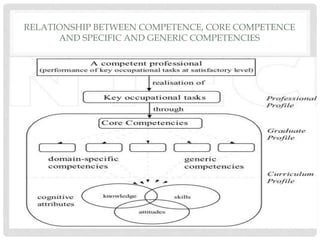
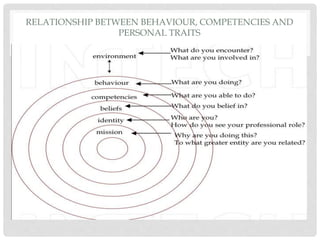
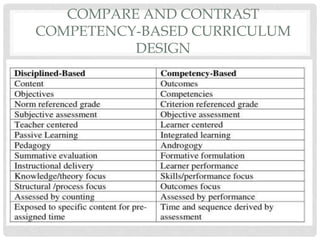
This document discusses competency-based education (CBE). It provides background on CBE, explaining that it was introduced in the 1960s in response to concerns about teaching skills for post-school life. It defines key terms like competence and competency. It also outlines characteristics of CBE, such as being learner-centered and focusing on developing competencies through application. The document lists criticisms of CBE, such as that it may minimize the role of disciplinary knowledge. Finally, it notes some advantages, like nationally agreed objectives, and disadvantages, like its focus on outcomes over learning processes.