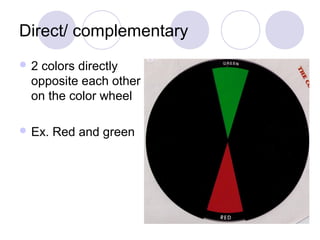
The document discusses primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. Primary colors are red, yellow, and blue. Secondary colors are formed by mixing two primary colors, and tertiary colors are formed by mixing a primary and secondary color. It also defines concepts like hue, value, tint, tone, shade, chroma, warm and cool colors, and color schemes including monochromatic, analogous, complementary, and neutral colors.