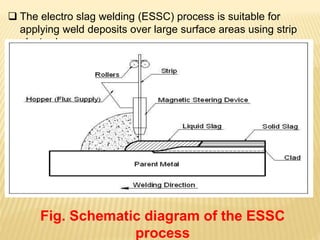
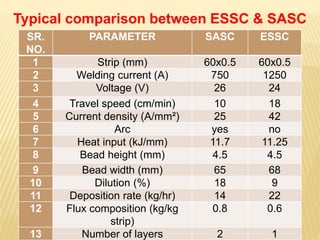
This document compares electroslag strip cladding (ESSC) and submerged arc strip cladding (SASC) welding processes. Both processes are used to apply corrosion-resistant alloy coatings to large steel components through an overlay welding method using metal strips. ESSC has a higher deposition rate and lower dilution from the base material compared to SASC, due to using a molten slag pool instead of an electric arc to melt the strip. Key differences highlighted include ESSC having higher welding currents, increased welding speeds, and lower flux consumption than SASC, resulting in more productive and cleaner welds. Examples of applications for strip cladding include pressure vessels, pipes, and steel mill rolls.