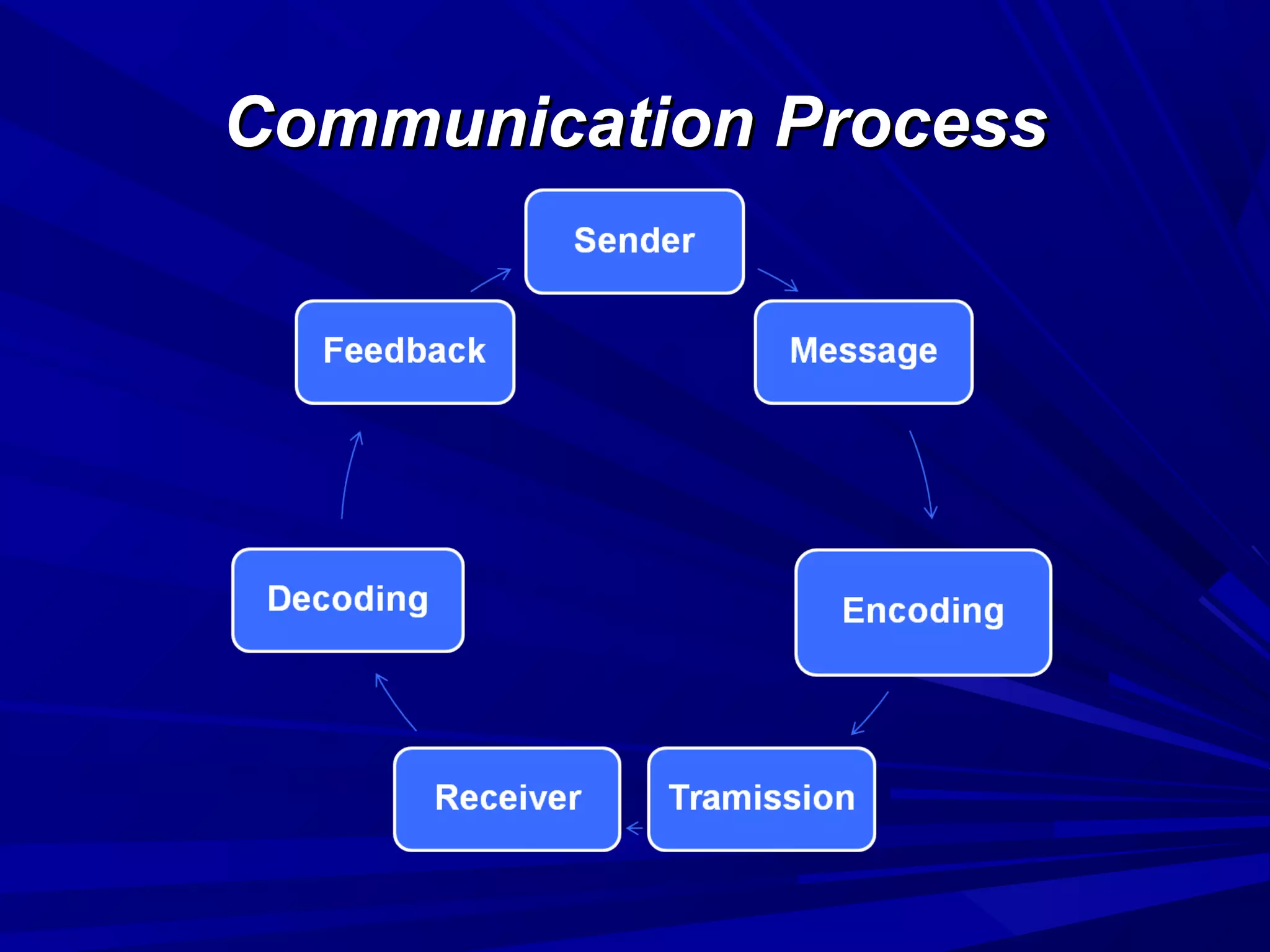
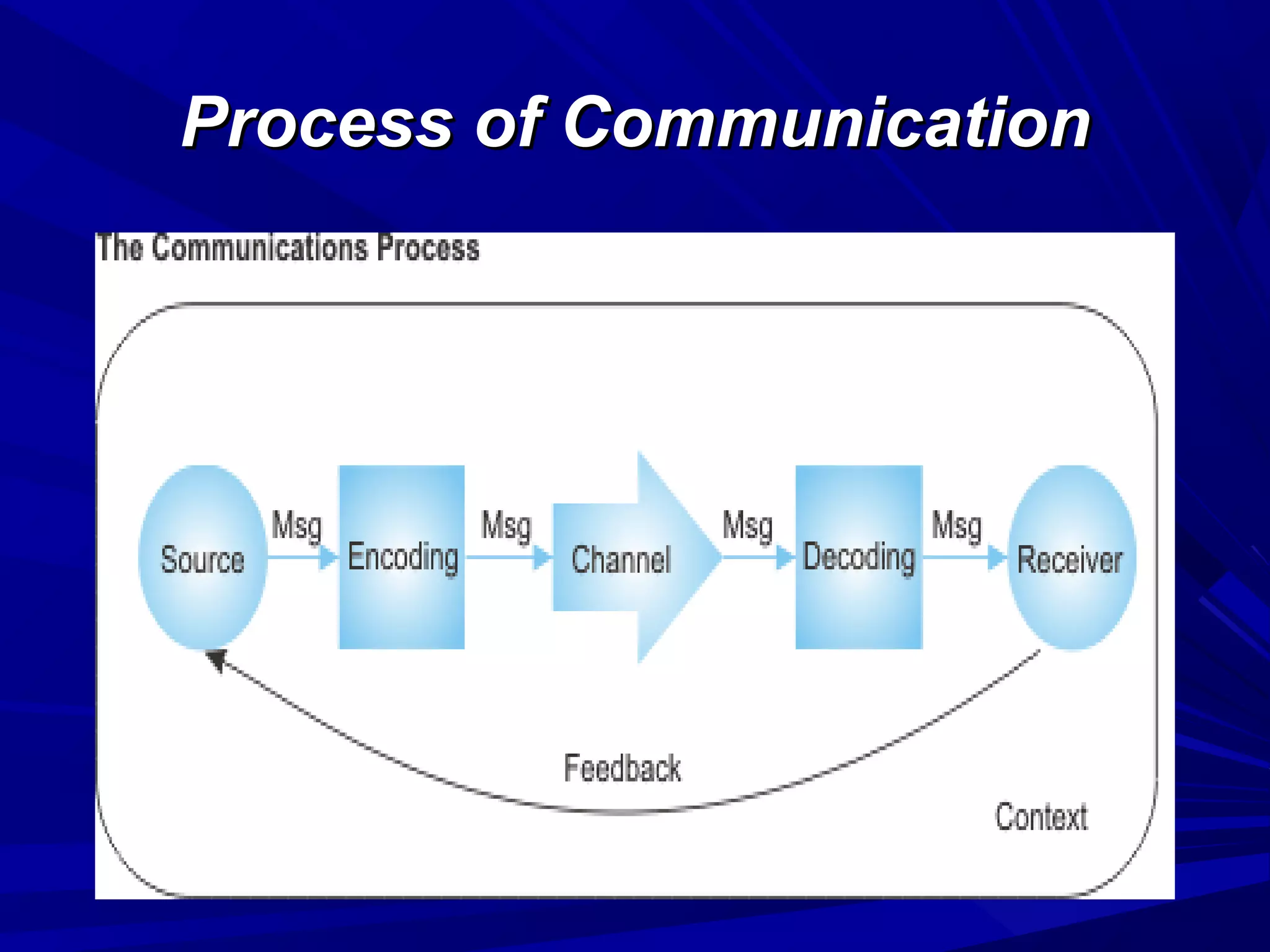
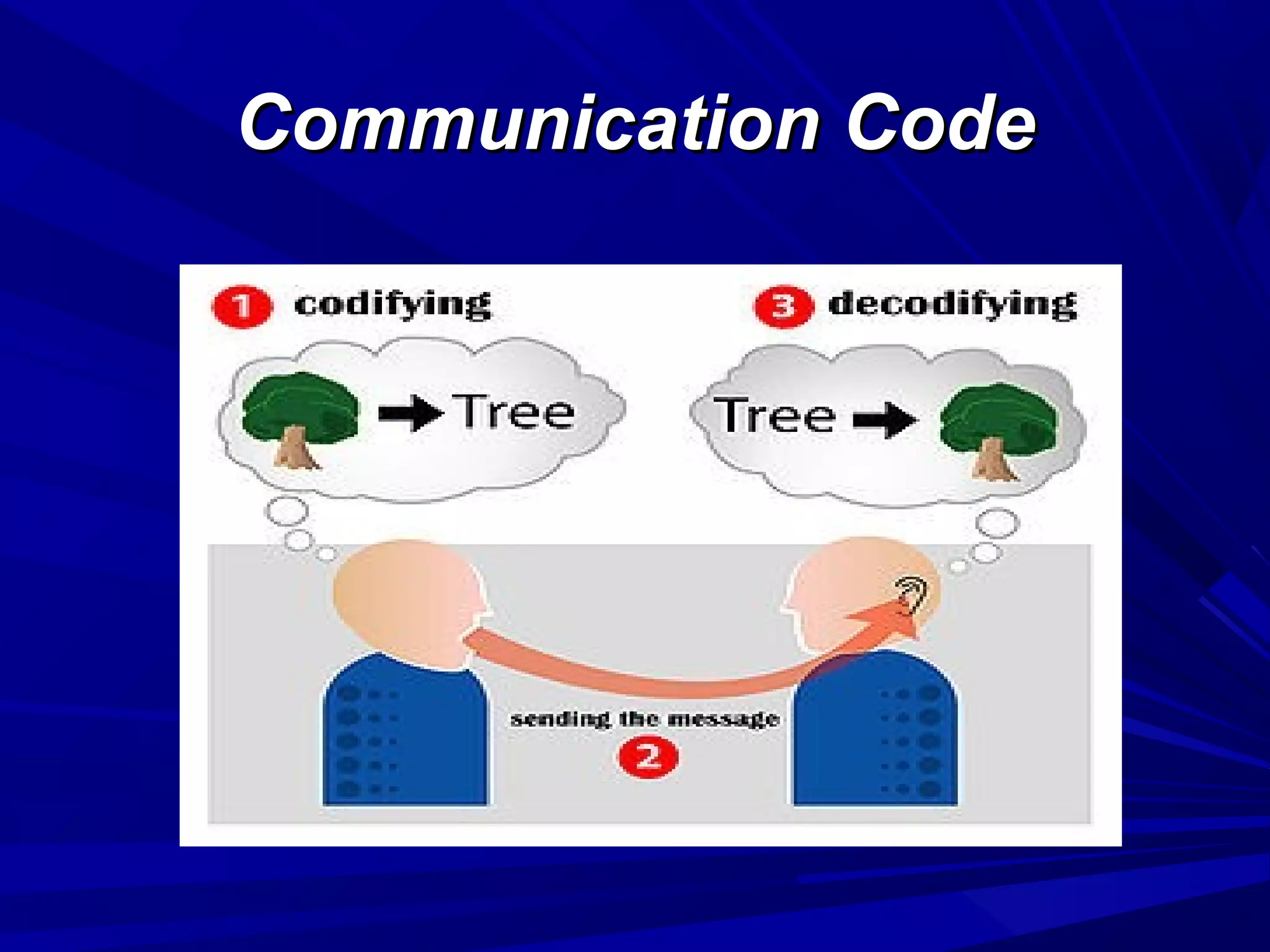
