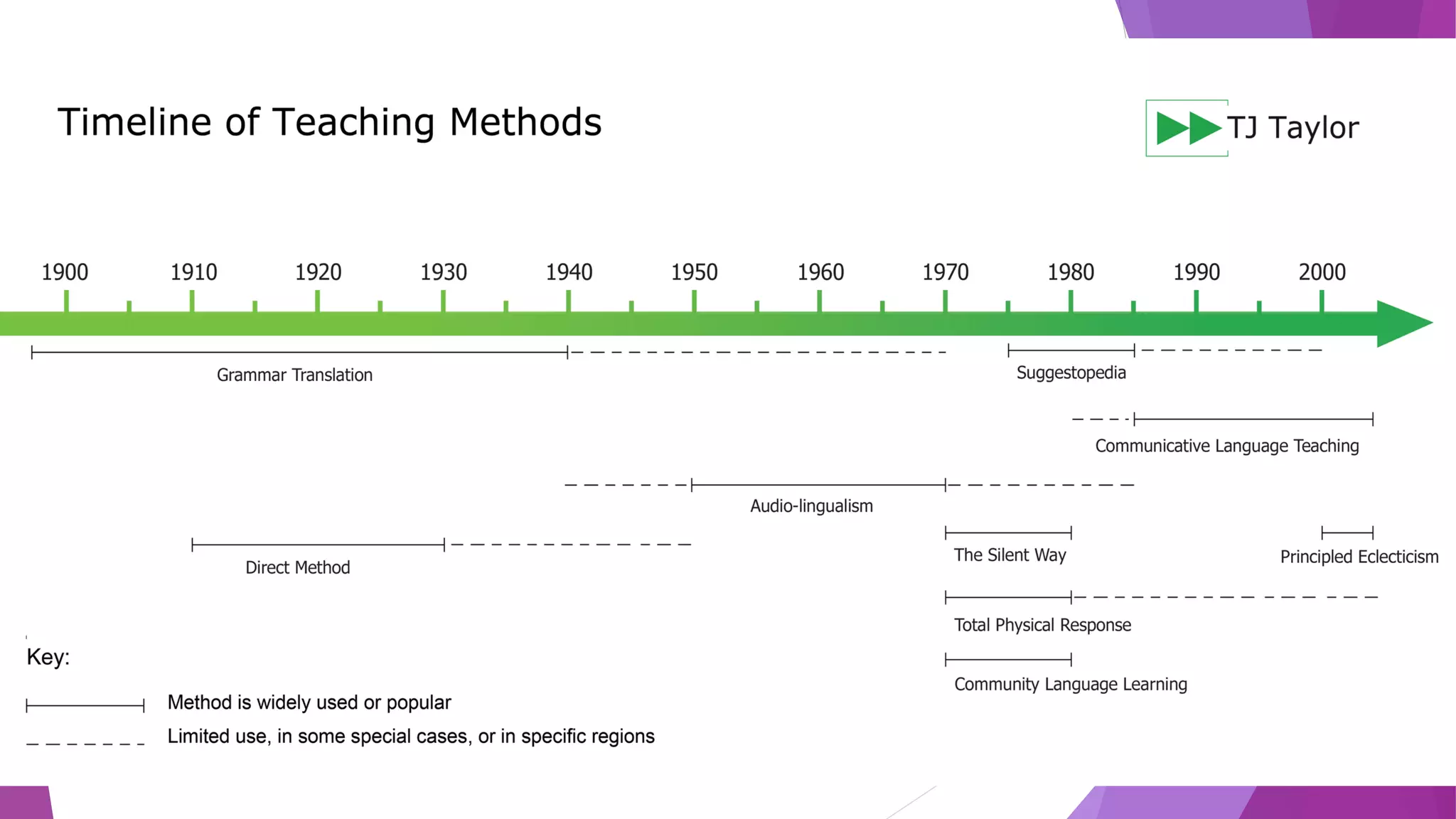
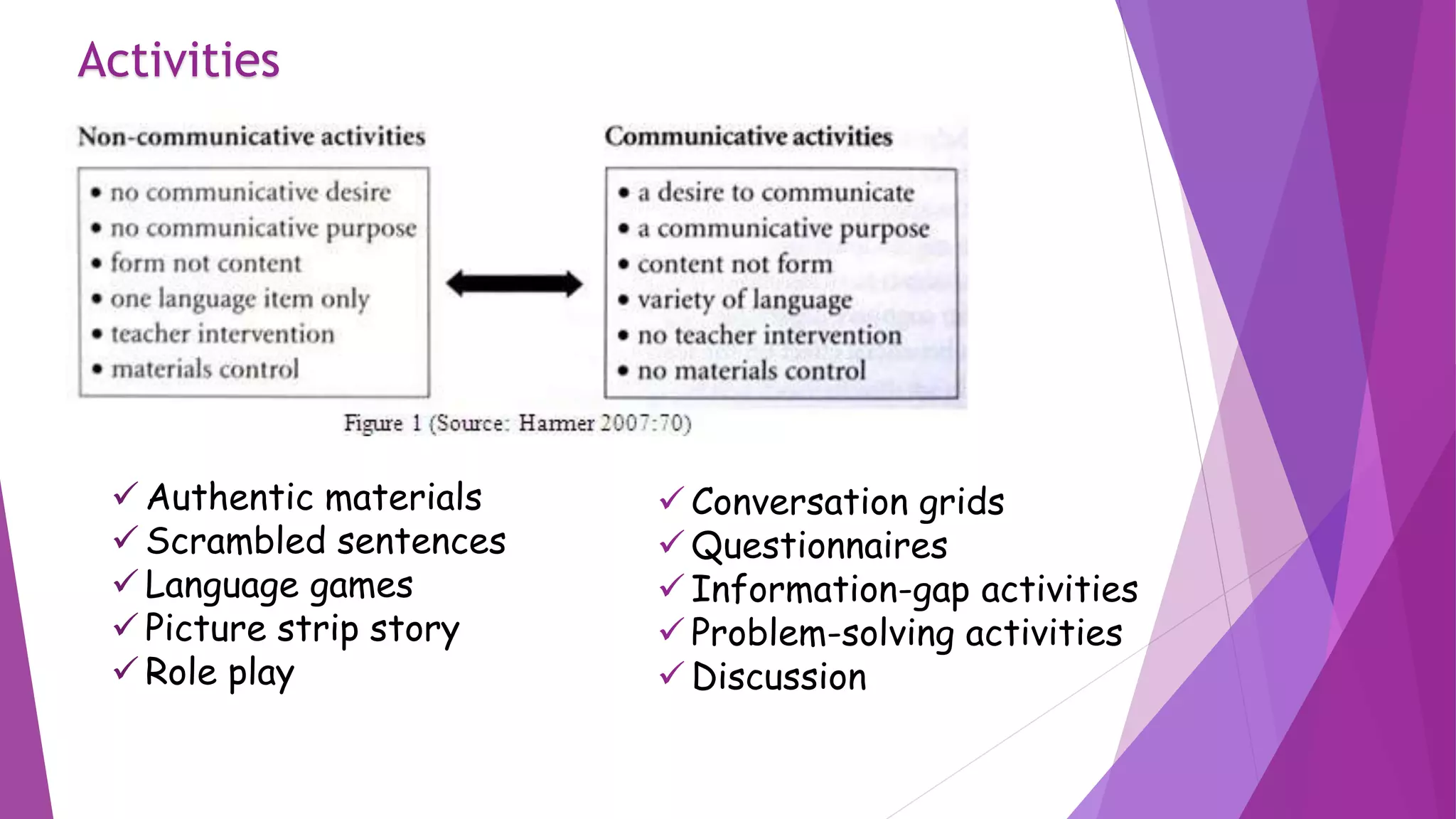
CLT is an approach to language teaching that developed in the 1960s as a reaction against previous structural and grammatical approaches. It focuses on developing students' communicative competence and ability to use language functionally. Some key principles are that meaning and communication should be prioritized over form, language is best learned through interaction, and fluency is the primary goal. The teacher acts as a facilitator, and students practice communicating through activities using authentic materials. Errors are tolerated as students focus on fluency, and evaluation assesses communicative ability.