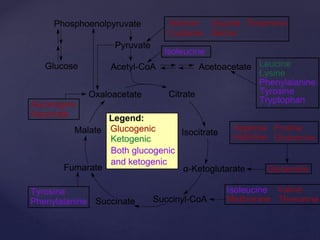
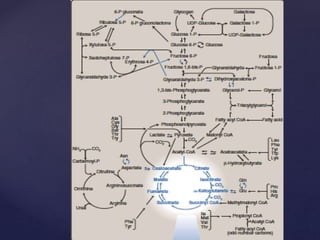
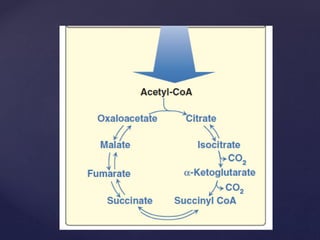
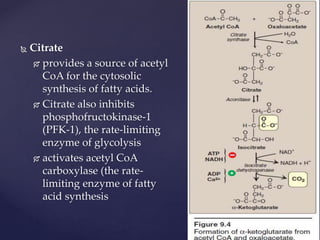
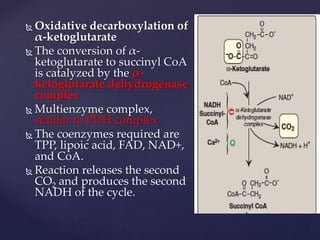
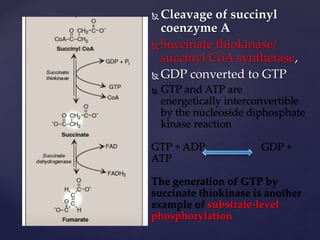
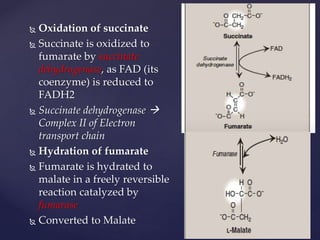
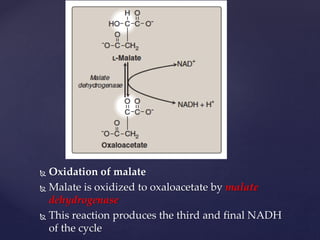
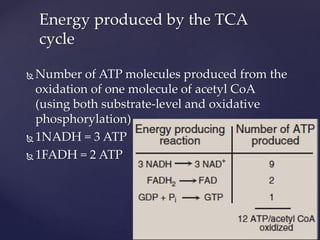
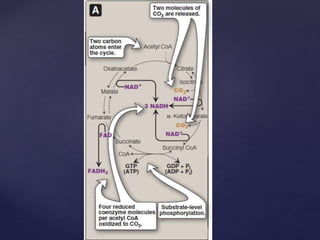
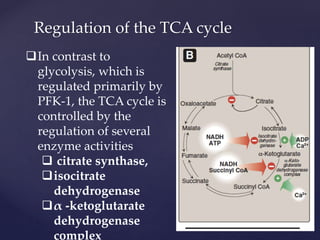
The TCA cycle, occurring in the mitochondria, is the final oxidative pathway where carbohydrates, amino acids, and fatty acids are metabolized to produce CO2 and ATP. It involves various enzymes and coenzymes, with regulatory mechanisms controlling activities at key steps. Deficiencies in enzymes, such as the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, can lead to significant clinical consequences, particularly in brain function.