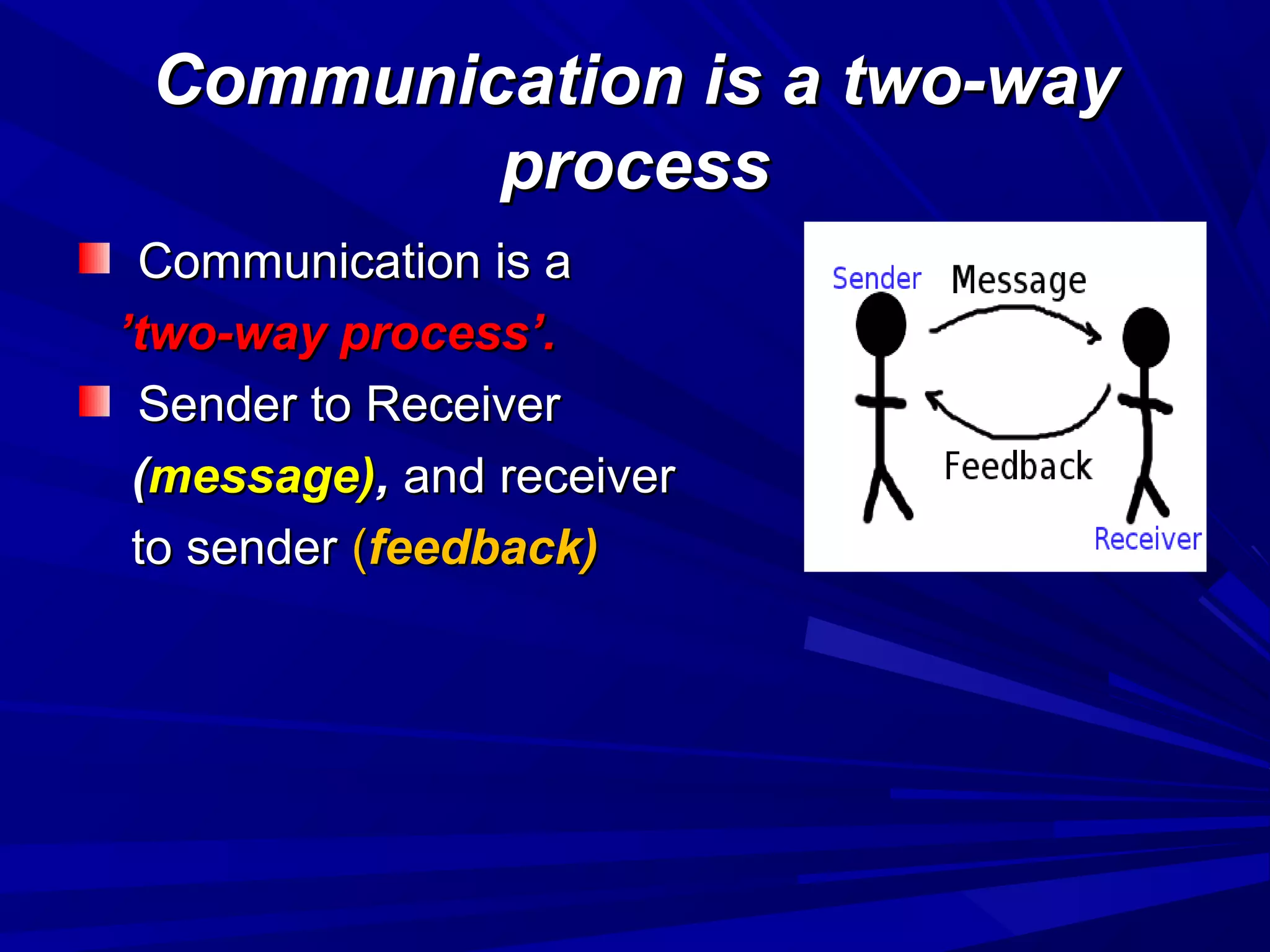
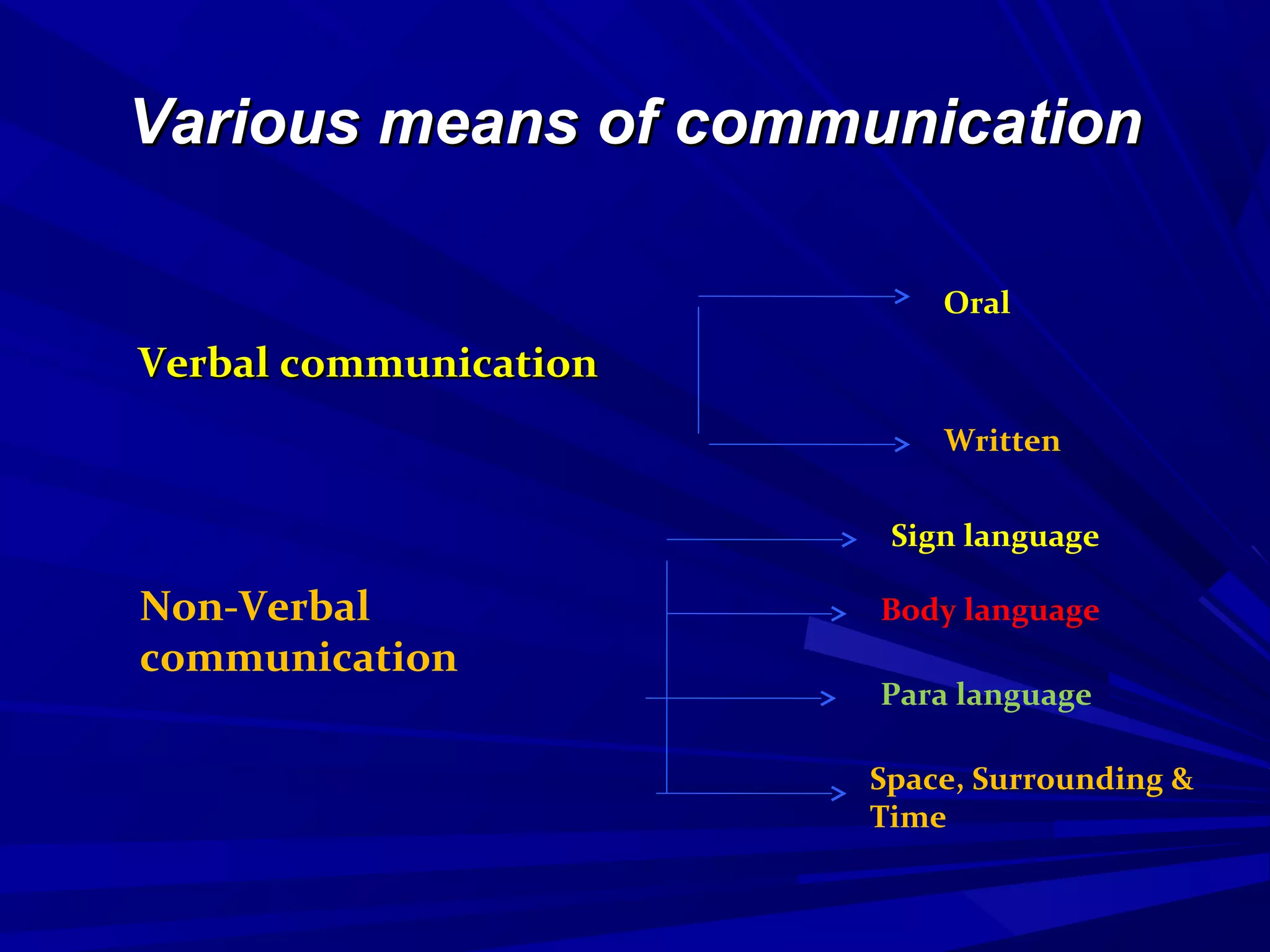
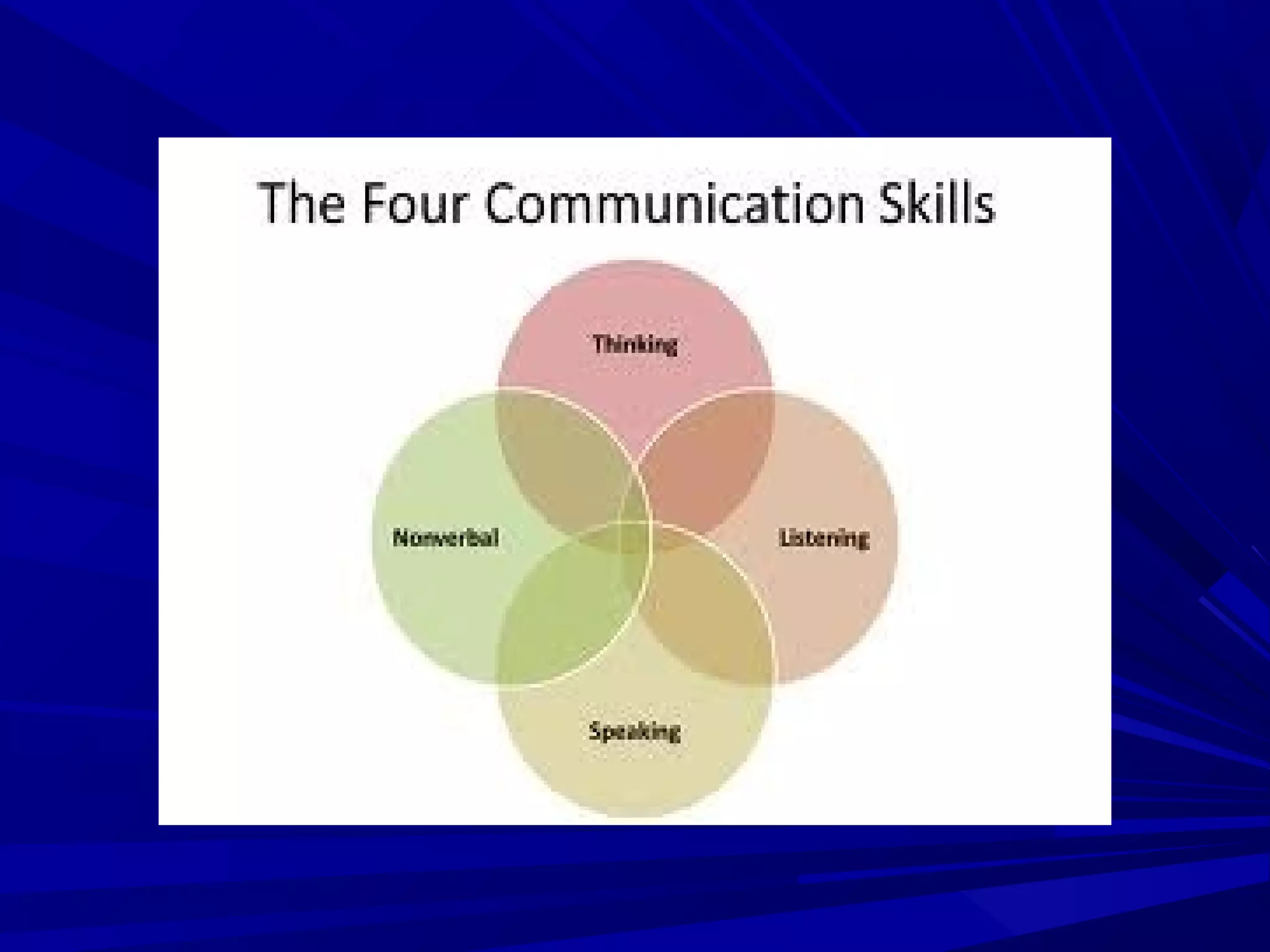
