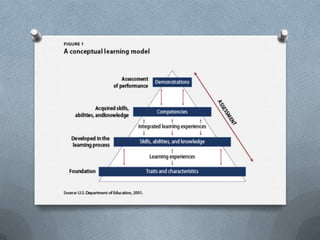
Competency-based education focuses on developing skills like lifelong learning, problem solving, self-management, and teamwork that are needed for the 21st century workforce. Assessment of competencies involves observing students applying their knowledge through individual and group assignments to determine their skills levels for different jobs. Competency levels range from applying basic knowledge to autonomously using a wide range of principles across unpredictable contexts while leading others. Motivating students is key, so teachers should focus on setting broad, flexible learning outcomes that allow students to enjoy and appreciate the learning process.