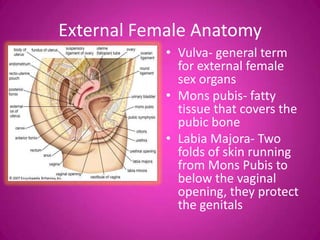
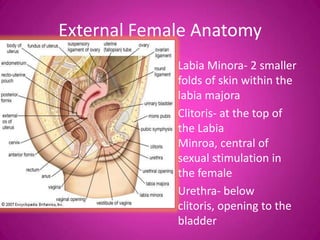
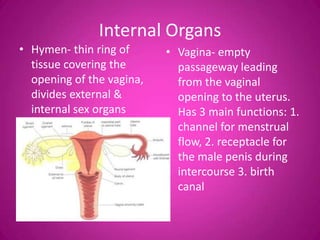
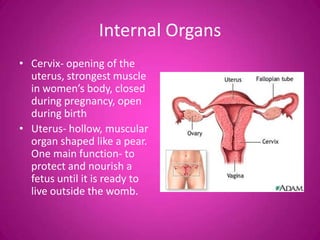
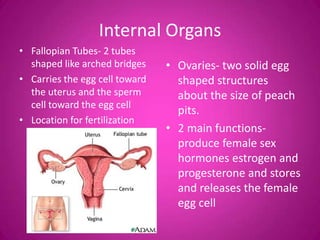
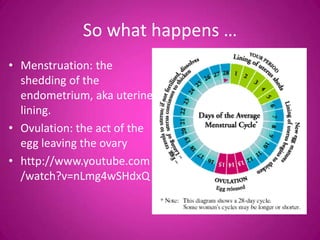
The document describes the key external and internal female reproductive organs. Externally, it outlines the vulva, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and urethra. Internally, it details the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It provides the main functions of each organ such as protection, nourishment of a fetus, production of hormones, storage and release of eggs.