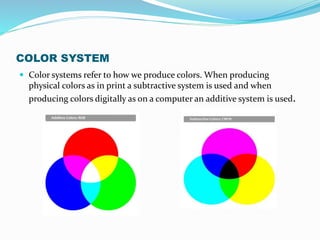
The document discusses color theory and how color is created and used. It explains that color is the product of light's spectrum being reflected or absorbed by the human eye and brain. Color theory principles and diagrams can be used to create color combinations. The color wheel is a visual representation that arranges colors by their chromatic relationship and shows how primary, secondary, and tertiary colors are formed by mixing others. Color schemes involve using groups of colors and how they are combined impacts moods and meanings conveyed. Color systems refer to how colors are produced digitally with monitors using RGB and physically with printers using CMYK.