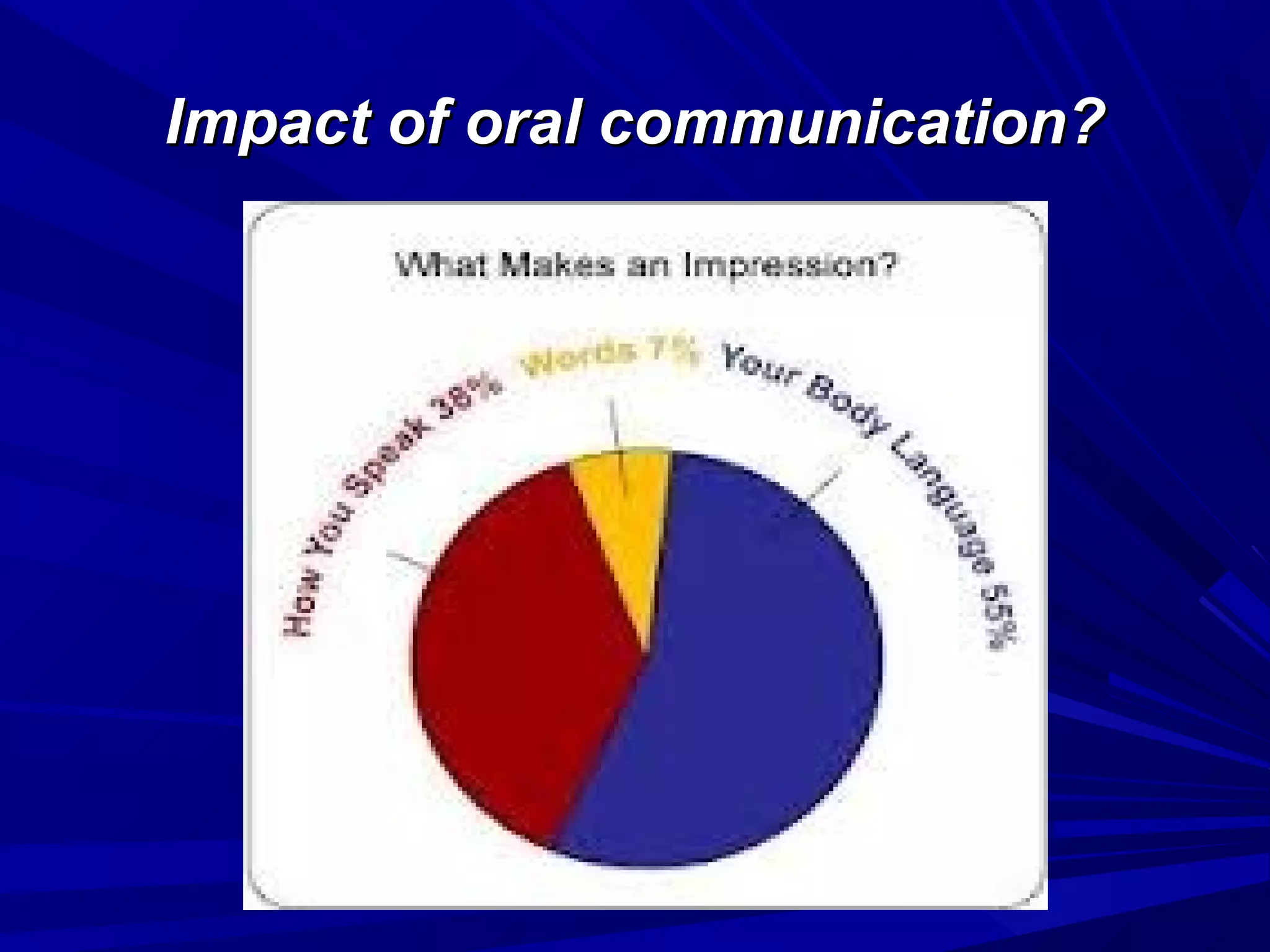
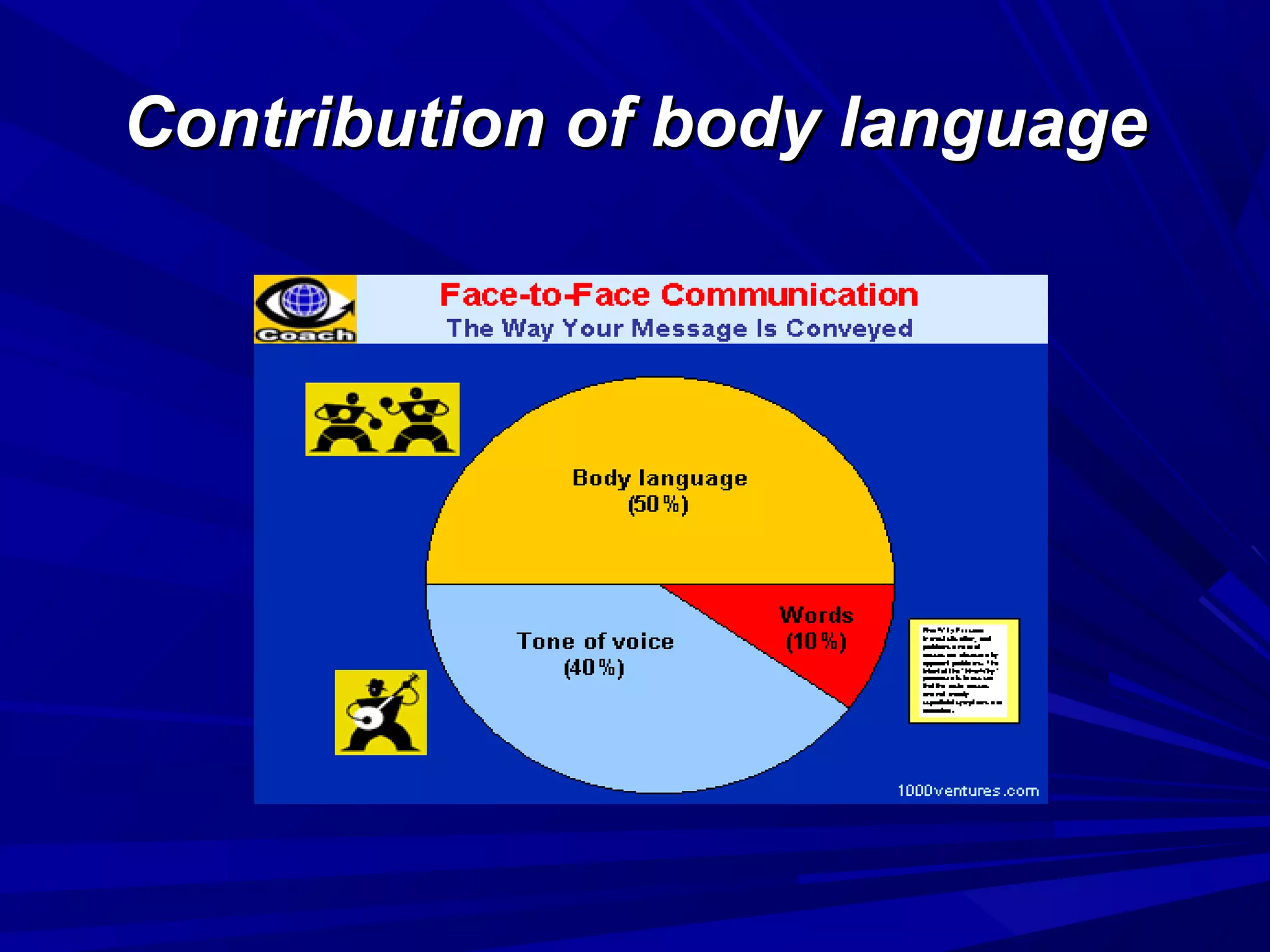
