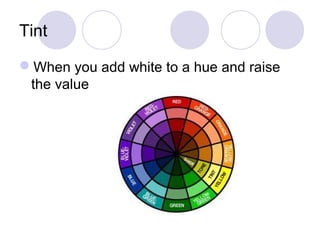
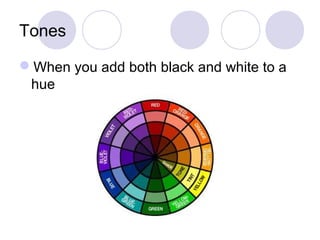
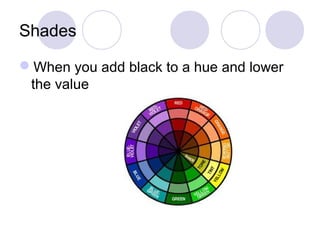
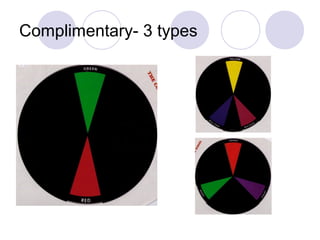
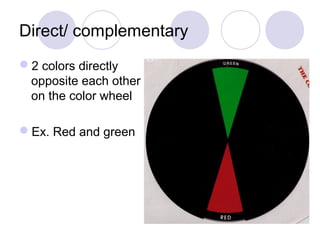
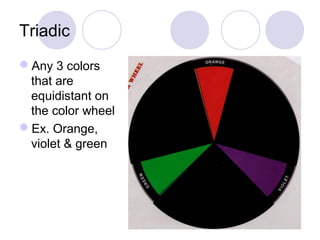
This document defines and describes different types of colors including primary, secondary, tertiary, hue, value, tint, tones, shades, chroma, warm and cool colors. It also discusses different color schemes such as monochromatic, analogous, complementary (direct, split complementary, triadic) and neutral colors. Primary colors are red, yellow and blue. Secondary colors are created by mixing two primary colors, and tertiary colors are created by mixing a primary and secondary color. Other terms like hue, value, tint, tones and shades describe attributes of colors.