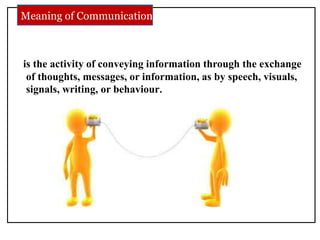
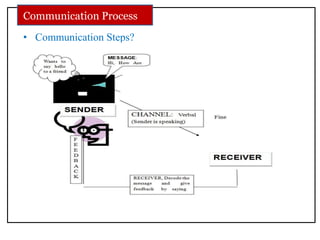
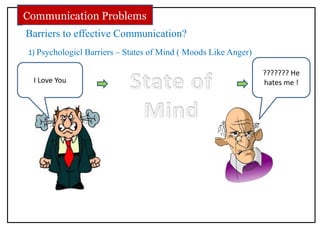
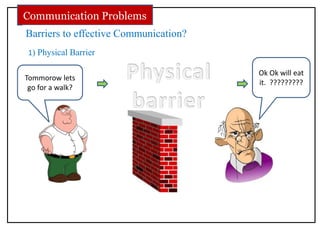
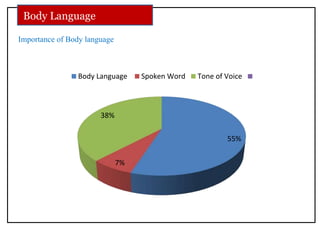
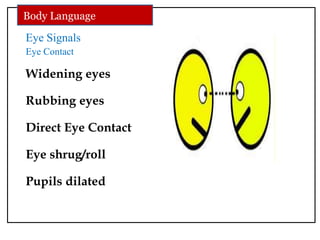
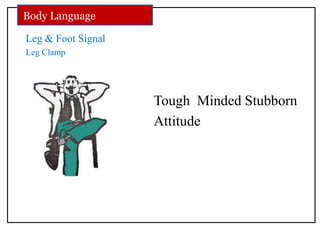
The document discusses communication skills and body language. It defines communication as the conveying of information through various means such as speech, writing, signals and behavior. It outlines the importance of developing good communication skills like using appropriate body language, vocabulary, tone of voice and listening skills. It also discusses the different types of communication and barriers to effective communication. A key section explores body language in detail, stating that 55% of communication is non-verbal. It examines various body language signals including eye contact, hand gestures, leg positioning and more, and how they communicate different meanings. The document emphasizes the importance of body language in communication.

































![Spaces
Intimate distance :
• [ 0-18 inches (46 cms)]
Personal distance :
• 18 inches to 4 ft ( arm’s length away)
Social distance :
• 4- 8 ft
Public distance:
• beyond 8 feet
Body Language](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communicationskills2-140505122242-phpapp02/85/Communication-skills-PPT-45-320.jpg)
