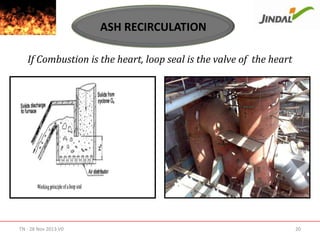
The document discusses the characteristics and factors affecting combustion in a Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion (CFBC) boiler. It emphasizes the importance of air distribution, coal quality, bed temperature, and furnace volume for achieving efficient combustion and minimizing emissions. Key operational practices and recommended parameters for maintaining combustion efficiency are also outlined.