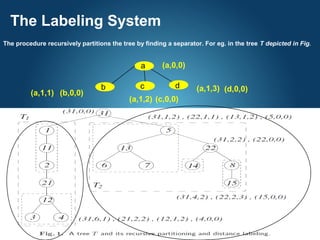
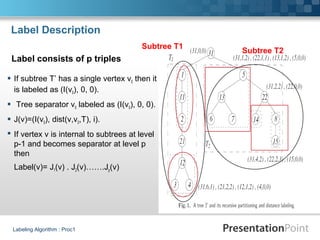
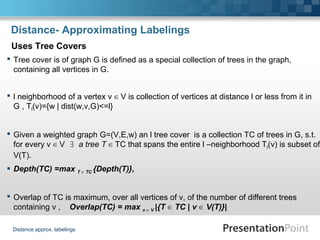
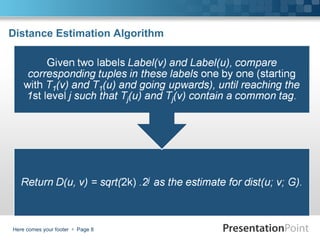
The document describes a proximity preserving labeling scheme for graphs. The scheme aims to label vertices such that the distance between any two vertices can be inferred from their labels. It uses tree separators to recursively partition trees. The labels consist of multiple triples, where each triple contains an identifier, distance from the separator, and other information. Given two labels, their distance can be computed by comparing the triples and looking at the subtree each belongs to. The scheme is also extended to approximate distance labeling for general graphs using tree covers.