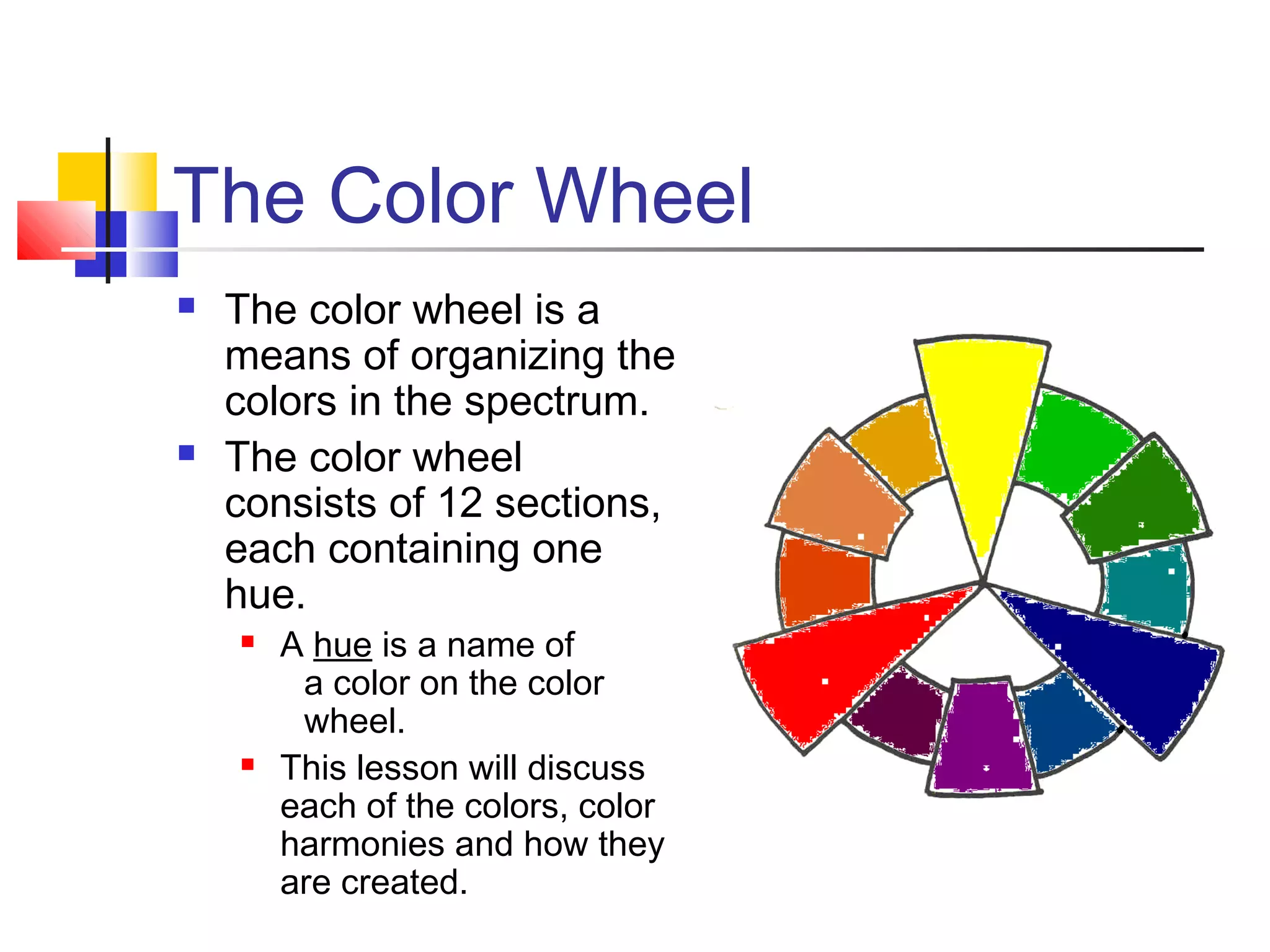
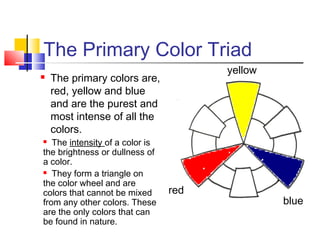
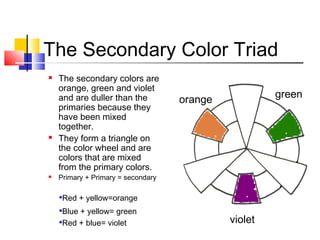
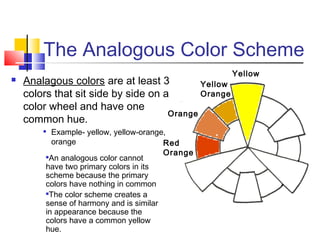
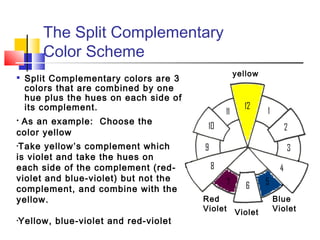
The document discusses the color wheel and various color schemes. It explains that the color wheel organizes hues and consists of 12 sections. The primary colors are red, yellow, and blue and are the purest colors. Secondary colors are orange, green, and violet, which are made by mixing primaries. Tertiary colors are made by mixing a primary with a secondary. Analogous, complementary, split complementary, monochromatic, and warm/cool color schemes are also explained. Neutral colors and emotional properties of different hues are described.