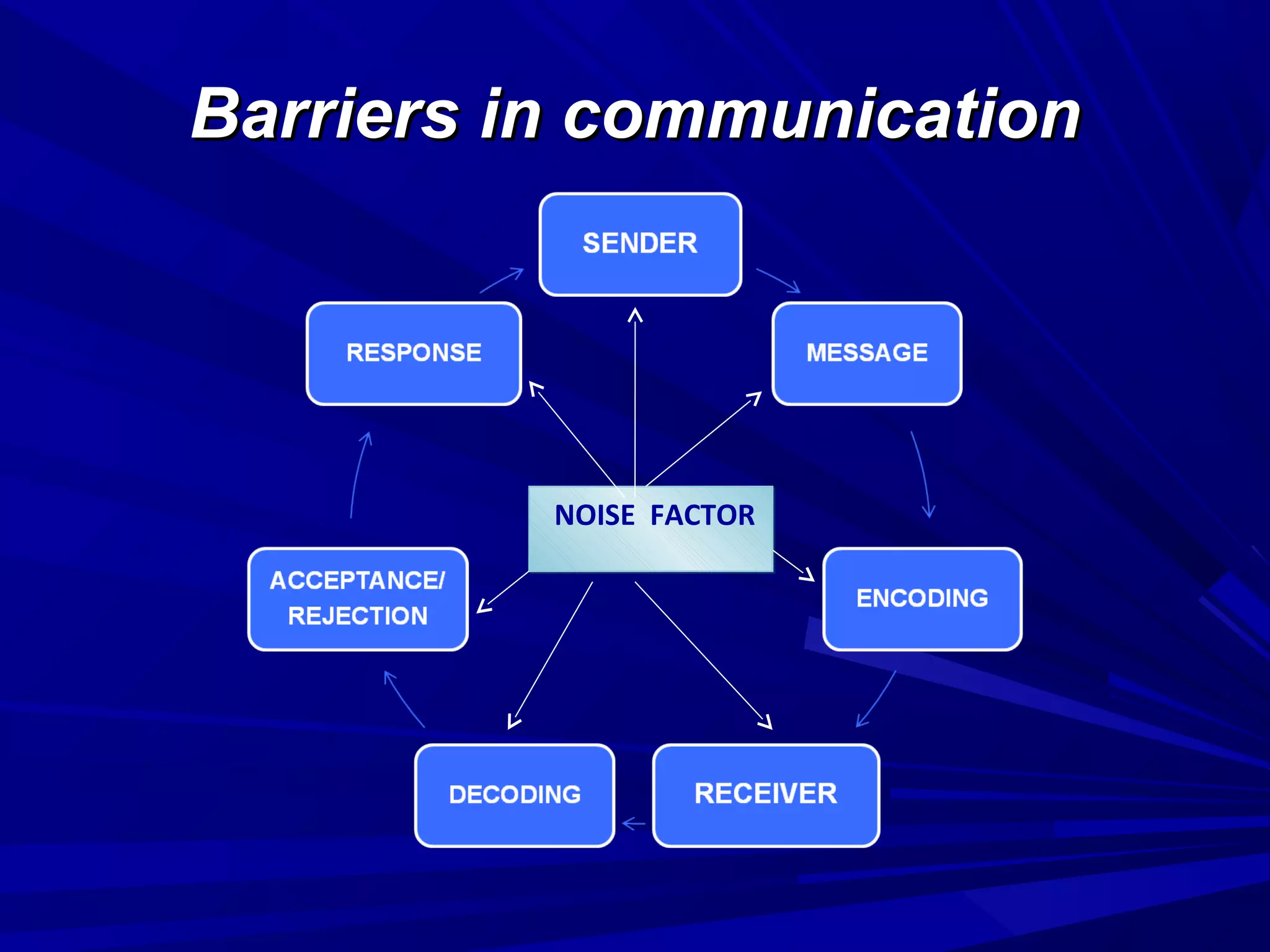
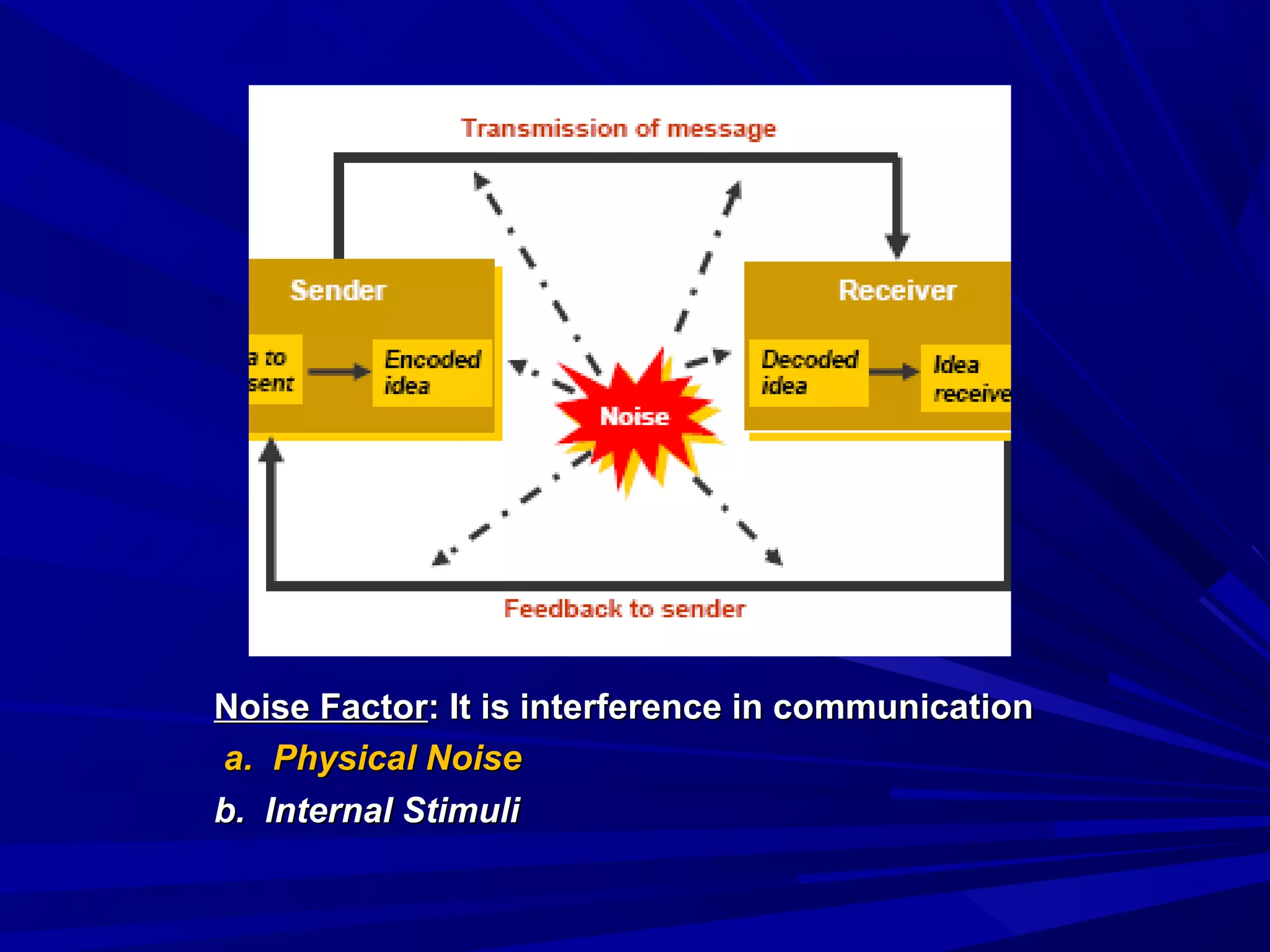
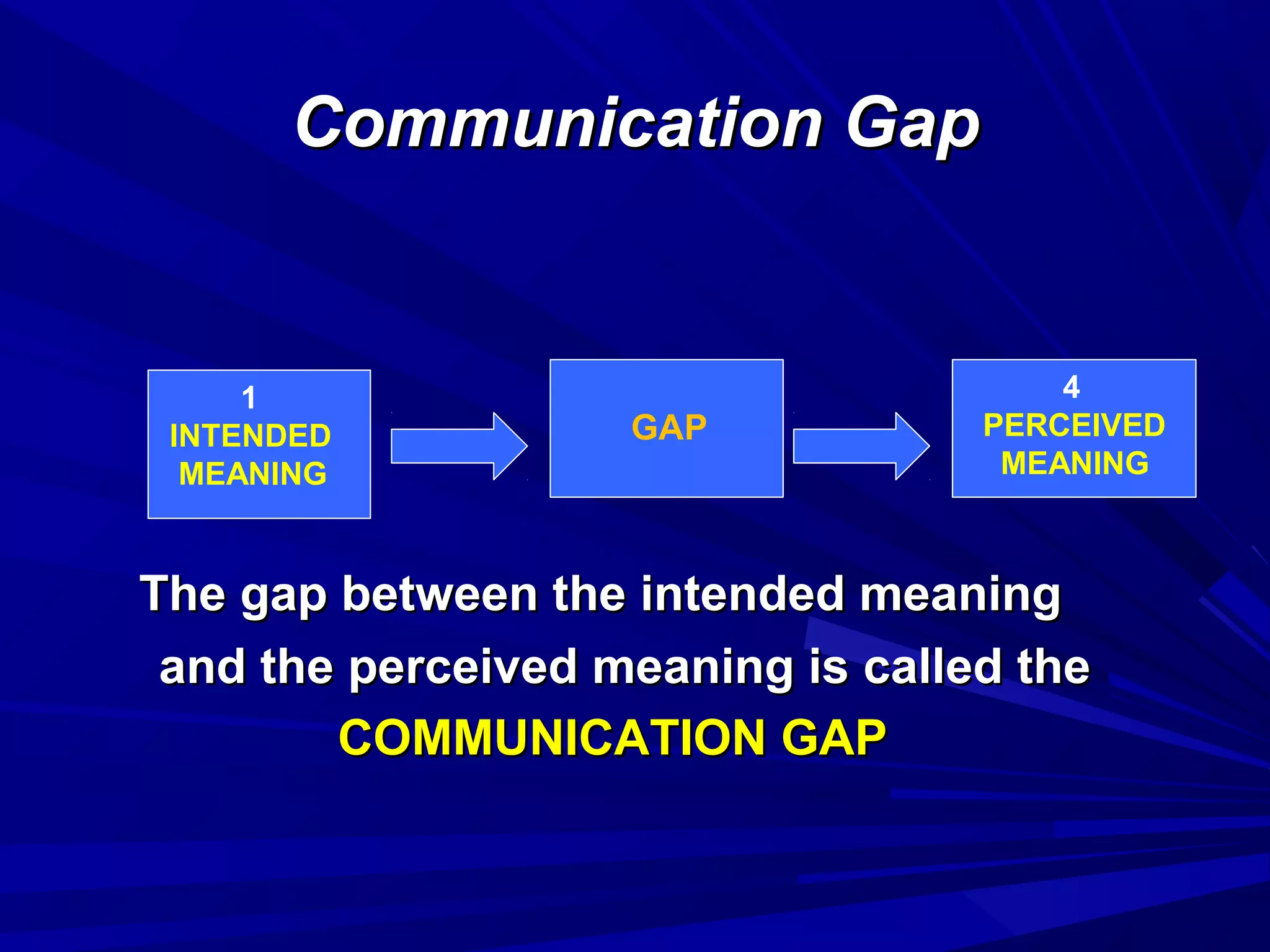
The document covers the fundamentals of communication, detailing the definition, process, and effective components essential for meaningful interaction among individuals. It emphasizes the roles of sender, receiver, message, and feedback in communication, as well as the barriers that can impede understanding. Additionally, it outlines various types of communication, both verbal and non-verbal, and provides tips for improving communication skills and presentations.