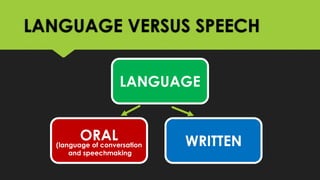
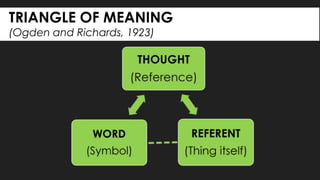
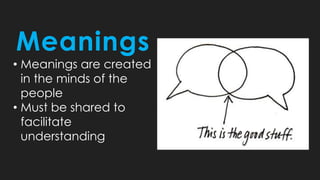
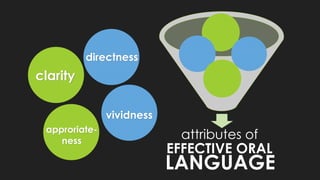
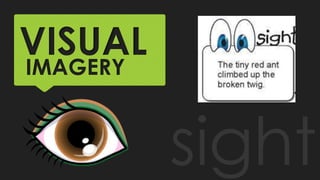
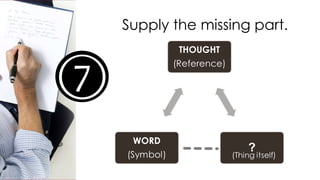
The document discusses key concepts about language including definitions, the nature and attributes of language, and strategies for effective oral language. It defines language as a system of symbols used to convey thought from one person to another. It also discusses that language is dynamic, words have multiple meanings, and meanings exist in people's minds rather than in words themselves. Language is influenced by culture and time. Effective oral language should be clear, direct, appropriate for the audience and occasion, and vivid through the use of imagery.