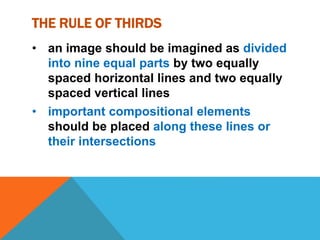
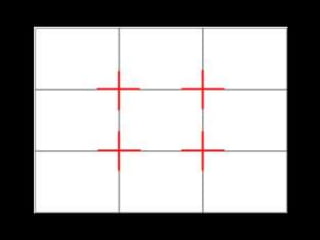
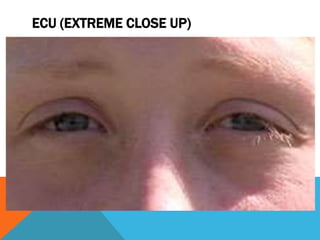
The document provides an overview of various filmmaking shots, detailing definitions and purposes ranging from extreme wide shots to point-of-view shots. It highlights the importance of composition techniques like the rule of thirds, which enhances viewer engagement. Additionally, it explains how different shot types contribute to storytelling by establishing settings, relationships, and emotional states.