This document discusses key concepts of communication including:
1. It defines communication as the process of expressing ideas, feelings, or sharing information between people.
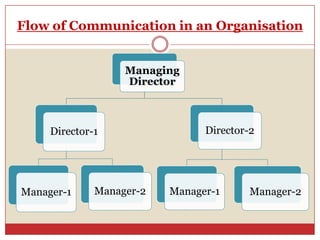
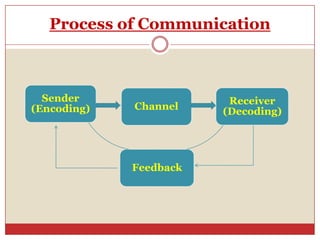
2. It outlines the main stages of the communication process - a sender sending a message through a channel to a receiver who then provides feedback.
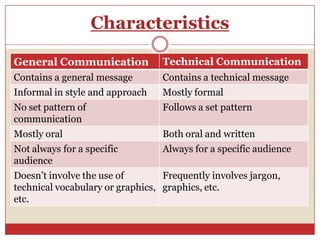
3. It discusses encoding as selecting words/symbols for a message and decoding as interpreting those words/symbols.





![Forms of Communication
There are five main Forms of Communication:
Face to face Communication:
[Examples:- casual conversation, formal interviews, personal meeting etc.]
Group Communication:
[Example:- meetings, conferences, group discussion etc.]
Written Communication:
[Example:- reports, memos, proposals, letters, e-mails etc.]
Oral Communication:
[Example:- telephonic conversation, casual conversation, voice messages, etc.]
Speaker – Audience Communication:
[Speeches, lectures, oral presentation, seminars, etc.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communication-intro-100702034036-phpapp02/85/Communication-intro-7-320.jpg)