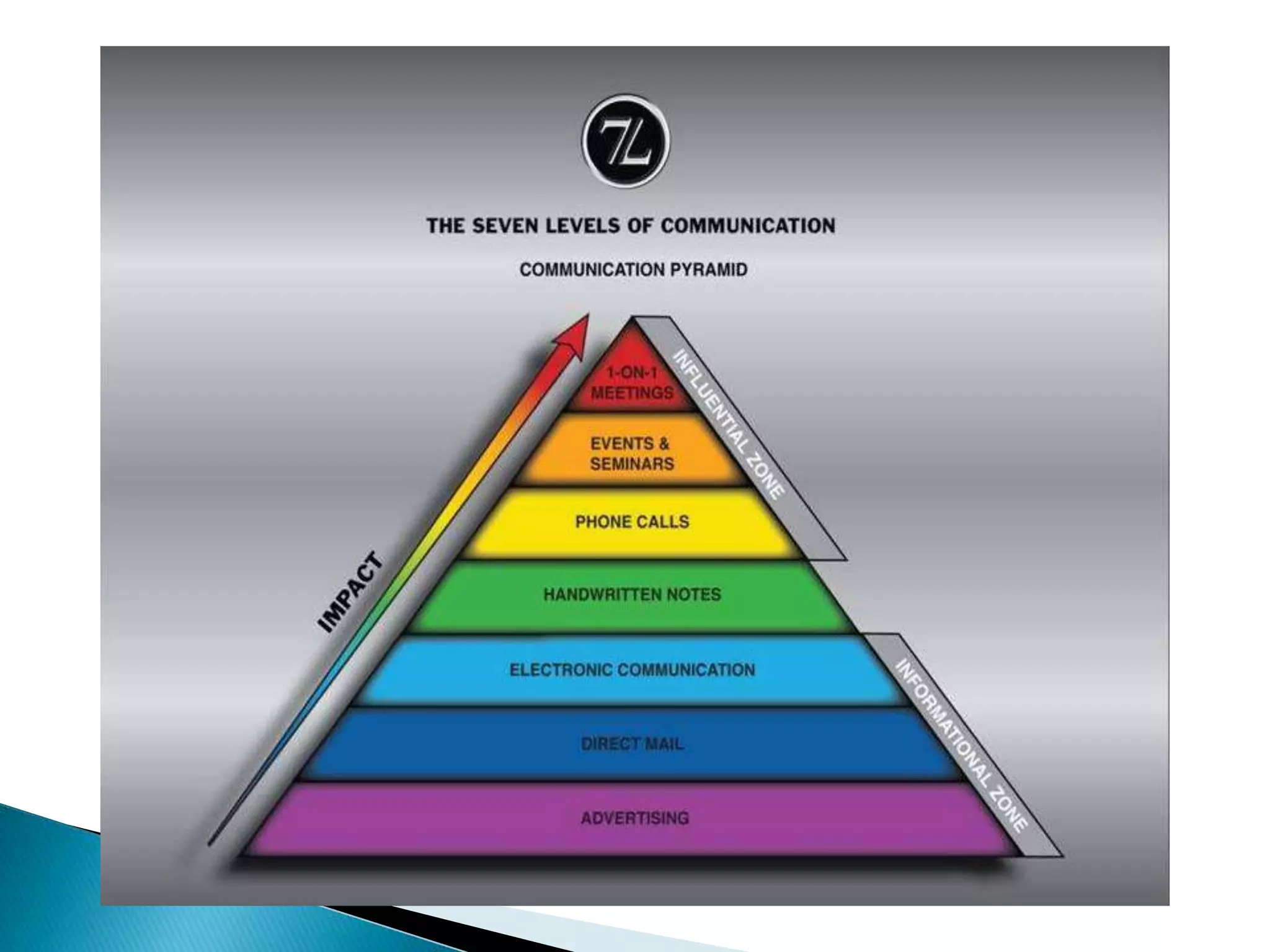
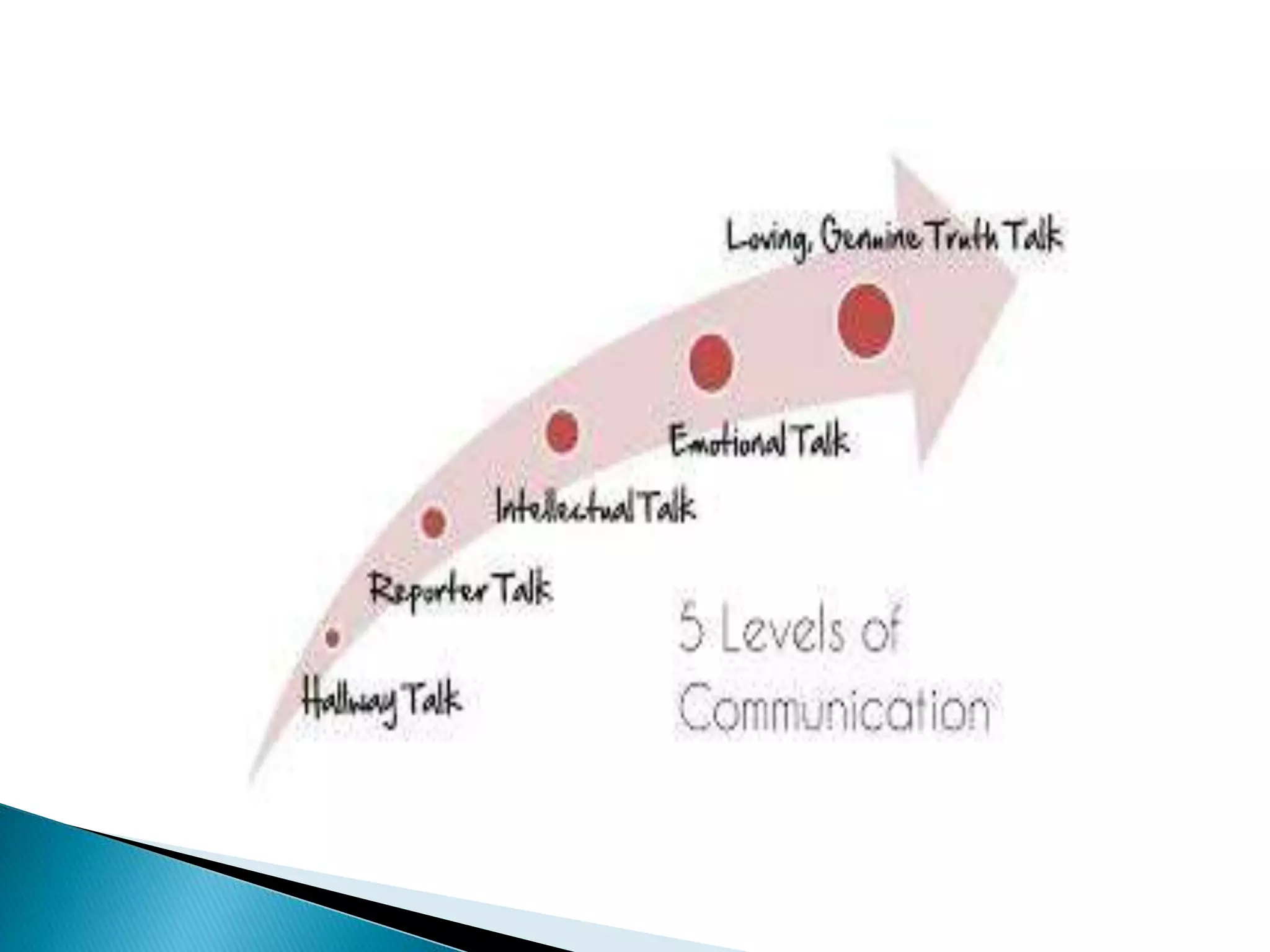
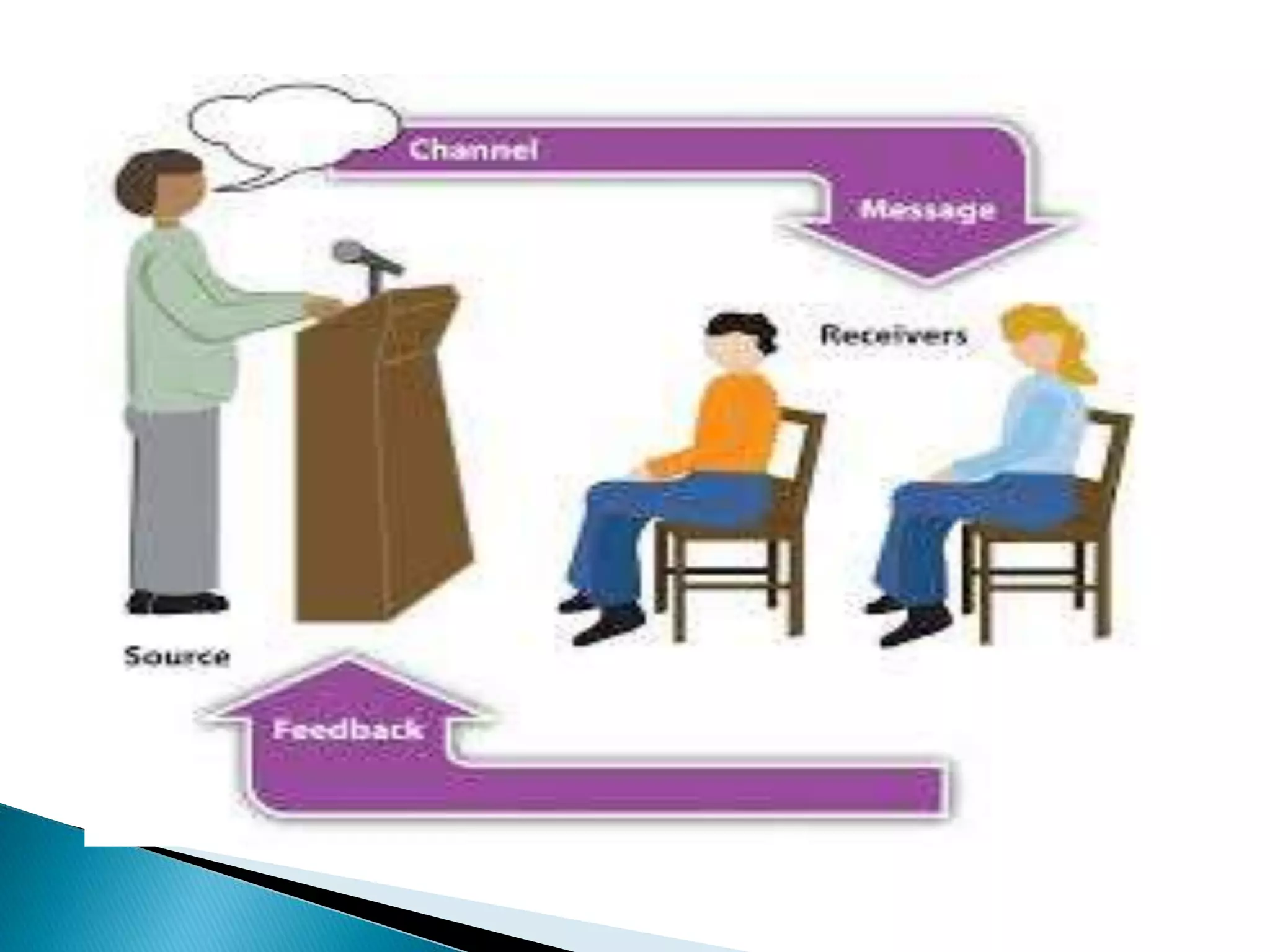
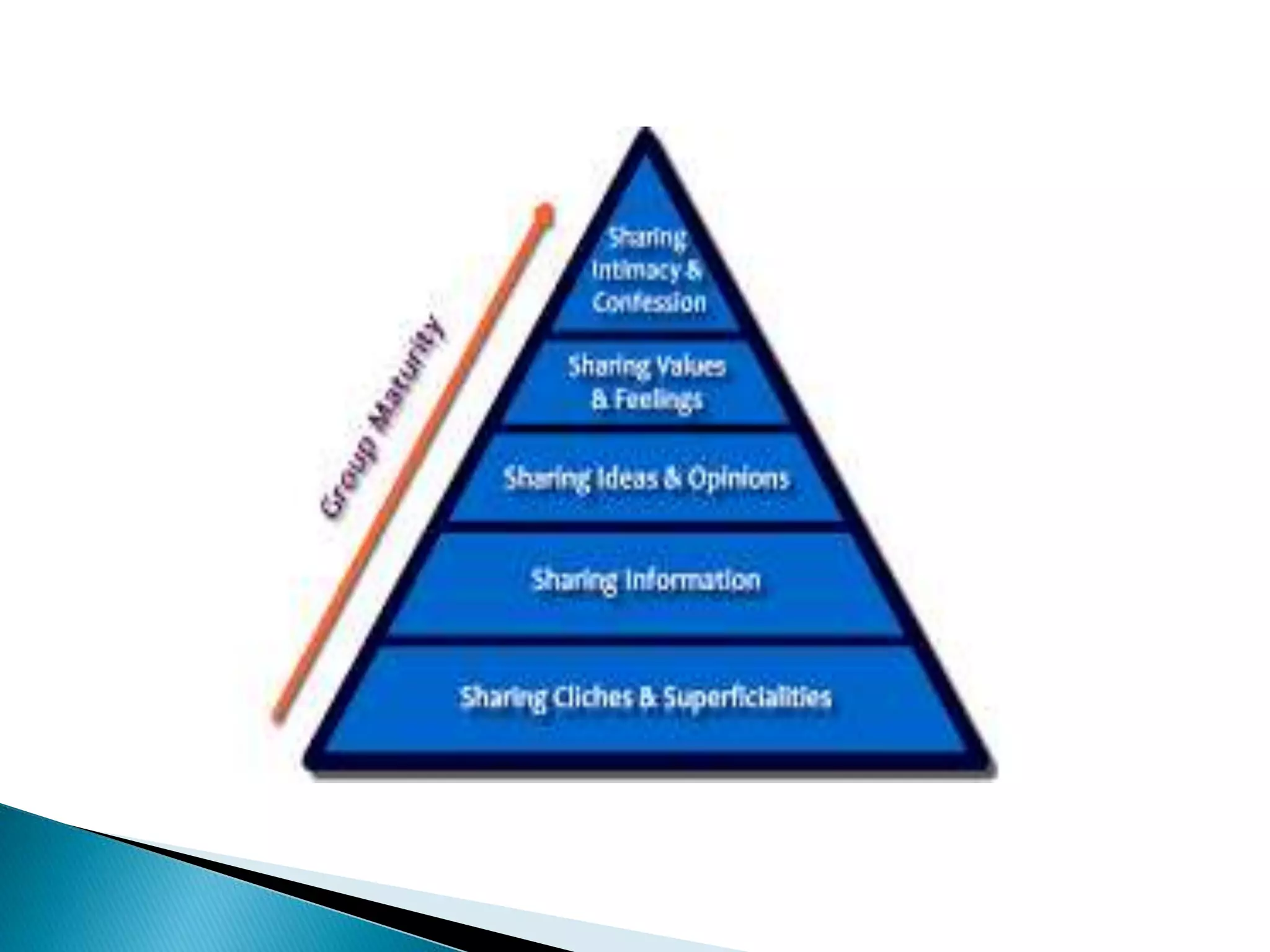
This document defines and describes different types of communication. It discusses verbal communication which uses spoken words, and notes that language can be arbitrary and lead to miscommunication. It also covers nonverbal communication through gestures and body language. Additionally, it outlines intrapersonal communication which is self-talk, interpersonal communication between people, public communication through speeches, and mass communication through various media. It concludes by mentioning extra personal communication between humans and non-humans.